Where is Disk Utility on a Mac? This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of locating and using Disk Utility, a powerful tool for managing storage devices on macOS. We will explore its functionality, interface, and advanced features, empowering you to effectively maintain and troubleshoot your storage devices.
Disk Utility is an essential tool for managing storage devices on your Mac. It allows you to format, partition, repair, and erase drives, ensuring optimal performance and data integrity. Understanding its location and functionality is crucial for efficient storage management.
Definition of Disk Utility
Disk Utility is a powerful built-in utility on macOS that provides comprehensive management and repair capabilities for storage devices connected to a Mac computer.
It enables users to perform various tasks related to storage devices, including formatting, partitioning, verifying, and repairing disk drives. Disk Utility offers a user-friendly interface that allows users to easily manage their storage devices and ensure their optimal performance.
Functionality in Managing Storage Devices
- Disk Partitioning:Disk Utility allows users to create, resize, and delete partitions on a storage device. Partitioning enables users to divide a single physical drive into multiple logical volumes, each with its own file system and storage space.
- Disk Formatting:Disk Utility supports various file system formats, including HFS+, APFS, and exFAT. Users can format a storage device to a specific file system based on their requirements for compatibility and performance.
- Disk Verification and Repair:Disk Utility includes advanced tools for verifying the integrity of a storage device and repairing any detected errors. It can perform disk scans to identify and fix issues such as bad sectors, directory errors, and file system inconsistencies.
- Disk Erasure:Disk Utility provides secure erasure options to permanently delete data from a storage device. This feature is useful when preparing a device for disposal or when ensuring complete data removal for security purposes.
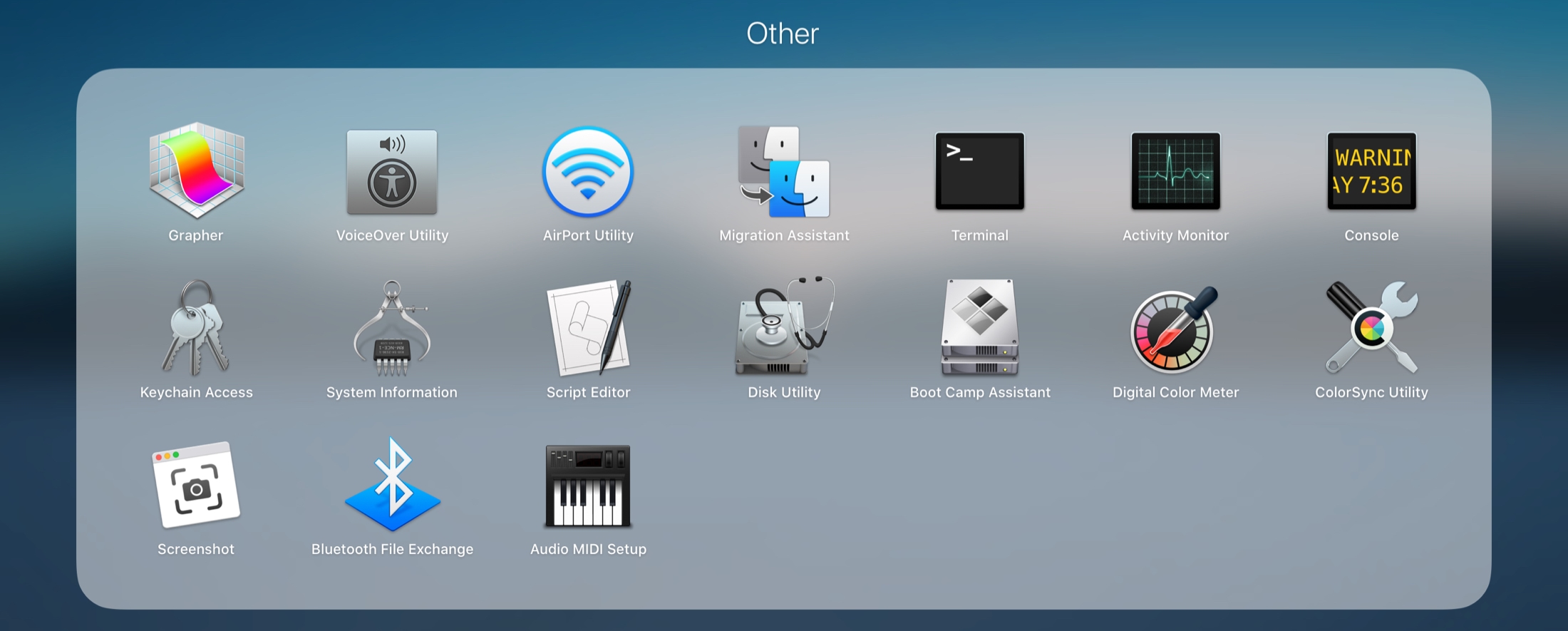
Location of Disk Utility on macOS: Where Is Disk Utility On A Mac
Disk Utility is a built-in application on macOS that allows users to manage and repair storage devices. It provides various tools for disk management, including partitioning, formatting, erasing, and repairing disks.
There are several ways to access Disk Utility on macOS:
Through the Applications Folder
1. Open the Finder.
2. Click on the “Applications” folder in the sidebar.
3. Scroll down and find the “Utilities” folder.
4. Open the “Utilities” folder and double-click on the “Disk Utility” application.
Through Spotlight
1. Click on the Spotlight icon in the menu bar.
