In today’s interconnected world, printers have become indispensable tools for both personal and professional use. However, accessing and managing these devices can sometimes be challenging, especially when it comes to finding their IP addresses. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of where to find the printer IP address, covering various methods and troubleshooting tips.
Whether you’re trying to connect your printer to a wireless network or troubleshoot connectivity issues, knowing its IP address is crucial. This guide will empower you with the knowledge and techniques to locate your printer’s IP address effortlessly.
Printer IP Address
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/009_find-printer-ip-address-4176356-0a309b21c5e548ff98fda7650a56a63a.jpg)
The printer IP address is a unique identifier assigned to a printer connected to a network. It allows computers and other devices on the same network to communicate with the printer.
Finding the Printer IP Address
To find the printer IP address, you can use the following methods:
- Windows:Open the Control Panel and navigate to “Network and Internet” > “Network and Sharing Center” > “Change adapter settings”. Right-click on the network adapter connected to the printer and select “Status”. Click on the “Details” button to view the IP address.
- Mac:Open the System Preferences and navigate to “Network”. Select the network adapter connected to the printer and click on the “Advanced” button. Click on the “TCP/IP” tab to view the IP address.
- Linux:Open a terminal window and type the following command:
ifconfig. The IP address of the network adapter connected to the printer will be listed.
Using Command-Line Tools
You can also use command-line tools to find the printer IP address:
- ipconfig (Windows):This command displays the IP address of all network adapters on the computer.
- ifconfig (Mac and Linux):This command displays the IP address of all network adapters on the computer.
- arp-a (Mac and Linux): This command displays the IP addresses of all devices on the network, including the printer.
Non-Networked Printers
If the printer is not connected to a network, you can find its IP address using a USB connection or a direct Ethernet connection:
- USB connection:Connect the printer to the computer using a USB cable. Open the printer’s control panel and navigate to the “Network” or “Wireless” settings. The IP address will be listed.
- Direct Ethernet connection:Connect the printer to the computer using an Ethernet cable. Open the printer’s control panel and navigate to the “Network” or “Wireless” settings. The IP address will be listed.
2. Network Settings: Where To Find The Printer Ip Address
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/011_find-printer-ip-address-4176356-3a2d8054d1cf46f4a4f0904759cc0854.jpg)
Network settings on a printer allow you to connect the printer to a network, such as a Wi-Fi network or an Ethernet network. Accessing the network settings on a printer varies depending on the make and model of the printer.
Typically, you can access the network settings by navigating through the printer’s menu or control panel. Once you have accessed the network settings, you can find the IP address of the printer.
Locating the IP Address
The IP address of the printer is usually displayed in the network settings menu. The IP address may be listed as “IP Address,” “IPv4 Address,” or “IPv6 Address.” The IP address will be a series of numbers separated by periods, such as “192.168.1.100”.
3.
Router Configuration
To locate the printer’s IP address via router configuration, you’ll need to access your router’s settings page and navigate to the connected devices section. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
: Accessing the Router’s Configuration Page
1. Open a web browser and type the router’s IP address into the address bar. The default IP address for most routers is 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1. If these don’t work, check the router’s documentation or the sticker on the bottom of the router.
2. Enter the router’s username and password. The default credentials are often “admin” for both the username and password. If you’ve changed these, use the credentials you set up.
: Finding the Connected Devices Section
1. Once you’re logged into the router’s configuration page, look for a section called “Connected Devices” or “DHCP Clients.” This section will list all the devices currently connected to your network.
2. Locate the entry for your printer in the list of connected devices. It may be listed by its name, IP address, or MAC address.
Finding your printer’s IP address is essential for troubleshooting printing issues. By following the steps in the relevant guide, you can easily locate this information. If you’re wondering about printing on watercolor paper, can you print on watercolor paper ?
The answer is yes, but it requires specific techniques and considerations. Once you have your printer’s IP address, you can access its settings and adjust them accordingly for optimal printing performance.
: Identifying the Printer’s IP Address
1. Once you’ve found the entry for your printer, look for the IP address field. This will be a numerical address like 192.168.1.100.
2. Make note of the printer’s IP address. You’ll need this information to access the printer’s web interface or configure other network settings.
4.
Third-Party Tools

Third-party software and online tools offer alternative methods to locate a printer’s IP address. These tools leverage various techniques to scan networks and identify devices, including printers.
