What’s collated printing? It’s a printing method that combines multiple printed sheets into a single, organized document. This process plays a crucial role in various industries, enhancing communication and streamlining organization. Dive into this comprehensive guide to uncover the intricacies of collated printing, its applications, and best practices.
Collated printing offers numerous advantages, including improved organization, enhanced readability, and professional presentation. However, it also comes with certain limitations, such as higher costs and potential for errors. Understanding these factors is essential for determining the suitability of collated printing for your specific needs.
Definition of Collated Printing

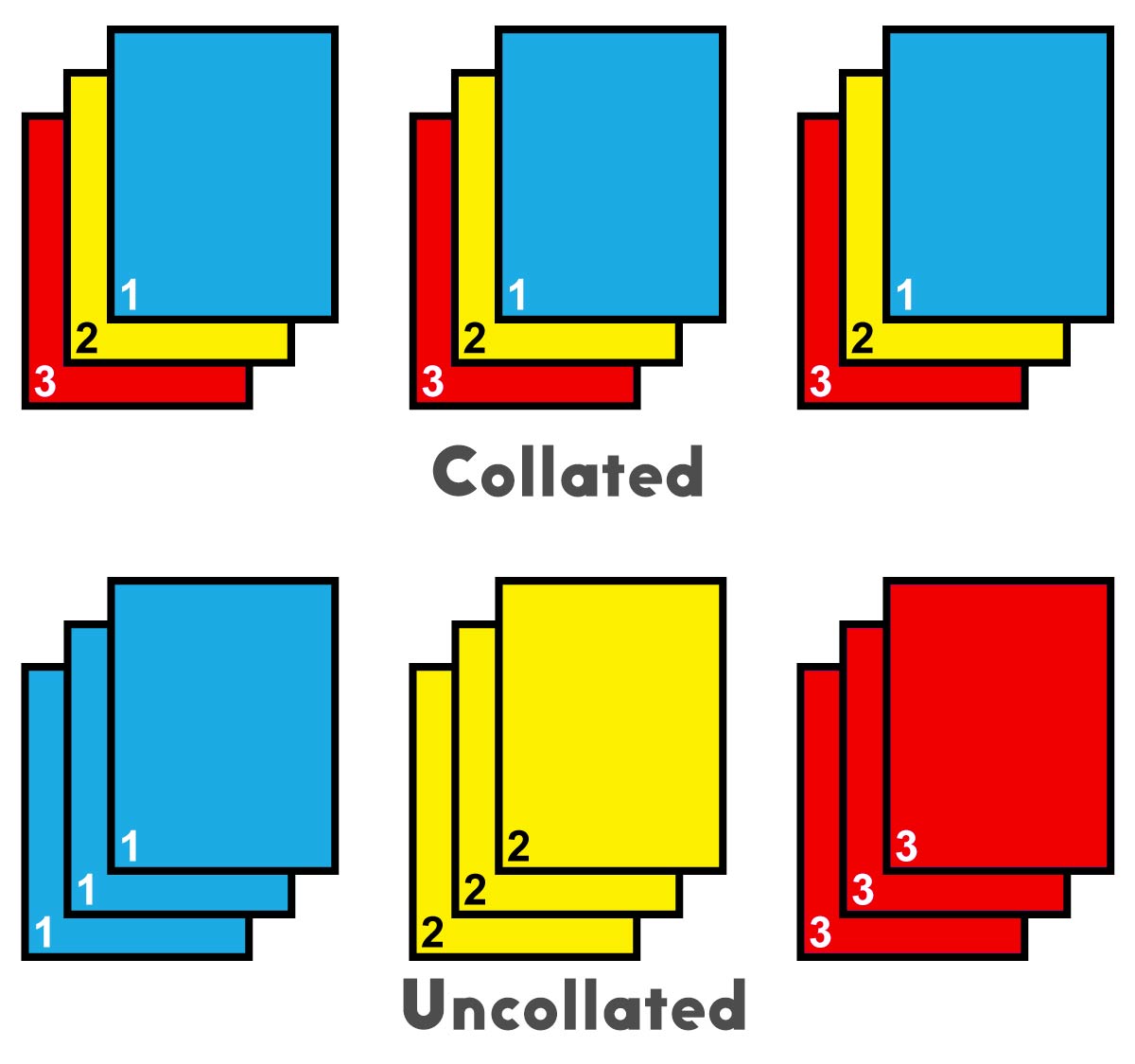
Collated printing is a printing process that combines multiple pages or documents into a single, organized set. It involves gathering and assembling individual sheets of paper, ensuring they are in the correct order, and then binding them together.
