What utilities do you pay for in an apartment – When renting an apartment, understanding what utilities you are responsible for is crucial for budgeting and managing your expenses. Essential utilities, typically included in the rent, are vital for comfortable and safe living. This article will delve into the essential utilities you may encounter in an apartment, their importance, and tips for reducing costs.
Essential Utilities
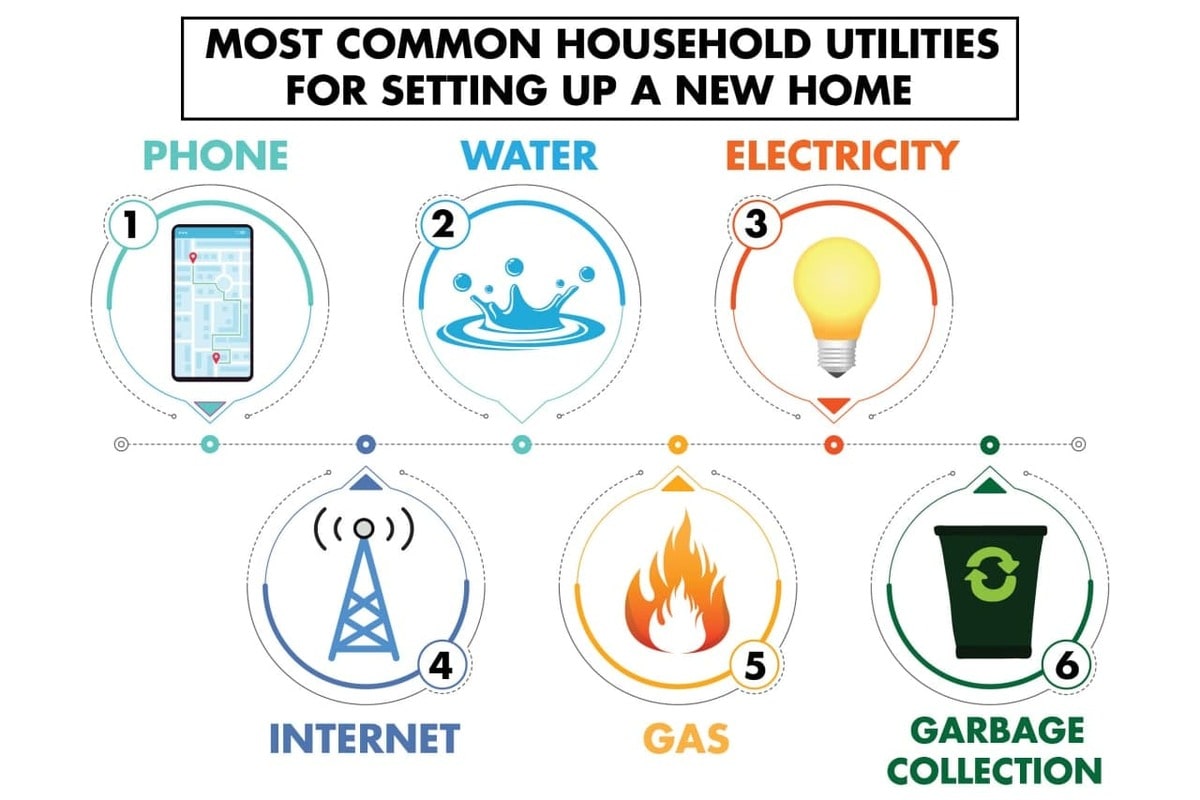
Essential utilities are services that are considered necessary for daily living and are typically included in the rent of an apartment. These utilities may vary depending on the location and type of apartment, but generally include:
- Electricity:Powers lights, appliances, and electronics.
- Water:Provides running water for drinking, cooking, and bathing.
- Sewer:Removes wastewater from the apartment.
- Gas:Used for heating, cooking, or water heating.
- Trash removal:Disposes of household waste.
The average cost of essential utilities varies widely depending on factors such as location, size of the apartment, and usage habits. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, the average monthly cost of electricity for an apartment in the United States is $115, while the average monthly cost of water is $50.
Gas costs can range from $50 to $200 per month, depending on usage and location.The cost of essential utilities can have a significant impact on a renter’s budget. In some cases, essential utilities can account for up to 30% of a renter’s monthly income.
Utilities paid in an apartment often include electricity, water, gas, and trash removal. Additionally, some apartments may charge for amenities such as parking, laundry, or fitness center access. For those interested in measuring body composition, calipers are a common tool.
Which body composition measurement utilizes calipers is a question that can be easily answered with a quick search online. Returning to the topic of apartment utilities, it’s important to factor these costs into your budget when considering renting.
To reduce their essential utility costs, renters can take steps such as:
- Conserving energy:Turning off lights when leaving a room, unplugging appliances when not in use, and using energy-efficient appliances.
- Reducing water usage:Taking shorter showers, fixing leaky faucets, and using low-flow appliances.
- Negotiating with utility companies:Some utility companies offer discounts or payment plans for low-income renters.
Optional Utilities
Optional utilities are services that may not be included in the rent of an apartment. These utilities are typically paid separately by the tenant and can include electricity, gas, water, trash removal, internet, and cable TV.
There are both advantages and disadvantages to having optional utilities. On the one hand, having optional utilities gives tenants greater control over their usage and costs. They can choose providers and plans that meet their specific needs and budget. On the other hand, having optional utilities can also lead to higher costs if not managed carefully.
Tenants are also responsible for maintenance and repairs.
Tips for Choosing the Right Optional Utilities
When choosing optional utilities, it is important to consider your usage patterns and budget. You should also research different providers and plans. Read reviews and compare prices. If possible, negotiate with providers to get the best deal.