One common approach employed by these tools is network scanning. They send out requests to every device connected to the network, and the devices that respond are identified. The tool can then cross-reference the MAC address of the responding device with a database to determine the manufacturer and model of the printer.
This information is then used to deduce the printer’s IP address.
Advantages of Using Third-Party Tools
- Convenience:Third-party tools provide a user-friendly interface that simplifies the process of finding a printer’s IP address, making it accessible to users with varying levels of technical expertise.
- Efficiency:These tools automate the scanning process, saving time and effort compared to manual methods.
- Additional Features:Some tools offer additional features, such as remote printer management and configuration, which can be useful for managing multiple printers on a network.
Disadvantages of Using Third-Party Tools
- Cost:Some third-party tools may require a paid subscription or license, which can add to the overall cost of printer management.
- Security Concerns:Granting access to third-party tools may pose security risks if they are not reputable or have vulnerabilities.
- Accuracy:The accuracy of third-party tools can vary depending on the tool’s capabilities and the network environment.
Examples of Third-Party Tools
- Angry IP Scanner:An open-source network scanner that can identify printers and other devices on a network.
- Advanced IP Scanner:A freeware network scanner with a user-friendly interface and support for multiple platforms.
- Printer IP Address Finder:An online tool that allows users to enter their printer’s model number to find its IP address.
Choosing and Using Third-Party Tools
When selecting a third-party tool, it is important to consider factors such as cost, ease of use, accuracy, and security. It is recommended to research and read reviews of different tools before making a decision.
To print your wedding photos, you’ll need to know the IP address of your printer. To find the IP address, you can check the printer’s settings or use a network scanner. Once you have the IP address, you can enter it into your computer’s web browser to access the printer’s web interface.
From there, you can upload your photos and print them. For more information on where to print wedding photos, visit where to print wedding photos. After printing your photos, you can store them in a safe place to preserve your memories for years to come.
Once a tool is chosen, it is important to follow the instructions provided by the tool’s developer to ensure accurate results. Additionally, it is essential to be mindful of the security implications of using third-party tools and to take appropriate precautions to protect the network and devices.
5. Dynamic vs Static IP Addresses
In a network, every device has an IP address that identifies it and allows it to communicate with other devices. IP addresses can be either dynamic or static.
Dynamic IP Addresses
A dynamic IP address is assigned automatically to a device by a DHCP server. This type of IP address is temporary and can change over time. Dynamic IP addresses are commonly used in home and small business networks because they are easy to configure and manage.
Advantages of Dynamic IP Addresses:
- Easy to configure and manage
- No need to manually assign IP addresses to devices
- IP addresses are automatically assigned and can change over time
Disadvantages of Dynamic IP Addresses:
- IP addresses can change over time, which can make it difficult to access devices remotely
- Not suitable for devices that require a permanent IP address, such as servers or printers
Static IP Addresses
A static IP address is a permanent IP address that is manually assigned to a device. This type of IP address does not change over time. Static IP addresses are commonly used in business networks and for devices that require a permanent IP address, such as servers or printers.
Advantages of Static IP Addresses:
- Permanent IP addresses that do not change over time
- Easy to access devices remotely
- Suitable for devices that require a permanent IP address
Disadvantages of Static IP Addresses:
- Need to manually assign IP addresses to devices
- Can be difficult to manage in large networks
Configuring a Static IP Address for a Printer
To configure a static IP address for a printer, you can either use the printer’s web interface or manually configure the IP address using the printer’s control panel.
Using the Printer’s Web Interface:
- Open a web browser and enter the printer’s IP address in the address bar.
- Log in to the printer’s web interface using the default username and password.
- Navigate to the “Network” or “TCP/IP” settings.
- Select the “Manual” or “Static” IP address option.
- Enter the desired IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
- Click “Apply” or “Save” to save the changes.
Manually Configuring the IP Address:
- Press the “Menu” button on the printer’s control panel.
- Navigate to the “Network” or “TCP/IP” settings.
- Select the “Manual” or “Static” IP address option.
- Use the arrow keys to enter the desired IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
- Press “OK” or “Enter” to save the changes.
Troubleshooting Static IP Address Configuration
If you are having trouble configuring a static IP address for your printer, try the following troubleshooting steps:
- Make sure that the IP address you are using is not already in use by another device on the network.