The primary purpose of collated printing is to create printed materials that are well-organized, easy to navigate, and visually appealing. It is commonly used for producing documents such as books, manuals, reports, and presentations.
Advantages of Collated Printing
- Enhanced Organization:Collated printing ensures that all pages are in the correct sequence, making it easier to find specific information.
- Improved Readability:By combining multiple pages into a single document, collated printing enhances readability and reduces the need for flipping through loose sheets.
- Professional Appearance:Collated and bound documents present a more polished and professional appearance, making them suitable for formal presentations and business purposes.
- Reduced Paper Waste:Collated printing eliminates the need for multiple copies of the same document, reducing paper waste and promoting sustainability.
Disadvantages of Collated Printing, What’s collated printing
- Higher Cost:Collated printing can be more expensive than printing individual pages due to the additional labor and materials required for binding.
- Limited Flexibility:Once collated and bound, it is difficult to make changes or add new pages to the document without reprinting the entire set.
- Bulkiness:Collated documents can be bulky and difficult to handle, especially for large volumes of pages.
- Environmental Impact:The binding materials used in collated printing, such as glue or staples, can contribute to environmental waste.
Methods of Collation

Collation methods refer to the techniques used to assemble and organize printed materials in a specific order. The choice of method depends on the type of printed material, the number of pages, and the desired finished product.
The following are some of the most common collation methods:
Hand Collation
Hand collation is a manual process where each page is gathered and assembled by hand. This method is typically used for small print runs or for projects that require a high degree of accuracy.
Advantages:
- High accuracy
- Suitable for small print runs
- Allows for customization
Disadvantages:
- Time-consuming
- Labor-intensive
- Prone to errors
Machine Collation
Machine collation uses automated equipment to gather and assemble printed materials. This method is faster and more efficient than hand collation, and it can be used for larger print runs.
Advantages:
- Fast and efficient
- Suitable for large print runs
- Reduces labor costs
Disadvantages:
- May not be as accurate as hand collation
- Requires specialized equipment
- Can be more expensive than hand collation
Perfect Binding
Perfect binding is a method of binding printed materials where the pages are glued together at the spine. This method is often used for books, magazines, and other publications.
Advantages:
- Durable and long-lasting
- Professional-looking
- Suitable for large print runs
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than other binding methods
- Not suitable for small print runs
- Difficult to make changes once bound
Saddle Stitching
Saddle stitching is a method of binding printed materials where the pages are stapled together at the spine. This method is often used for booklets, pamphlets, and other short publications.
Advantages:
- Affordable
- Quick and easy to produce
- Suitable for small print runs
Disadvantages:
- Not as durable as perfect binding
- Not suitable for large print runs
- Difficult to make changes once bound
Spiral Binding
Spiral binding is a method of binding printed materials where the pages are held together by a spiral wire. This method is often used for notebooks, calendars, and other documents that need to be able to lay flat.
Advantages:
- Durable and long-lasting
- Allows documents to lay flat
- Easy to make changes
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than other binding methods
- Not suitable for large print runs
- Can be bulky
Best Method for Different Types of Printed Materials
The best collation method for a particular type of printed material will depend on the factors such as the number of pages, the desired finished product, and the budget. The following table provides a general guide to the best collation methods for different types of printed materials:
| Type of Printed Material | Best Collation Method |
|---|---|
| Books | Perfect binding |
| Magazines | Perfect binding |
| Booklets | Saddle stitching |
| Pamphlets | Saddle stitching |
| Notebooks | Spiral binding |
| Calendars | Spiral binding |
Types of Collated Printing

Collated printing involves gathering and assembling multiple printed sheets in a specific order to create a complete document. Various types of collated printing exist, each with unique characteristics and applications.
The most common types of collated printing include:
Saddle Stitching
Saddle stitching is a method where sheets are folded in half and stapled together at the spine. It is a cost-effective and widely used technique for booklets, magazines, and brochures with a low page count (typically under 64 pages).