2. Type “Disk Utility” in the search field.
3. Click on the “Disk Utility” icon in the search results.
Through the Utilities Folder in Launchpad
1. Open Launchpad.
2. Click on the “Utilities” folder.
3. Drag the “Disk Utility” icon to the Dock or Desktop for easy access.
Interface and Layout of Disk Utility
The main interface of Disk Utility on macOS consists of a menu bar, sidebar, and main panel.The menu bar provides access to various commands and options, including File, Edit, View, and Help. The sidebar displays a list of available storage devices and volumes, allowing users to select and manage them.The main panel displays information about the selected storage device or volume, including its name, size, format, and usage.
It also provides access to various tools and features for managing and repairing storage devices and volumes, such as First Aid, Partition, and Erase.
Using Disk Utility to Manage Storage Devices
Disk Utility provides a comprehensive set of tools for managing storage devices connected to a Mac. These include internal hard drives, external hard drives, SSDs, and USB flash drives. Disk Utility allows users to view information about these devices, format them, partition them, and erase them.
Viewing Storage Devices
To view the storage devices connected to a Mac, open Disk Utility and click on the “External” tab in the sidebar. This will display a list of all external storage devices that are currently connected to the Mac. The list will include the device’s name, capacity, and type.
Formatting Storage Devices
Formatting a storage device erases all data on the device and prepares it for use with a specific file system. Disk Utility supports a variety of file systems, including HFS+, APFS, and exFAT. To format a storage device, select the device in the sidebar and click on the “Erase” tab.
Then, select the desired file system from the “Format” drop-down menu and click on the “Erase” button.
Disk Utility, a built-in macOS tool, can be found in the Applications folder under the Utilities subfolder. It provides various disk management functions. If you encounter issues using Disk Utility’s “Kickstart” feature, refer to why is utility kickstart disabled for potential reasons and solutions.
Disk Utility remains a versatile tool for managing storage devices on macOS.
Partitioning Storage Devices
Partitioning a storage device divides it into multiple logical volumes. This can be useful for organizing data or for creating separate volumes for different operating systems. To partition a storage device, select the device in the sidebar and click on the “Partition” tab.
Then, click on the “Add” button to create a new partition. You can specify the size and format of the new partition.