- Check that the subnet mask and default gateway are correct.
- Restart the printer and the router.
- Contact your network administrator for assistance.
6.
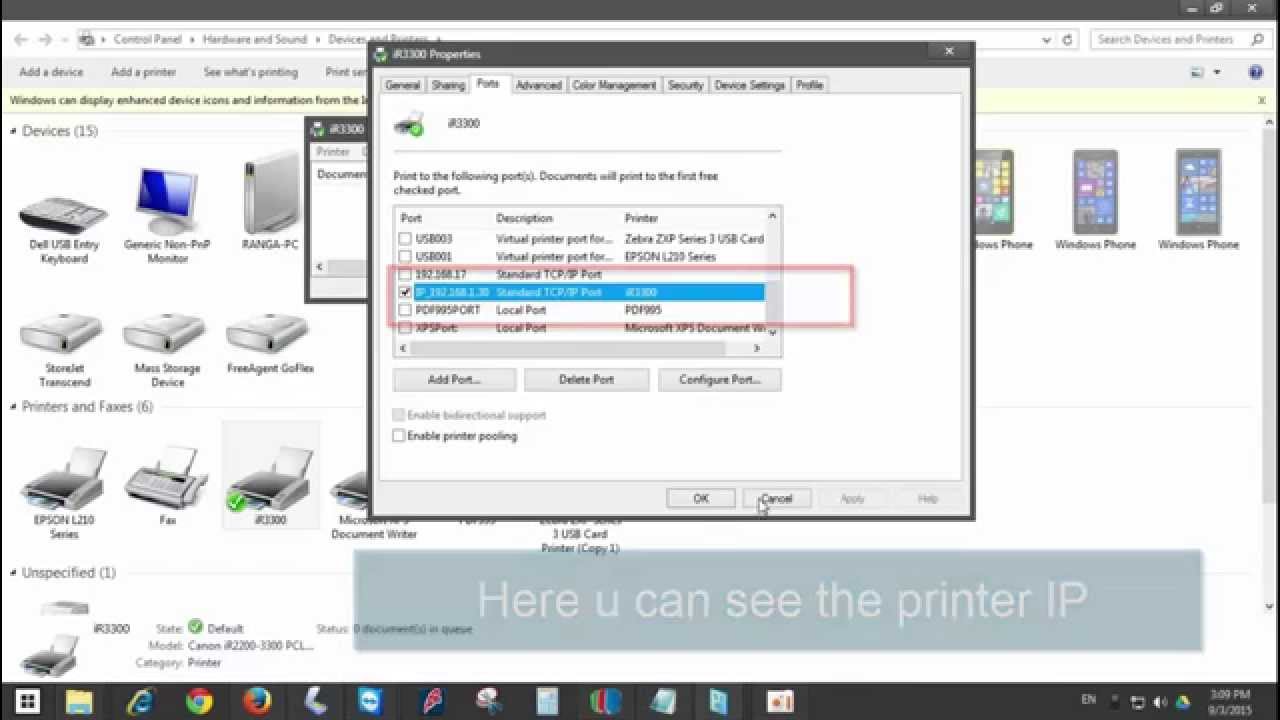
Printer Properties
Accessing the printer properties provides a convenient way to locate the printer’s IP address. Different operating systems may have variations in the steps, but generally, follow these instructions:
- For Windows users, navigate to the “Control Panel” and select “Printers and Scanners.” Right-click on the desired printer and choose “Printer Properties.”
- For macOS users, go to “System Preferences” and select “Printers & Scanners.” Right-click on the printer and choose “Options & Supplies.”
IP Address Location
Once in the printer properties, locate the “General” or “Status” tab. Within this tab, you should find the printer’s IP address listed under “Location” or “Network Address.”
The IP address may be displayed in various formats, such as IPv4 (e.g., 192.168.1.100) or IPv6 (e.g., fe80::215:5dff:fe07:204c). IPv4 addresses are more common in home networks, while IPv6 is becoming more prevalent in enterprise environments.
Significance of Printer IP Address
The printer’s IP address is crucial for network communication. It allows computers and other devices on the network to identify and connect to the printer. Knowing the IP address enables you to:
- Access the printer’s web interface for configuration and management.
- Troubleshoot network connectivity issues.
- Share the printer with multiple devices on the network.
