What’s considered a utility bill – Understanding what constitutes a utility bill is crucial for managing your household expenses effectively. Utility bills are invoices that detail the charges for essential services that provide comfort, convenience, and functionality to your home. These services include electricity, water, gas, and other utilities that are indispensable for modern living.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the components of a utility bill, explore the different types of utilities, and provide practical tips for reducing your utility costs. By gaining a clear understanding of your utility bills, you can make informed decisions about your energy consumption and financial planning.
Definition of Utility Bill
A utility bill is a statement that Artikels the charges for services provided by utility companies. These services are essential for everyday life and include electricity, gas, water, and sometimes other services like sewage or trash removal.
Utility bills serve several important purposes. They provide a record of usage, allowing customers to track their consumption and identify areas where they can reduce it. They also help customers budget by providing a predictable expense. Additionally, utility bills can be used as proof of residency or income for various purposes.
Components of a Utility Bill
Utility bills typically include several key components:
| Service | Usage | Unit Price | Total Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electricity | kWh | $0.10/kWh | $10.00 |
| Gas | therms | $0.50/therm | $20.00 |
| Water | gallons | $0.01/gallon | $5.00 |
| Sewage | gallons | $0.02/gallon | $2.00 |
Understanding Utility Usage
Understanding the usage data on a utility bill is crucial for managing consumption and expenses. The units of measurement used for different utilities vary, so it’s important to familiarize yourself with them.
- Electricity is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), which represent the amount of electricity used over time.
- Gas is measured in therms, which represent the amount of heat energy delivered.
- Water is measured in gallons, which represent the volume of water consumed.
Billing Cycles and Payment Options
Utility bills typically have a regular billing cycle, such as monthly or quarterly. Customers receive a bill at the end of each cycle, which Artikels the charges for the previous period.
Various payment options are available to customers, including online payments, mail-in payments, and automatic withdrawals from a bank account.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation
Utility bills play a vital role in promoting energy efficiency and conservation. By providing information about usage, customers can identify areas where they can reduce their consumption and save money.
- For electricity, energy-efficient appliances and lighting can significantly reduce consumption.
- For gas, using programmable thermostats and insulating the home can improve efficiency.
- For water, low-flow fixtures and xeriscaping can reduce usage.
Troubleshooting Utility Bills
Occasionally, customers may encounter issues with their utility bills. Common issues include:
- Inaccurate readings: If the usage data on the bill seems incorrect, customers can contact the utility company to have the meter checked.
- Billing errors: If there is an error in the calculation of the bill, customers should contact the utility company to have it corrected.
- Overdue payments: If a payment is not made on time, customers may incur late fees and penalties. It’s important to make payments promptly to avoid these additional charges.
Components of a Utility Bill
A utility bill is a statement that provides details about the consumption and charges for utilities such as electricity, gas, water, or trash removal. It typically consists of several sections, each serving a specific purpose.
The following are the typical sections or components found on a utility bill:
Account Summary
- Account number:A unique identifier for the customer’s account.
- Billing period:The start and end dates of the billing cycle.
- Current charges:The total amount due for the current billing period.
- Past due amount:Any unpaid balance from previous billing periods.
- Payment due date:The date by which payment is due to avoid late fees.
Usage Details
- Meter readings:The current and previous meter readings, indicating the amount of utility consumed during the billing period.
- Consumption history:A graph or table showing the customer’s usage patterns over time.
- Usage tiers:For tiered rate structures, this section shows the amount of consumption in each tier and the corresponding rates.
Charges
- Base charges:A fixed monthly fee that covers the basic cost of providing service.
- Usage charges:The amount charged for the actual consumption of the utility, calculated based on the applicable rate structure.
- Taxes and surcharges:Additional fees imposed by government entities or the utility company for various purposes.
Payment Information, What’s considered a utility bill
- Payment methods:The available options for making payments, such as online, by mail, or through automatic withdrawal.
- Contact information:The utility company’s contact information for inquiries or customer service.
Understanding the different sections of a utility bill is crucial for managing utility costs and resolving any billing issues.