Erasing Storage Devices
Erasing a storage device deletes all data on the device and makes it inaccessible. This can be useful for securely erasing data before disposing of a storage device or for troubleshooting problems with a storage device. To erase a storage device, select the device in the sidebar and click on the “Erase” tab.
Then, click on the “Erase” button.
Repairing and Verifying Storage Devices
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/005_use-disk-utility-to-clone-macs-drive-4042367-5bc4e77946e0fb002698ce0b.jpg)
Disk Utility includes a feature called “First Aid” that allows users to repair and verify storage devices. This feature can be used to fix a variety of issues, including file system errors, bad sectors, and directory problems.
Using the “First Aid” Feature, Where is disk utility on a mac
To repair or verify a storage device using the “First Aid” feature, follow these steps:
- Launch Disk Utility.
- Select the storage device you want to repair or verify.
- Click on the “First Aid” tab.
- Click on the “Repair Disk” or “Verify Disk” button.
If the “Repair Disk” button is disabled, it means that the storage device is not damaged and does not need to be repaired. If the “Verify Disk” button is disabled, it means that the storage device has been verified and no errors were found.
Repair Options
The “First Aid” feature offers two repair options:
- Repair Disk:This option attempts to repair all errors on the storage device. It is the most comprehensive repair option and should be used if you are experiencing problems with the storage device.
- Verify Disk:This option checks the storage device for errors but does not attempt to repair them. It is a good option if you want to check the health of the storage device without making any changes.
Interpreting the Results
After the “First Aid” feature has finished repairing or verifying the storage device, it will display a report of the results. The report will include the following information:
- The status of the repair or verification.
- Any errors that were found.
- Any repairs that were made.
If the report shows that the storage device was repaired successfully, you can continue using it as normal. If the report shows that the storage device could not be repaired, you may need to replace it.
Troubleshooting Common Storage Device Issues
The “First Aid” feature can be used to troubleshoot a variety of common storage device issues, including:
- File system errors
- Bad sectors
- Directory problems
- Slow performance
- Unexpected shutdowns
If you are experiencing any of these issues, you can try using the “First Aid” feature to repair the storage device. If the “First Aid” feature is unable to repair the storage device, you may need to replace it.
Creating and Managing Partitions
Disk Utility provides comprehensive tools for managing storage devices, including the ability to create, resize, delete, and format partitions. Partitions divide a physical storage device into logical units, allowing for the organization and management of data.
Partition Schemes and File Systems
Disk Utility supports various partition schemes and file systems, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
| Partition Scheme | File System | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| GUID Partition Table (GPT) | Apple File System (APFS) | Modern, supports large drives, multiple partitions | Not compatible with older macOS versions |
| Master Boot Record (MBR) | HFS+ (Mac OS Extended) | Compatible with older macOS versions, supports up to 4 primary partitions | Limitations on partition size and number |
| MBR | FAT32 | Widely compatible with other operating systems | Limited partition size (up to 32GB) |
Creating Partitions
To create a partition in Disk Utility:
- Select the storage device in the sidebar.
- Click the “Partition” tab.
- Click the “+” button to add a new partition.
- Set the partition size, name, and file system.
- Click “Apply” to create the partition.
Resizing, Deleting, and Formatting Partitions
To resize, delete, or format a partition:
- Select the partition in the sidebar.
- Click the “Resize,” “Delete,” or “Erase” button.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the operation.
Choosing the Right Partition Scheme and File System
The choice of partition scheme and file system depends on factors such as compatibility, performance, and storage capacity. For modern macOS systems, GPT and APFS are recommended.
Partition Management Software
For advanced partitioning tasks, third-party partition management software can provide additional features such as RAID configuration and bootcamp partition management.
Logical Volumes and RAID Arrays
Disk Utility allows for the creation and management of logical volumes, which combine multiple physical storage devices into a single logical unit. It also supports the creation of RAID arrays, which provide data redundancy and improved performance.