Perfect Binding
Perfect binding involves gluing the spine of the assembled sheets together. It produces a more durable and professional-looking document compared to saddle stitching. Perfect binding is suitable for books, reports, and manuals with a higher page count.
Spiral Binding
Spiral binding uses a continuous wire or plastic coil to bind the sheets together. It allows the document to lie flat when opened and is often used for notebooks, calendars, and presentations.
Applications of Collated Printing
Collated printing finds extensive use in various industries and serves diverse purposes, ranging from enhancing communication to streamlining organization. By combining multiple documents into a single, cohesive unit, collated printing offers numerous benefits for businesses and organizations.
Industries and Purposes
Collated printing is commonly employed in the following industries and for the following purposes:
- Legal:Court documents, contracts, pleadings, and other legal materials that require a specific order and organization.
- Medical:Patient charts, medical records, and insurance forms that need to be presented in a logical and sequential manner.
- Education:Student handouts, textbooks, and study materials that benefit from being assembled in a structured format.
- Business:Presentations, reports, proposals, and other business documents that require a professional and organized appearance.
- Marketing:Brochures, flyers, and catalogs that are designed to be easily navigated and visually appealing.
Benefits of Collated Printing
Collated printing offers several key advantages for businesses and organizations:
- Improved Communication:Collated printing ensures that all necessary documents are presented in a coherent and organized manner, enhancing communication and understanding.
- Increased Efficiency:By combining multiple documents into a single unit, collated printing eliminates the need to manually assemble and organize documents, saving time and effort.
- Enhanced Organization:Collated printing helps maintain a structured and organized filing system, making it easier to retrieve and manage documents.
- Professional Appearance:Collated printing creates a polished and professional appearance for documents, which can make a positive impression on clients and stakeholders.
- Reduced Costs:Collated printing can reduce printing costs by eliminating the need for separate printing jobs for each document.
Real-World Examples
Here are some real-world examples of how collated printing enhances communication and organization:
- In the legal industry, collated printing is used to assemble court documents in the correct order, ensuring that all necessary information is presented to the judge and jury in a logical and coherent manner.
- In the medical field, collated printing is used to create patient charts that include all relevant medical records, test results, and treatment plans, providing a comprehensive overview of the patient’s health history.
- In the business world, collated printing is used to create presentations and reports that combine text, graphics, and data into a single, cohesive document, making it easier for audiences to follow and understand the information presented.
Summary Table
The following table summarizes the industries, purposes, and benefits of collated printing:
| Industry | Purpose | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Legal | Court documents, contracts, pleadings | Improved communication, increased efficiency, enhanced organization |
| Medical | Patient charts, medical records, insurance forms | Improved communication, enhanced organization, professional appearance |
| Education | Student handouts, textbooks, study materials | Increased efficiency, enhanced organization, professional appearance |
| Business | Presentations, reports, proposals | Improved communication, increased efficiency, professional appearance |
| Marketing | Brochures, flyers, catalogs | Improved communication, increased efficiency, enhanced organization |
Equipment for Collation: What’s Collated Printing
Collating equipment plays a crucial role in the post-press process, enabling the efficient assembly and organization of printed materials. Various types of equipment are utilized for collation, each with specific functions and capabilities.
The choice of equipment depends on factors such as the volume of materials, the complexity of the collation process, and the desired speed and accuracy.
Types of Collating Equipment
- Gatherer-Stitcher: A versatile machine that combines the functions of gathering and stitching. It collects individual printed sheets in the correct sequence and then staples or stitches them together, producing booklets or brochures.
- Collator: A specialized machine designed specifically for collating printed sheets. It aligns and stacks the sheets in the desired order, preparing them for subsequent binding or packaging.
- Saddle Stitcher: A machine that stitches printed sheets together along the center fold, creating booklets or brochures. It is typically used for smaller publications with a limited number of pages.
- Perfect Binder: A machine that binds printed sheets together using a hot melt adhesive, creating a durable and professional-looking finish. It is commonly used for books, magazines, and other high-volume publications.
- Spiral Binder: A machine that binds printed sheets together using a spiral coil, allowing the publication to be opened flat. It is often used for presentations, manuals, and other documents that require frequent referencing.