Types of Utilities: What’s Considered A Utility Bill
Utilities are essential services that provide convenience and comfort in our daily lives. They can be categorized into different types based on their necessity and purpose.
The following table provides a comprehensive overview of the different types of utilities, along with examples and brief descriptions:
| Category | Examples | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Essential Utilities | Electricity, water, gas | Utilities that are necessary for daily living and are typically regulated by government agencies. |
| Non-Essential Utilities | Internet, cable TV, phone | Utilities that are not essential for daily living but provide convenience and entertainment. |
| Other Utilities | Trash removal, recycling, sewer | Utilities that are typically provided by local governments or private companies. |
Usage Charges
Usage charges are the primary component of a utility bill and reflect the actual consumption of the utility service during a billing period. These charges are calculated based on the amount of electricity, gas, water, or other resources used.
The calculation of usage charges involves multiplying the consumption amount by the applicable rate or tariff. The consumption amount is typically measured in units such as kilowatt-hours (kWh) for electricity, cubic feet (cf) for gas, or gallons for water. The rate or tariff is set by the utility company and varies depending on factors such as the type of utility service, location, and time of day or season.
Factors Influencing Usage Charges
Several factors can influence the usage charges on a utility bill. These include:
- Consumption patterns:The amount of utility service consumed during a billing period directly impacts the usage charges. Higher consumption generally leads to higher charges.
- Rate structure:Utility companies may use different rate structures, such as flat rates, tiered rates, or time-of-use rates. The rate structure determines how the consumption amount is charged.
- Time of day or season:Some utility companies implement time-of-use rates, which vary the cost of electricity based on the time of day or season. Peak hours, when demand is high, typically have higher rates.
- Location:Utility rates can vary depending on the geographical location. Factors such as the cost of fuel, infrastructure, and local regulations can influence the rates.
Fixed Charges

Fixed charges on a utility bill are non-usage-based fees that are applied regardless of the amount of utility consumed. These charges cover the fixed costs associated with providing utility services, such as infrastructure maintenance, customer service, and billing.Fixed charges are determined by the utility company and are typically based on the size of the customer’s property, the type of utility service, and the location of the property.
For example, a larger property with multiple utility connections may have higher fixed charges than a smaller property with fewer connections.
Purpose of Fixed Charges
Fixed charges are included on utility bills to ensure that the utility company can recover its fixed costs, regardless of the amount of utility consumed by individual customers. This ensures that all customers contribute to the upkeep and maintenance of the utility infrastructure.
Payment Options

Utility bills typically offer various payment options to accommodate customer preferences and convenience. Each payment method comes with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Online Payment
Online payment through a utility company’s website or mobile app is a convenient and secure option. Customers can make one-time payments or set up automatic payments.
Automatic Payment
Automatic payment authorizes the utility company to deduct the bill amount directly from the customer’s bank account on the due date. This eliminates the risk of late payments and ensures timely bill settlement.
Mail-In Payment
Mail-in payment involves sending a check or money order through the postal service. This method is widely accepted but can take several days to process, potentially resulting in late fees if not mailed promptly.
In-Person Payment
Customers can make in-person payments at designated payment centers or the utility company’s office. This option allows for immediate payment processing but may require travel and queuing.
Prepaid Payment
Prepaid payment involves purchasing a certain amount of utility credit in advance. This method provides control over expenses and eliminates the risk of late payments. However, it may require frequent top-ups.
The choice of payment option depends on individual preferences, convenience, and financial situation. Online and automatic payments offer the greatest convenience, while mail-in and in-person payments may incur additional fees or require more effort. Prepaid payment provides control over expenses but may not be suitable for all customers.
Billing Cycles
Billing cycles are the predetermined periods for which utility companies calculate and send out bills to their customers. These cycles typically range from monthly to quarterly, and they play a crucial role in determining the frequency and timing of utility bill payments.
The frequency of billing cycles can be influenced by several factors, including:
Frequency of Meter Readings
- For utilities that require meter readings (e.g., electricity, gas, water), the billing cycle is often aligned with the frequency of meter readings.
- Monthly meter readings typically result in monthly billing cycles, while quarterly meter readings lead to quarterly billing cycles.