Cloning and Restoring Drives
Disk Utility offers robust capabilities for cloning and restoring drives, ensuring data integrity and facilitating efficient drive management.
Cloning Drives
Disk Utility enables the cloning of one drive to another, creating an exact replica of the source drive. This is particularly useful for creating backups, upgrading to a larger drive, or migrating data to a new computer. Selecting Source and Destination Drives:
- Select the source drive containing the data to be cloned.
- Choose the destination drive with sufficient capacity to accommodate the clone.
Cloning Options:
Clone (Default)
Creates an exact replica of the source drive, including all data and partitions.
Clone (Encrypted)
Encrypts the cloned drive for enhanced security.
Clone (Sparse Bundle)
Creates a sparse bundle image file containing the cloned drive, allowing for space-efficient storage. Verifying the Cloned Drive:After cloning, verify the integrity of the cloned drive using Disk Utility’s “Verify Disk” function.
To determine the location of Disk Utility on a Mac, navigate to the Utilities folder within the Applications directory. This folder houses various system tools, including Disk Utility, which allows for managing and repairing storage devices. In a different context, utilization review nurses play a crucial role in assessing the appropriateness of healthcare services.
They evaluate patient medical records, review utilization data , and determine whether treatments and procedures align with established guidelines and medical necessity criteria. Returning to the topic of Disk Utility, once located in the Utilities folder, users can access its features for managing storage devices on their Mac.
Restoring Drives
Disk Utility can restore a drive from a backup created using Time Machine or Disk Utility itself. Creating a Backup:
- Connect an external drive or use an existing Time Machine backup.
- In Disk Utility, select the source drive and choose “New Image” from the “File” menu.
- Select the destination backup location and click “Save.”
Selecting Backup File and Destination Drive:
- Select the backup file created previously.
- Choose the destination drive to restore the backup to.
Restore Options:
Restore (Default)
Replaces the contents of the destination drive with the contents of the backup.
Restore Encrypted (Encrypted Backups Only)
Restores the backup to the destination drive while maintaining encryption.
Restore Sparse Bundle
Restores the backup to a sparse bundle image file on the destination drive. Verifying the Restored Drive:After restoring, verify the integrity of the restored drive using Disk Utility’s “Verify Disk” function.
Erasing and Formatting Storage Devices
Disk Utility provides powerful options for erasing and formatting storage devices, enabling users to securely wipe data or prepare drives for specific file systems and usage scenarios.
Erase Options
When erasing a storage device, Disk Utility offers various erase options, each with varying levels of security and speed:
- Quick Erase:Performs a quick erase, which is faster but less secure as it doesn’t overwrite the existing data on the drive.
- Secure Erase:Overwrites the entire drive multiple times, making it difficult to recover data. However, it is slower than Quick Erase.
- Custom Erase:Allows users to specify the number of passes for overwriting the drive, providing a customizable level of security.
Format Options
Disk Utility supports formatting storage devices to various file systems, including:
- Mac OS Extended (HFS+):The default file system for macOS, optimized for performance and reliability.
- APFS (Apple File System):A newer file system introduced with macOS High Sierra, designed for improved performance and data protection.
- FAT32:A widely compatible file system suitable for use with both macOS and Windows systems.
- NTFS:The default file system for Windows, but can be read-only on macOS without additional software.
Advanced Features of Disk Utility

Disk Utility offers a range of advanced features that enable users to perform in-depth diagnostics and troubleshooting on their storage devices. One such feature is S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) status monitoring.
S.M.A.R.T. Status Monitoring
S.M.A.R.T. is a self-monitoring system built into many modern storage devices, including hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). It continuously monitors the device’s health and performance, tracking various parameters such as temperature, read/write errors, and power-on hours.By accessing the S.M.A.R.T.
status information in Disk Utility, users can gain valuable insights into the condition of their storage devices. If any potential issues are detected, such as an increase in bad sectors or excessive read/write errors, Disk Utility can provide early warnings, allowing users to take preventive measures before data loss occurs.Using S.M.A.R.T.
status monitoring in Disk Utility is straightforward. Select the desired storage device in the sidebar and click on the “S.M.A.R.T.” tab. The tab will display a table listing various S.M.A.R.T. attributes, along with their current values, thresholds, and worst values.