Changing Printer IP Address
In certain scenarios, you may need to change the printer’s IP address. This can be done through the printer’s web interface or its control panel. The specific steps may vary depending on the printer model.
Note:Changing the IP address may affect network connectivity. Ensure you have the correct IP address before making any changes.
7.
Advanced Troubleshooting
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/003_find-printer-ip-address-4176356-f3cb86a611014263a01f3da6ea619800.jpg)
Finding the printer IP address can occasionally present challenges. To address these issues effectively, it’s crucial to employ advanced troubleshooting techniques.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Resolving connectivity problems, incorrect IP addresses, and other related errors requires a systematic approach. Verify network connections, check for IP address conflicts, and ensure the printer is correctly configured.
Advanced Techniques
For complex IP address issues, advanced techniques like using network diagnostic tools, packet sniffing, and examining router logs can provide valuable insights. These methods allow for a deeper analysis of network traffic and identification of potential problems.
8. Line Tools
Ping and Traceroute
Line tools, such as ping and traceroute, are essential for troubleshooting IP address issues. Ping sends packets to a specified IP address and measures the time it takes for the packets to return. This can help diagnose connectivity problems, as well as identify the source of delays or packet loss.
Traceroute, on the other hand, traces the path that packets take from the source to the destination. This can help identify any intermediate devices that may be causing problems, such as routers or firewalls.
Using Ping and Traceroute
To use ping, simply open a command prompt and type “ping” followed by the IP address you want to test. For example, to ping Google’s DNS server, you would type “ping 8.8.8.8”.
To use traceroute, type “traceroute” followed by the IP address you want to trace. For example, to trace the path to Google’s DNS server, you would type “traceroute 8.8.8.8”.
Interpreting the Results
The results of ping and traceroute can be interpreted to identify a variety of network problems. For example, if ping returns a “Request timed out” message, it means that the packets were not able to reach the destination. This could be due to a variety of factors, such as a firewall blocking the packets or a physical connection problem.
Traceroute can help identify the specific device that is causing the problem. If the traceroute output shows that the packets are being dropped at a particular hop, then that device is likely the source of the problem.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
In addition to ping and traceroute, there are a number of other line tools that can be used for advanced troubleshooting. These tools include:
- Wireshark: A network protocol analyzer that can capture and analyze network traffic.
- MTR: A tool that combines the functionality of ping and traceroute into a single command.
- Nmap: A tool that can scan a network for open ports and vulnerabilities.
Table: Ping vs. Traceroute
| Feature | Ping | Traceroute |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Tests connectivity to a single IP address | Traces the path of packets to a destination |
| Output | Round-trip time and packet loss | List of intermediate devices and hop-by-hop latency |
| Uses | Diagnosing connectivity problems | Identifying the source of delays or packet loss |
| Limitations | Cannot identify intermediate devices | May not be able to trace packets through firewalls |
9.
Network Protocols
Network protocols play a crucial role in assigning and managing IP addresses on a network. Two key protocols in this context are TCP/IP and DHCP.TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is a suite of communication protocols that govern how devices on a network communicate.
It defines the rules for data transmission, addressing, and error handling. IP addresses are assigned to devices on a network using the Internet Protocol (IP), which is part of the TCP/IP suite.DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a network protocol that automates the assignment of IP addresses to devices on a network.
When a device connects to a DHCP-enabled network, it sends a DHCP request to a DHCP server. The DHCP server then assigns an IP address to the device from a pool of available addresses.
Verifying Network Protocol Settings
To verify the network protocol settings on your printer and computer, follow these steps:
1. Printer
Access the printer’s network settings menu.
Look for options related to TCP/IP or IP configuration.
Check the IP address assigned to the printer.
2. Computer
Open the network settings on your computer.
Find the IP address assigned to your computer.
Check if the IP addresses of the printer and computer are on the same subnet (have the same first three octets).
Resolving Issues Related to Network Protocols
If you encounter issues related to network protocols, try the following troubleshooting steps:
Check for DHCP conflicts
If multiple devices on the network are using the same IP address, it can lead to conflicts. Check the DHCP server logs or use a network scanner to identify any duplicate IP addresses.
Disable and re-enable the network adapter
On both the printer and computer, disable and then re-enable the network adapter. This can sometimes resolve minor network issues.