Customer Preferences
- Some utility companies offer customers the option to choose their preferred billing cycle, such as monthly, bi-monthly, or quarterly.
- Customers may select a cycle that aligns with their financial situation or payment preferences.
Company Policies
- Utility companies may establish their own billing cycle policies based on operational efficiency, customer convenience, and regulatory requirements.
- These policies may vary from company to company and may be subject to change over time.
Consequences of Late Payments on Utility Bills
Late payments on utility bills can have severe consequences, including:
- Late payment fees
- Service disconnection
- Damage to credit score
Understanding Your Bill
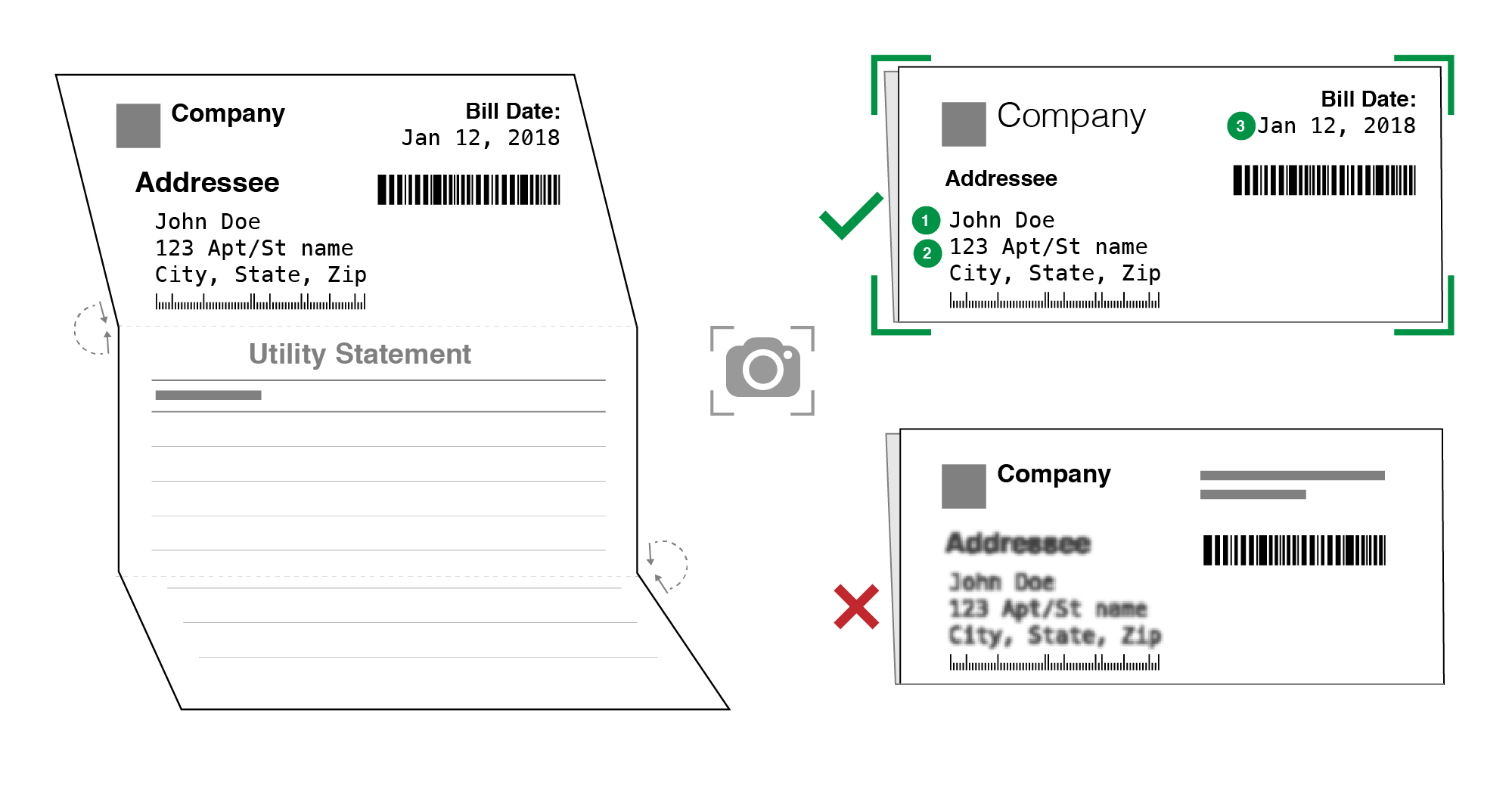
Understanding your utility bill can help you manage your energy consumption and avoid surprises. Here are some tips and strategies for interpreting your bill:
Review your bill regularly to familiarize yourself with its format and the charges included. Identify the different sections of the bill, such as usage charges, fixed charges, and payment options.