By comparing the current values to the thresholds and worst values, users can assess the health of their storage device and identify any potential issues that require attention.
Troubleshooting Common Disk Utility Issues
Disk Utility is a robust tool, but it can sometimes encounter issues. Here’s a guide to common problems and their solutions:
Common Issues and Solutions
- Disk Utility can’t repair a disk:This can be caused by file system corruption or hardware failure. Try using a third-party disk repair tool or contacting Apple support.
- Disk Utility can’t mount a disk:This can be caused by a damaged file system or a problem with the disk’s hardware. Try using DiskWarrior or another third-party disk repair tool to fix the file system. If the disk is physically damaged, you may need to replace it.
- Disk Utility can’t create a new partition:This can be caused by a number of factors, including a full disk or an invalid partition scheme. Try deleting some files or creating a smaller partition.
- Disk Utility can’t erase a disk:This can be caused by a number of factors, including a write-protected disk or a damaged file system. Try using a third-party disk erase tool or contacting Apple support.
Error Messages and Troubleshooting Tips
- “The disk you inserted was not readable by this computer”:This error message can occur if the disk is formatted for a different operating system or if the disk is physically damaged. Try using a disk repair tool or contacting Apple support.
- “The operation couldn’t be completed because the disk image file couldn’t be opened”:This error message can occur if the disk image file is corrupted or if you don’t have the necessary permissions to open the file. Try downloading the disk image file again or contacting the person who provided you with the file.
- “The disk you inserted is not recognized”:This error message can occur if the disk is not properly formatted or if the disk is physically damaged. Try using a disk repair tool or contacting Apple support.
Additional Resources
Disk Utility for External Storage Devices
Disk Utility can also be used to manage external storage devices, such as USB drives and SD cards. When working with external storage devices, it’s important to consider the following:
- Formatting:External storage devices can be formatted using different file systems, such as FAT32, exFAT, and NTFS. The choice of file system depends on the intended use of the device and the compatibility with different operating systems.
- Partitioning:External storage devices can be partitioned into multiple volumes, allowing you to organize and manage your data more effectively.
Connecting an External Storage Device
To connect an external storage device to your computer, follow these steps:
- Connect the external storage device to an available USB port or SD card slot on your computer.
- The device should be automatically recognized by your computer and mounted on the desktop.
Opening Disk Utility
To open Disk Utility, follow these steps:
- Click on the Findericon in the Dock.
- Click on Applicationsin the menu bar.
- Scroll down and click on Utilities.
- Double-click on Disk Utility.
Selecting the External Storage Device
Once Disk Utility is open, select the external storage device from the sidebar on the left.
Formatting the External Storage Device
To format the external storage device, follow these steps:
- Select the external storage device in the sidebar.
- Click on the Erasetab.
- Choose a file system from the Formatdrop-down menu.
- Enter a name for the volume in the Namefield.
- Click on the Erasebutton.
Partitioning the External Storage Device
To partition the external storage device, follow these steps:
- Select the external storage device in the sidebar.
- Click on the Partitiontab.
- Click on the +button to add a new partition.
- Enter a size for the partition in the Sizefield.
- Choose a file system from the Formatdrop-down menu.
- Enter a name for the partition in the Namefield.
- Click on the Applybutton.
Disk Utility for RAID Management

Disk Utility provides robust capabilities for managing RAID configurations on macOS, enabling users to create, configure, repair, and troubleshoot RAID arrays. This powerful tool offers a comprehensive set of features for managing storage devices, ensuring data integrity and reliability.