– Preparation
Effective preparation is essential for successful data collation. It involves organizing source materials, establishing a system for identifying and tracking duplicates, and developing a standardized format for data entry.
By carefully preparing the data, the collation process can be streamlined, and the accuracy and completeness of the final dataset can be ensured.
Gather and Organize Source Materials
The first step in data collation is to gather and organize the source materials. This may involve collecting data from multiple databases, spreadsheets, or other sources.
Once the data has been gathered, it is important to organize it in a logical and consistent manner. This will make it easier to identify and track duplicates, and to develop a standardized format for data entry.
Establish a System for Identifying and Tracking Duplicates
Duplicates are a common challenge in data collation. To avoid duplicate data in the final dataset, it is important to establish a system for identifying and tracking duplicates.
This system may involve using a unique identifier for each data record, or by comparing data records based on specific criteria.
Develop a Standardized Format for Data Entry
To ensure the accuracy and completeness of the final dataset, it is important to develop a standardized format for data entry.
This format should specify the data type for each field, the allowable values for each field, and the required format for each field.
Collation Automation

Collation automation refers to the use of technology to streamline and enhance the collation process. It involves employing automated systems and equipment to perform tasks such as sorting, assembling, and packaging printed materials.
Automation in collation offers numerous benefits, including:
- Increased efficiency:Automated systems can process large volumes of printed materials quickly and accurately, reducing manual labor and minimizing errors.
- Improved accuracy:Automation eliminates human error, ensuring that printed materials are assembled and packaged correctly.
- Reduced costs:By automating collation tasks, businesses can save on labor costs and improve overall productivity.
- Enhanced flexibility:Automated systems can be easily reconfigured to handle different types of printed materials, making them suitable for various applications.
However, there are also challenges associated with automating collation tasks:
- High initial investment:Implementing automated collation systems can require a significant upfront investment.
- Technical expertise:Operating and maintaining automated systems requires technical expertise, which may not be readily available within an organization.
- Complexity of materials:Some printed materials may be difficult to automate due to their size, shape, or fragility.
Despite these challenges, collation automation continues to gain popularity as businesses seek to improve efficiency, accuracy, and productivity in their printing operations.
Cost Considerations
Collated printing costs can vary based on several factors, including:
- Volume:Higher volumes generally result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
- Complexity:More complex collating jobs, such as those involving multiple documents or special handling, may incur higher costs.
- Materials:The type of paper, ink, and other materials used can impact costs.
- Equipment:The cost of equipment used for collation, such as collators or binding machines, can also factor into the overall cost.
- Labor:If manual collation is required, labor costs can add to the total cost.
Tips for Optimizing Costs
To optimize costs while maintaining quality, consider the following tips:
- Plan ahead:Planning ahead and consolidating print jobs can help reduce costs by minimizing the number of setups and reducing waste.
- Choose the right equipment:Selecting the appropriate equipment for the job can help improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Automate the process:Automation can help reduce labor costs and improve accuracy.
- Negotiate with vendors:Negotiating with vendors for materials and equipment can help secure better pricing.
- Consider outsourcing:In some cases, outsourcing collating services to a specialized provider may be more cost-effective than handling it in-house.
Sustainability in Collation

The collation process, while efficient, can have an environmental impact. It is crucial to consider the sustainability of the materials and techniques used in collation to minimize this impact.
Sustainable practices in collation involve using eco-friendly materials and reducing waste throughout the process. This includes:
Sustainable Materials
- Using recycled paper or paper from sustainably managed forests.
- Opting for biodegradable or compostable materials for binding and packaging.
- Choosing inks and adhesives with low volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions.
Waste Reduction
- Minimizing paper waste by optimizing cutting and collating processes.
- Recycling or reusing scrap paper and materials.
- Implementing automated collation systems to reduce human error and material wastage.
By adopting sustainable practices, collation can be made more environmentally friendly, reducing its carbon footprint and contributing to a greener printing industry.
Collated printing is a method of printing that involves gathering multiple pages of a document into a single set, typically in the order in which they will be read. This process is often used for documents that will be bound or stapled together, such as booklets or reports.