Common Areas of Confusion
- Usage charges:These charges vary based on your actual energy consumption, measured in units such as kilowatt-hours (kWh) for electricity or cubic feet (CF) for natural gas.
- Fixed charges:These charges are not usage-based and cover the cost of maintaining the utility infrastructure, such as power lines or gas pipelines.
- Taxes and fees:These additional charges may be included on your bill and can vary depending on your location and the type of utility.
If you have questions about your bill, contact your utility provider for clarification. They can explain the charges and help you understand how to reduce your energy consumption.
Energy Efficiency and Bill Reduction
Energy efficiency measures can significantly impact utility bills by reducing energy consumption and lowering costs. Implementing energy-saving practices can lead to substantial savings on monthly utility expenses.
One of the most effective ways to reduce energy consumption is to identify and address energy-intensive appliances and systems within the household. These typically include heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, refrigerators, washing machines, and dryers. By upgrading to energy-efficient models or implementing energy-saving measures, significant energy savings can be achieved.
Specific Energy-Saving Measures
- Lighting:Replacing incandescent bulbs with LED or CFL bulbs can reduce lighting energy consumption by up to 80%.
- Heating and Cooling:Installing programmable thermostats, sealing air leaks, and using energy-efficient appliances can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs.
- Appliances:Choosing Energy Star-rated appliances can save energy and lower utility bills.
- Water Heating:Installing low-flow showerheads and faucets, as well as insulating water heaters, can reduce water heating costs.
Data from the U.S. Department of Energy shows that implementing energy efficiency measures can lead to savings of up to 30% on utility bills. Case studies have demonstrated that households that have adopted energy-saving practices have experienced significant reductions in their monthly energy expenses.
Environmental Sustainability
In addition to reducing utility bills, energy efficiency measures also contribute to environmental sustainability. By reducing energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions are lowered, contributing to the fight against climate change.
Smart Meters and Utility Bills
Smart meters are advanced metering devices that provide more detailed information about energy consumption than traditional meters. They are becoming increasingly common in homes and businesses as they offer several advantages, including more accurate billing, real-time monitoring of energy usage, and improved energy efficiency.
Smart meters communicate with the utility company wirelessly, sending regular updates on energy consumption. This allows the utility company to track usage more accurately and send bills that reflect the actual amount of energy used. In addition, smart meters can provide real-time data on energy consumption, which can help consumers identify areas where they can reduce their energy usage.
Utility bills, typically comprising charges for services such as electricity, gas, water, and waste removal, are essential expenses for property owners. Understanding the components of a utility bill is crucial for budgeting and managing finances. In certain instances, a utility easement may be granted to utility companies to access and maintain infrastructure on a property.
The value of such easements can vary depending on factors like location and the scope of the easement. For more insights on utility easement valuations, refer to how much is a utility easement worth.
Usage Tracking and Billing Accuracy
Smart meters track energy consumption in real-time, providing more accurate data than traditional meters. Traditional meters only measure energy consumption at the end of the billing period, which can lead to inaccurate bills if energy usage fluctuates throughout the month.
Smart meters, on the other hand, provide real-time data, which allows the utility company to send bills that reflect the actual amount of energy used.
Utility Assistance Programs
Utility assistance programs are designed to provide financial aid and support to low-income or struggling customers who face difficulties paying their utility bills. These programs offer various forms of assistance, including bill payment assistance, income-based discounts, and payment plans.