Creating RAID Arrays
To create a RAID array using Disk Utility, follow these steps:
- Launch Disk Utility and select “File” > “New RAID Assistant.”
- Choose the desired RAID level from the options presented.
- Select the physical disks to include in the RAID array.
- Specify the RAID configuration options, such as stripe size and spare disk allocation.
- Click “Create” to initiate the RAID creation process.
Configuring RAID Arrays
Disk Utility allows users to modify RAID array configurations, including adding or removing disks, changing stripe sizes, and adjusting spare disk allocation. To configure a RAID array:
- Select the RAID array in Disk Utility.
- Click the “RAID” tab.
- Make the desired configuration changes.
- Click “Apply” to save the changes.
Repairing RAID Arrays
Disk Utility can be used to repair RAID arrays that encounter errors or failures. To repair a RAID array:
- Select the RAID array in Disk Utility.
- Click the “First Aid” tab.
- Click “Repair Disk.”
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the repair process.
Troubleshooting RAID Issues
Disk Utility provides tools for troubleshooting common RAID issues, such as disk failures, configuration errors, and performance problems. To troubleshoot a RAID issue:
- Select the RAID array in Disk Utility.
- Click the “Info” tab.
- Review the array status and error messages.
- Use the “Repair Disk” or “Rebuild” options to resolve the issue.
Disk Utility in Recovery Mode
Disk Utility plays a critical role in macOS Recovery Mode, providing essential tools for troubleshooting and resolving disk-related issues. When booting into Recovery Mode (typically by holding down Command + R during startup), Disk Utility can be accessed from the Utilities menu.
Key Features and Functions
In Recovery Mode, Disk Utility offers a range of capabilities, including:
- Repairing and verifying storage devices
- Creating and managing partitions
- Cloning and restoring drives
- Erasing and formatting storage devices
- Advanced features such as S.M.A.R.T. status checks and terminal commands
Troubleshooting Disk Issues
Disk Utility in Recovery Mode is particularly valuable for troubleshooting disk problems. It can be used to:
- Repair file system errors and logical disk issues
- Recover lost data from corrupted or damaged storage devices
- Diagnose and resolve physical disk failures
- Repartition drives to correct disk space allocation problems
- Erase and reformat drives to remove viruses or malware
Best Practices
When using Disk Utility in Recovery Mode, it is essential to follow best practices:
- Back up your data before performing any operations.
- Use caution when erasing or formatting drives, as data cannot be recovered after these actions.
- Repair permissions and verify the startup disk regularly to prevent disk issues.
- Seek professional assistance if you encounter complex disk problems that cannot be resolved using Disk Utility.
“Disk Utility in macOS Recovery Mode provides a powerful set of tools for diagnosing and resolving disk issues. By using these tools effectively, you can ensure the health and integrity of your storage devices.”
Apple Support
Alternative Storage Device Management Tools for macOS
Disk Utility is a powerful tool for managing storage devices on macOS, but it may not be the best option for all users. Several alternative tools offer a range of features and capabilities that can be more suitable for specific tasks or workflows.