Reset the DHCP server
If the DHCP server is not functioning correctly, reset it to clear any errors or glitches.
Contact your network administrator
If you are unable to resolve the issue yourself, contact your network administrator for assistance.
10. Printer Drivers
Printer drivers play a crucial role in the IP address assignment process. They act as software intermediaries between the printer and the computer, facilitating communication and ensuring proper functionality.
Updating or Reinstalling Printer Drivers
Outdated or corrupt printer drivers can lead to incorrect IP address assignment. Regular updates are recommended to ensure optimal performance and address any potential issues. Reinstallation may also be necessary if the drivers become damaged or malfunction.
Importance of Correct Printer Driver
Using the correct printer driver is essential for accurate IP address assignment. Each printer model has specific driver requirements, and using an incompatible driver can result in incorrect IP address configuration or even hardware damage.
Checking Printer Driver Version, Where to find the printer ip address
To check the current printer driver version:
- Go to the Device Manager on your computer.
- Expand the “Printers” category.
- Right-click on the printer and select “Properties.”
- Click on the “Driver” tab.
- The driver version will be displayed under “Driver Version.”
Printer Driver Versions and IP Address Assignment
The following table summarizes different printer driver versions and their corresponding IP address assignment methods:
| Driver Version | IP Address Assignment Method |
|---|---|
| PCL 6 | Manual configuration or DHCP |
| PCL 5 | Manual configuration only |
| PostScript | Manual configuration or Bonjour (zero-configuration networking) |
Warning:Using an incorrect printer driver can lead to incorrect IP address assignment, hardware damage, or security vulnerabilities. Always download and install the latest driver from the manufacturer’s official website.
11. IP Address Range
IP addresses are assigned to devices on a network to identify them and allow communication. IP address ranges define a group of valid IP addresses that can be used on a particular network. A subnet is a portion of an IP address range that is assigned to a specific segment of the network.
To determine the valid IP address range for a network, you need to know the network’s subnet mask. The subnet mask defines which bits of the IP address are used for the network address and which bits are used for the host address.
For example, a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 indicates that the first three octets of the IP address are used for the network address and the last octet is used for the host address.
Once you know the network’s subnet mask, you can calculate the valid IP address range by using the following formula:
Network address = IP address AND subnet mask
Broadcast address = Network address OR NOT subnet mask
Valid IP address range = Network address + 1 to Broadcast address – 1
For example, if the IP address is 192.168.1.100 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, the network address would be 192.168.1.0, the broadcast address would be 192.168.1.255, and the valid IP address range would be 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254.
When configuring the printer’s IP address, it is important to choose an IP address that is within the valid IP address range for the network. You should also avoid using the network address or the broadcast address.
IP Address Conflicts
An IP address conflict occurs when two or more devices on a network are assigned the same IP address. This can cause network problems, such as devices being unable to communicate with each other. To avoid IP address conflicts, you should use a DHCP server to assign IP addresses to devices on the network.
Firewall and Security
Firewalls and security settings play a crucial role in determining the accessibility of IP addresses on a network. A firewall acts as a barrier between a private network and the public internet, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined rules.
When it comes to accessing the IP address of a printer, firewall settings can impact connectivity.
Firewall Configuration
To allow access to the printer’s IP address, it is necessary to configure firewall rules that permit communication between the devices on the network. This involves creating an inbound rule that allows traffic from the specific IP address or range of IP addresses where the printer is located.
Additionally, an outbound rule may be required to allow traffic from the computer or device attempting to access the printer.
Best Practices for Securing Printer Network Connection
Securing the printer’s network connection is essential to prevent unauthorized access and potential security breaches. Some best practices include:
- Use Strong Passwords:Set strong and unique passwords for the printer’s network interface and administrative console.
- Enable Network Encryption:Implement encryption protocols such as WPA2 or WPA3 to secure wireless network connections and prevent eavesdropping.
- Limit Access:Configure firewall rules to restrict access to the printer’s IP address only to authorized devices and users.
- Regular Firmware Updates:Keep the printer’s firmware up to date to patch security vulnerabilities and improve overall network security.
- Physical Security:Place the printer in a secure location to prevent unauthorized physical access.
Network Diagram for Finding Printer IP Address
A network diagram provides a visual representation of the network components and their interconnections. It helps in understanding the network topology, IP address assignment, and the path taken by data packets to reach the printer.