Eligibility for utility assistance programs typically depends on factors such as income level, household size, and proof of financial hardship. Applicants may be required to provide documentation to verify their eligibility, such as income statements, proof of residency, and identification documents.
Eligibility Criteria and Application Process
- Income Requirements:Most utility assistance programs have income eligibility guidelines. Households with incomes below a certain threshold may qualify for assistance.
- Household Size:Some programs consider household size when determining eligibility. Larger households may receive higher levels of assistance.
- Proof of Financial Hardship:Applicants may need to provide documentation of financial hardship, such as unemployment, medical expenses, or unexpected financial burdens.
- Application Process:Applications for utility assistance programs can be obtained from utility companies, community organizations, or online. The application process may involve completing a form and providing supporting documentation.
Income-Based Discounts and Payment Plans
Many utility companies offer income-based discounts or payment plans to eligible customers. These programs provide reduced rates or flexible payment options to make utility bills more affordable.
- Income-Based Discounts:Customers who meet income eligibility requirements may qualify for a percentage discount on their utility bills.
- Payment Plans:Utility companies may offer payment plans that allow customers to spread out their bill payments over a longer period, reducing the monthly financial burden.
Table of Utility Assistance Programs
| Program | Eligibility Requirements | Application Process | Benefits Provided |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP) | Low-income households, income below poverty level | Contact local utility company or community action agency | Financial assistance with heating and cooling costs |
| Weatherization Assistance Program (WAP) | Low-income households, income below 150% of poverty level | Contact local community action agency | Home energy efficiency improvements, such as insulation and weatherstripping |
| Utility Discount Programs | Income-based eligibility, varies by utility company | Contact utility company | Reduced rates on utility bills |
| Payment Assistance Plans | Financial hardship, income verification required | Contact utility company | Flexible payment options to reduce monthly burden |
Real-Life Examples of Utility Assistance
Utility assistance programs have provided significant support to individuals and families in need. For example, the LIHEAP program has helped millions of low-income households afford their heating and cooling costs during extreme weather conditions.
In one case, a single mother with two young children faced financial hardship after losing her job. She was struggling to keep up with her utility bills and was at risk of having her electricity disconnected. Through a local community action agency, she applied for LIHEAP assistance and received a grant that covered a portion of her outstanding bill, preventing her from losing essential services.
How to Apply for Utility Assistance
To apply for utility assistance, follow these steps:
- Contact your utility company or a local community organization.They can provide information about available programs and eligibility requirements.
- Gather necessary documentation.This may include proof of income, household size, and financial hardship.
- Complete the application form.Be sure to provide accurate and complete information.
- Submit the application and supporting documentation.Follow the instructions provided by the utility company or community organization.
Remember, each utility company and community organization may have its own application process and requirements. It’s important to contact them directly for the most up-to-date information.
Contact Information
- National Energy Assistance Referral (NEAR) Program:1-866-674-6327
- National Low Income Energy Consortium (NLIEC):https://nliec.org/
- Local utility companies:Contact information can be found on utility bills or websites.
- Community action agencies:Contact information can be found online or through local government websites.
Utility Scams and Fraud
Utility scams and fraudulent practices are prevalent and can target unsuspecting customers. It is crucial to be aware of these tactics and take necessary precautions to protect yourself and your finances.
Utility bills, which cover essential services like electricity, gas, and water, are a common household expense. If you’re wondering where to find your utility bills on a Mac, check the Utilities folder. This folder contains various system tools and applications, including the System Information utility, which provides detailed information about your Mac’s hardware and software.
By accessing the Utilities folder, you can conveniently view and manage your utility bills, ensuring timely payments and avoiding service interruptions.
Common Utility Scams
Some common utility scams include:
- Imposter Scams:Scammers posing as utility company employees may call, text, or visit your home, demanding immediate payment or threatening to disconnect service.
- Overpayment Scams:Scammers may request an overpayment for your utility bill, claiming it is a refund or credit, and then disappear with the funds.
- Phishing Scams:Scammers send emails or text messages that appear to be from your utility company, requesting personal information or payment details.
- Charity Scams:Scammers may solicit donations for fake utility assistance programs or charities that do not exist.