Features Comparison of Alternative Tools
The following table compares the key features of several popular alternative storage device management tools for macOS:| Tool | Storage Device Support | File System Support | Partitioning and Formatting Capabilities | Cloning and Imaging Functionality | Data Recovery Capabilities | Benchmarking and Performance Testing | Price and Licensing ||—|—|—|—|—|—|—|—|| [Carbon Copy Cloner](https://bombich.com/) | Internal and external drives, RAID arrays | HFS+, APFS, FAT, exFAT, NTFS | Create, resize, and delete partitions | Full disk cloning, incremental backups | File and folder recovery | Built-in benchmark tool | $39.99 || [SuperDuper!](https://www.shirt-pocket.com/) | Internal and external drives, RAID arrays | HFS+, APFS, FAT, exFAT, NTFS | Create, resize, and delete partitions | Full disk cloning, incremental backups | File and folder recovery | Built-in benchmark tool | $29.95 || [Acronis Cyber Protect Home Office](https://www.acronis.com/en-us/personal/cyber-protect-home-office/) | Internal and external drives, RAID arrays, virtual machines | HFS+, APFS, FAT, exFAT, NTFS, ext2, ext3, ext4 | Create, resize, and delete partitions | Full disk cloning, incremental backups, cloud backups | File and folder recovery, ransomware protection | Built-in benchmark tool | $49.99 per year || [Paragon Hard Disk Manager](https://www.paragon-software.com/home/mac-manager/) | Internal and external drives, RAID arrays | HFS+, APFS, FAT, exFAT, NTFS, ext2, ext3, ext4 | Create, resize, and delete partitions | Full disk cloning, incremental backups, cloud backups | File and folder recovery, data migration | Built-in benchmark tool | $79.95 || [Disk Drill](https://www.cleverfiles.com/disk-drill-mac.html) | Internal and external drives, RAID arrays, USB flash drives, memory cards | HFS+, APFS, FAT, exFAT, NTFS, ext2, ext3, ext4 | Create, resize, and delete partitions | Data recovery only | Advanced data recovery algorithms | Built-in benchmark tool | $89 |
Best Practices for Using Disk Utility
Disk Utility is a powerful tool, but it can also be destructive if used improperly. Here are some tips and best practices for using Disk Utility effectively:
- Always back up your data before using Disk Utility.This is the most important rule of thumb, as any changes you make to your storage devices using Disk Utility could potentially result in data loss.
- Understand what you’re doing before you make any changes.Disk Utility is a complex tool, and it’s important to understand the consequences of any changes you make before you proceed.
- Use the Preview feature to see what changes will be made before you commit them.This can help you avoid making any mistakes that could lead to data loss.
- Be patient.Disk Utility can take a while to complete some operations, especially on large storage devices.
- If you’re not sure how to use Disk Utility, don’t be afraid to ask for help.There are many resources available online, and you can also contact Apple support for assistance.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Here are some common pitfalls to avoid when using Disk Utility:
- Don’t delete or reformat a partition without first backing up the data on it.This could result in permanent data loss.
- Don’t create a new partition that is too small.This could prevent you from installing an operating system or other software on the partition.
- Don’t use Disk Utility to repair a storage device that is physically damaged.This could make the damage worse.
- Don’t use Disk Utility to recover data from a storage device that has been formatted.This could overwrite the data and make it impossible to recover.
- Don’t use Disk Utility to resize a partition that contains an operating system.This could damage the operating system and make it unbootable.
Ensuring Data Integrity
Here are some tips for ensuring data integrity when using Disk Utility:
- Always use the Preview feature before committing any changes.This can help you avoid making any mistakes that could lead to data loss.
- Back up your data regularly.This is the best way to protect your data in the event of a hardware failure or other data loss event.
- Use a reliable storage device.This will help to prevent data corruption and other problems.
- Keep your software up to date.This will help to ensure that you have the latest security patches and bug fixes.
- Be careful when using third-party software.Some third-party software can damage your storage devices or data.
Q&A
How do I open Disk Utility?
You can open Disk Utility through the Applications folder or by using Spotlight search.
What is the “First Aid” feature in Disk Utility?
The “First Aid” feature allows you to repair and verify storage devices, resolving common issues and preventing data loss.
Can I use Disk Utility to create and manage partitions?
Yes, Disk Utility provides options for creating, resizing, deleting, and formatting partitions, allowing you to organize your storage space efficiently.
How do I clone a drive using Disk Utility?
Disk Utility allows you to clone one drive to another, creating an exact copy for backup or data migration purposes.
What are the advanced features of Disk Utility?
Disk Utility includes advanced features such as S.M.A.R.T. status monitoring, allowing you to diagnose and troubleshoot storage device issues.