Network Components and IP Addresses
| Component | IP Address |
|---|---|
| Computer | 192.168.1.10 |
| Printer | 192.168.1.100 |
| Router | 192.168.1.1 |
Flowchart for Finding Printer IP Address
- Check if the printer is connected to the network.
- Access the router’s configuration page.
- Find the DHCP client list or attached devices list.
- Locate the printer’s MAC address in the list.
- Obtain the corresponding IP address assigned to the printer.
Code Snippet in Python
“`pythonimport subprocessdef get_printer_ip_address(): # Get the MAC address of the printer mac_address = subprocess.check_output(“arp-a | grep
# Get the IP address associated with the MAC address ip_address = subprocess.check_output(“arp -a | grep ” + mac_address + ” | awk ‘print $2′”, shell=True)
return ip_address.decode(“utf-8”).strip() “`
Explanation
The network diagram illustrates the network components involved in finding the printer IP address. The computer and printer are connected to the router, which assigns IP addresses to devices on the network.
The flowchart provides a step-by-step guide to finding the printer IP address. It involves accessing the router’s configuration page, finding the printer’s MAC address in the DHCP client list, and obtaining the corresponding IP address.
The Python code snippet demonstrates how to programmatically find the printer IP address using the `subprocess` module. It retrieves the printer’s MAC address using the `arp` command and then uses it to obtain the IP address associated with it.
14. Troubleshooting Table
If you encounter difficulties finding your printer’s IP address, refer to the troubleshooting table below for common issues and their corresponding solutions.
The table provides a clear and concise overview of potential problems, their possible causes, recommended solutions, and the estimated time required to resolve each issue.
Troubleshooting Table
| Issue | Possible Causes | Solutions | Estimated Time to Resolve |
|---|---|---|---|
| Printer not connected to the network | – Physical connection issues (e.g., loose cables, damaged ports)
| – Check all physical connections (power, Ethernet/Wi-Fi)
| 15-30 minutes |
| Incorrect IP address or subnet mask | – Manual IP configuration errors
| – Manually assign a static IP address to the printer
| 30-60 minutes |
| Firewall or antivirus software blocking communication | – Firewall rules preventing printer access
| – Create firewall exceptions for the printer’s IP address and ports
| 15-30 minutes |
| Network driver issues | – Outdated or corrupted network drivers
| – Update or reinstall the printer’s network drivers
| 15-30 minutes |
| DNS resolution problems | – Incorrect DNS settings on the printer or network
| – Verify DNS settings on the printer and router
| 30-60 minutes |
15. Frequently Asked Questions

Below is a compilation of frequently asked questions (FAQs) regarding how to find a printer’s IP address. Each question is answered concisely and informatively to provide users with quick and easy access to the information they need.
How can I find the IP address of my printer?
There are several methods to find the IP address of your printer. These include checking the printer’s control panel, using network settings, configuring your router, employing third-party tools, and examining the printer’s properties.
What is the difference between a static and a dynamic IP address?
A static IP address is a permanent IP address assigned to a device on a network. A dynamic IP address, on the other hand, is a temporary IP address assigned to a device by a DHCP server and can change over time.
How do I change the IP address of my printer?
The process of changing the IP address of your printer varies depending on the printer model and network configuration. Generally, you can change the IP address through the printer’s control panel, network settings, or using a third-party tool.
What are the potential issues that can prevent me from finding my printer’s IP address?
Several factors can prevent you from finding your printer’s IP address, including incorrect network settings, firewall or security restrictions, and outdated printer drivers.
How can I troubleshoot problems related to finding my printer’s IP address?
If you encounter issues finding your printer’s IP address, you can try advanced troubleshooting techniques such as using command-line tools, checking network protocols, and verifying the printer drivers.
FAQ Explained
How do I find the IP address of my printer connected to a Windows computer?
Go to Control Panel > Devices and Printers > Right-click on your printer > Printer Properties > Ports tab > Look for the IP address under “Printer Name or IP Address”.
Can I find the IP address of my printer without connecting it to a network?
Yes, you can use a USB cable to connect the printer directly to your computer and access its IP address through the printer’s control panel or web interface.
What if I can’t find the IP address of my printer using the provided methods?
Try using third-party software or online tools specifically designed to discover printer IP addresses. These tools can scan your network and identify your printer’s IP address.