How to Protect Against Utility Scams
To protect yourself from utility scams, consider the following tips:
- Verify the Identity:Always ask for identification from anyone claiming to be a utility company employee.
- Never Share Personal Information:Do not provide personal or financial information over the phone, email, or text message.
- Be Wary of Unusual Requests:If a utility company asks for immediate payment or threatens to disconnect service, contact the company directly to verify.
- Report Suspicious Activity:If you suspect a scam, report it to your utility company and local authorities immediately.
Reporting Utility Scams
If you have been a victim of a utility scam, it is essential to report it to the following authorities:
- Your Utility Company:Contact your utility company to report the scam and protect your account.
- Local Law Enforcement:File a police report to document the incident and assist with any potential investigation.
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC):Report the scam to the FTC at www.ftc.gov/complaint or by calling 1-877-FTC-HELP.
By staying informed and taking appropriate precautions, you can protect yourself from utility scams and fraudulent practices.
Utility Companies and Customer Service
Utility companies play a crucial role in providing essential services to residential and commercial customers. They are responsible for delivering electricity, gas, water, and other utilities to homes and businesses. Customer service is an integral part of their operations, ensuring that customers receive timely and efficient assistance with their accounts and any issues they may encounter.To contact utility companies, customers can typically use various channels such as phone, email, online portals, and in-person visits to customer service centers.
Utility companies strive to provide responsive and helpful customer service, addressing billing inquiries, resolving complaints, and offering guidance on energy efficiency measures.
Resolving Billing Issues
Customers may encounter billing issues or concerns from time to time. These could include errors in billing statements, disputes over charges, or questions about payment options. Utility companies have established processes to handle such issues promptly and effectively. Customers should contact their utility provider to report any billing discrepancies or concerns.
Representatives will investigate the matter, review account details, and work towards resolving the issue fairly and accurately.
Complaint Resolution
If a customer has a complaint about the service provided by the utility company, they should follow the established complaint resolution process. This typically involves contacting the customer service department and clearly outlining the complaint. Utility companies have dedicated teams responsible for handling complaints, investigating the matter, and providing a timely and appropriate resolution.
Customers should expect a fair and impartial investigation and a response that addresses their concerns.
Utility Regulations and Oversight
Utility regulations and oversight play a critical role in ensuring that utility companies provide safe, reliable, and affordable services to consumers. Government agencies at the federal, state, and local levels have the responsibility to regulate utility companies and oversee their operations.
The purpose of utility regulations and oversight is to protect consumers from unfair or discriminatory practices, ensure the provision of safe and reliable utility services, and promote competition and efficiency in the utility industry.
Specific Regulations and Oversight Measures
Government agencies implement various specific regulations and oversight measures to achieve these goals. These measures include:
- Setting rates and tariffs for utility services
- Establishing safety standards and regulations
- Monitoring utility companies’ financial performance
- Investigating consumer complaints
- Enforcing compliance with regulations
Effectiveness of Utility Regulations and Oversight
Utility regulations and oversight have been generally effective in protecting consumers and ensuring the provision of safe and reliable utility services. However, there are always opportunities for improvement.
One challenge is the need to balance the interests of consumers, utility companies, and other stakeholders. Another challenge is the need to keep pace with technological changes and new developments in the utility industry.
Improving Utility Regulations and Oversight
There are a number of ways to improve utility regulations and oversight. These include:
- Increasing transparency and accountability in the regulatory process
- Promoting competition and efficiency in the utility industry
- Investing in research and development to support innovation
- Educating consumers about their rights and responsibilities
FAQ Explained
What are the most common types of utilities included in a bill?
The most common types of utilities included in a bill are electricity, water, gas, and sewage.
How can I reduce my utility costs?
There are several ways to reduce your utility costs, such as turning off lights when leaving a room, unplugging electronics when not in use, and using energy-efficient appliances.
What should I do if I have a dispute with my utility company?
If you have a dispute with your utility company, you should first try to resolve it directly with the company. If you are unable to resolve the dispute, you may contact your state’s public utility commission or consumer protection agency.