To find the IP address of a printer that is connected to a network, you can follow these steps: how to find ip address of printer. Once you have the IP address of the printer, you can use it to connect to the printer from your computer or mobile device.
Design Considerations
Creating collated materials that are visually appealing and effective requires careful consideration of design principles. Effective design ensures that the materials are easy to read, understand, and navigate, while also conveying the intended message clearly and effectively.
Layout
The layout of collated materials should be organized and logical, with a clear hierarchy of information. The most important information should be placed prominently, with supporting information and details arranged in a way that is easy to follow. White space and negative space should be used effectively to enhance readability and create visual interest.
Typography
The choice of typography can significantly impact the readability and overall appearance of collated materials. Sans-serif fonts are generally easier to read on screen, while serif fonts are more traditional and may be more appropriate for printed materials. The font size and line spacing should be carefully considered to ensure that the text is easy to read and does not cause eye strain.
Color Usage
Color can be used to create visual interest, highlight important information, and convey a specific message or tone. However, it is important to use color judiciously and avoid overwhelming the reader with too many colors or patterns. A consistent color palette should be used throughout the materials to create a cohesive and professional appearance.
Consistency and Branding
Consistency in design is essential for creating a recognizable and memorable brand identity. Collated materials should use the same fonts, colors, and overall design style to create a unified and cohesive look. This helps to establish brand recognition and makes it easier for readers to identify and recall the materials.
White Space and Negative Space
White space and negative space are important elements of design that can be used to create visual interest and enhance readability. White space refers to the areas of a page that are not occupied by text or images, while negative space refers to the space between elements on a page.
Effective use of white space and negative space can help to create a clean and uncluttered design that is easy to read and navigate.
Visually Appealing and Engaging Materials
Collated materials should be visually appealing and engaging to capture the reader’s attention and encourage them to read and interact with the content. This can be achieved through the use of high-quality images, graphics, and interactive elements. However, it is important to avoid overloading the materials with too much visual content, as this can be distracting and overwhelming.
Convey a Specific Message or Tone
Design can be used to convey a specific message or tone in collated materials. For example, a bright and colorful design may be used to create a cheerful and inviting tone, while a more muted and subdued design may be used to convey a more serious or professional tone.
The choice of design elements should be carefully considered to ensure that they align with the intended message and tone of the materials.
User Experience (UX)
User experience (UX) is an important consideration in the design of collated materials. The materials should be easy to navigate and interact with, and the information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand and find. This can be achieved through the use of clear and concise language, well-organized content, and intuitive navigation.
Accessible and Inclusive Design
Collated materials should be designed to be accessible and inclusive to all users, regardless of their abilities or disabilities. This includes using fonts that are easy to read, providing alternative text for images, and ensuring that the materials are compatible with assistive technologies.
By making materials accessible and inclusive, you can ensure that everyone can access and benefit from the information they contain.
Testing and Iteration
Testing and iteration are essential parts of the design process. Once collated materials have been designed, they should be tested with users to ensure that they are effective and meet the intended goals. Based on the feedback from users, the materials can be iterated and improved to create a better overall experience.
Trends in Collated Printing
Collated printing is a rapidly evolving field, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time. These trends are being driven by the evolving needs of customers, who are increasingly demanding faster, more efficient, and more cost-effective printing solutions.
Digital Collation
Digital collation is a process that uses digital technology to collate documents. This process is faster and more efficient than traditional collation methods, and it can also be used to create more complex and customized documents. Digital collation is becoming increasingly popular, as it offers a number of advantages over traditional methods.For example, Ricoh’s Pro C9200 series digital press incorporates an inline booklet maker and a multi-folding unit, enabling efficient collation and finishing of booklets in-house.
This eliminates the need for outsourcing or manual collation, saving time and costs.
Automated Collation
Automated collation is a process that uses machines to collate documents. This process is even faster and more efficient than digital collation, and it can be used to collate large volumes of documents. Automated collation is becoming increasingly popular, as it can save businesses a significant amount of time and money.One example of automated collation is the use of robotic arms in the printing and packaging industry.
These robots can quickly and accurately collate large volumes of documents, freeing up human workers for other tasks.
Collated printing is a process of printing multiple copies of a document in a specific order, such as collating pages into sets. One common question about printers is whether they can print in color. For example, the Brother MFC-870DWI is a popular printer, and many people want to know if it can print in color.
You can find out if the Brother MFC-870DWI can print in color by clicking here: can the brother mfc 870dwi print color. Collated printing is a useful feature for businesses and individuals who need to print large quantities of documents.
Sustainability in Collation
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in all industries, and the printing industry is no exception. Collated printing can be made more sustainable by using recycled paper, soy-based inks, and other environmentally friendly materials.For instance, Xerox’s iGen 5 Press incorporates sustainable features such as low-energy LED curing, reduced waste, and the use of recycled materials.
This press helps reduce environmental impact while delivering high-quality print output.
The Future of Collated Printing
The future of collated printing is bright. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even faster, more efficient, and more cost-effective collation solutions. These solutions will help businesses save time and money, and they will also help to reduce the environmental impact of printing.
Comparison with Other Printing Methods
Collated printing offers distinct advantages and disadvantages compared to other printing methods, such as digital printing and offset printing. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the most suitable method for specific applications.
Digital printing excels in short-run, on-demand printing, offering fast turnaround times and variable data printing capabilities. It is ideal for personalized marketing materials, small business cards, and quick turnaround projects.
Strengths of Digital Printing:
- Fast turnaround times
- Variable data printing
- Suitable for short-run printing
Offset printing, on the other hand, is more cost-effective for large print runs and produces high-quality results. It is commonly used for brochures, magazines, and packaging. However, offset printing requires longer setup times and is less suitable for variable data printing.
Strengths of Offset Printing:
- Cost-effective for large print runs
- High-quality results
- Suitable for brochures, magazines, and packaging
In summary, collated printing offers the benefits of both digital and offset printing, providing a balance of cost-effectiveness, speed, and quality. It is a versatile printing method suitable for a wide range of applications.
Case Studies of Successful Collated Printing Projects
Collated printing has proven its effectiveness in addressing complex communication and organizational challenges. Here are some notable case studies:
Project: Enhancing Communication for a Multinational Corporation
A global manufacturing company faced challenges in communicating effectively with its diverse workforce across multiple locations and languages. Collated printing was implemented to create tailored communication packages for each employee, including translated documents, company updates, and training materials. This streamlined communication, improved employee engagement, and fostered a sense of unity.
Project: Streamlining Patient Records for a Healthcare Provider
A healthcare provider needed to improve the organization and accessibility of patient records. Collated printing was used to create comprehensive patient files, combining medical history, test results, and treatment plans. This enhanced patient care by providing healthcare professionals with easy access to essential information.
Project: Improving Customer Engagement for a Non-Profit Organization
A non-profit organization aimed to increase donor engagement and drive fundraising efforts. Collated printing was used to create personalized direct mail campaigns, combining donor information, impact stories, and donation requests. This targeted approach resulted in increased donor response rates and revenue.
Key Findings and Metrics
- Improved communication: Collated printing enabled tailored and targeted communication, leading to increased employee engagement and customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced organization: Collated printing streamlined record-keeping and improved accessibility to essential information, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced errors.
- Cost savings: By automating collation processes, companies experienced significant cost savings on labor and materials.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
- Tailor communication: Collated printing allows for customization, ensuring that each recipient receives relevant and personalized information.
- Automate processes: Collation automation reduces manual labor, saves time, and improves accuracy.
- Consider sustainability: Choose environmentally friendly materials and printing processes to minimize the environmental impact.
FAQ
What are the key advantages of collated printing?
Collated printing offers several key advantages, including improved organization, enhanced readability, professional presentation, and increased efficiency.
What are the different methods of collating printed materials?
Common methods of collating printed materials include saddle stitching, perfect binding, and spiral binding. Each method offers unique advantages and disadvantages, depending on the specific requirements of the project.
How can I choose the best method for my collated printing project?
To choose the best method for your collated printing project, consider factors such as the number of pages, desired binding style, budget, and turnaround time.
What are some tips for creating effective collated materials?
For effective collated materials, focus on clear and concise content, logical organization, consistent branding, and visually appealing design.
How can I reduce the environmental impact of collated printing?
To reduce the environmental impact of collated printing, consider using recycled paper, vegetable-based inks, and sustainable binding materials.