Additional Considerations
Some utilities, such as electricity and water, may be essential for daily living. It is important to factor in the cost of optional utilities when budgeting for apartment rent. Landlords may have specific requirements or restrictions regarding optional utilities.
Utility Usage

Monitoring and tracking utility usage is crucial for understanding consumption patterns, identifying areas for improvement, and reducing expenses. Regular readings of utility meters (electricity, gas, water) provide data that can be analyzed to assess usage trends.
Utility consumption is influenced by several factors, including the size and layout of the apartment, the number of occupants, and individual usage habits. Climate conditions, appliance efficiency, and insulation also play a significant role.
Strategies for Reducing Utility Usage
- Appliance Efficiency:Opt for energy-efficient appliances with Energy Star ratings.
- Usage Monitoring:Install smart meters or use monitoring devices to track usage in real-time.
- Lighting:Use LED or CFL bulbs, and turn off lights when not in use.
- Heating and Cooling:Adjust thermostat settings to optimize energy consumption. Consider programmable thermostats or ceiling fans.
- Water Conservation:Install low-flow showerheads and faucets, and fix any leaks promptly.
- Phantom Loads:Unplug electronic devices and chargers when not in use to reduce standby power consumption.
Utility Bills

Utility bills are statements that provide a detailed breakdown of the charges associated with the consumption of utilities such as electricity, gas, water, and waste disposal. These bills are typically issued monthly and serve as a means for utility companies to collect payment for the services rendered.
Understanding utility bills is crucial for managing household expenses and identifying potential billing errors. The following sections will discuss the different components of a utility bill, explain how to read and understand them, and provide tips on identifying and resolving billing errors.
Components of a Utility Bill
- Account Number:A unique identifier assigned to the customer’s account.
- Billing Period:The specific time frame covered by the bill.
- Service Address:The address of the property where the utilities are being used.
- Meter Readings:The current and previous meter readings for each utility.
- Usage Charges:The charges based on the amount of utility consumed during the billing period.
- Fixed Charges:Regular charges that do not vary based on usage, such as connection fees or maintenance costs.
- Taxes and Fees:Applicable taxes and fees imposed by government agencies.
- Payment Information:Instructions on how to make payments, including due date and payment methods.
Reading and Understanding Utility Bills
Reading and understanding utility bills can be straightforward with some basic knowledge. Here are some steps to follow:
- Identify the Account Number:Locate the account number and make sure it matches your account.
- Review the Billing Period:Check the billing period to ensure it aligns with your usage.
- Compare Meter Readings:Note the current and previous meter readings. The difference between these readings represents your usage during the billing period.
- Calculate Usage Charges:Multiply the usage amount by the applicable unit rate to determine the usage charges.
- Add Fixed Charges:Include any fixed charges that are not based on usage.
- Review Taxes and Fees:Add any applicable taxes and fees to the total.
- Verify Payment Information:Check the due date and payment instructions to ensure timely payment.
Identifying and Resolving Billing Errors
Occasionally, billing errors may occur. Here are some tips for identifying and resolving them:
- Compare Meter Readings:Check if the meter readings on the bill match your own readings.
- Review Usage Charges:Verify that the usage charges are calculated correctly based on your usage and the applicable rates.
- Check Fixed Charges:Ensure that the fixed charges are accurate and not duplicated.
- Contact the Utility Company:If you suspect an error, contact the utility company promptly. Provide clear details about the discrepancy.
- Gather Evidence:Keep copies of your utility bills, meter readings, and any other relevant documentation to support your claim.
- Be Patient:Resolving billing errors may take some time. Follow up with the utility company regularly to track the progress.
Utility Assistance Programs
Utility assistance programs are designed to provide financial assistance to low-income households struggling to pay their utility bills. These programs can help families avoid service disconnections, maintain a safe and healthy living environment, and reduce the financial burden associated with utility costs.
Eligibility requirements and application processes vary depending on the specific program and location. Generally, households must meet income guidelines and provide proof of financial hardship to qualify. Common forms of assistance include bill payment assistance, energy efficiency upgrades, and weatherization services.
Benefits of Participating in Utility Assistance Programs
- Financial assistance:Utility assistance programs can provide direct financial assistance to help households pay their utility bills, reducing the risk of service disconnections and late fees.
- Energy efficiency upgrades:Some programs offer energy efficiency upgrades, such as insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and lighting, which can help households reduce their energy consumption and lower their utility bills over time.
- Weatherization services:Weatherization services, such as air sealing and insulation, can help households improve the energy efficiency of their homes, making them more comfortable and reducing energy costs.
- Peace of mind:Participating in utility assistance programs can provide peace of mind for households that are struggling to pay their utility bills, knowing that they have access to financial assistance and support.
Smart Utilities
Smart utilities utilize advanced technologies to optimize energy consumption and enhance convenience in residential and commercial settings. These systems leverage sensors, automation, and data analytics to monitor and control utility usage, providing numerous benefits, including cost savings, environmental sustainability, and improved user experience.
Smart Utility Devices
Smart utility devices play a pivotal role in implementing smart utility systems. These devices come in various forms, each designed to monitor and manage specific utilities. Examples include:
- Smart thermostats:Regulate indoor temperature based on user preferences and occupancy patterns, optimizing heating and cooling efficiency.
- Smart lighting systems:Control lighting levels and schedules remotely, reducing energy waste and enhancing convenience.
- Smart water meters:Monitor water usage in real-time, detecting leaks and promoting water conservation.
- Smart energy monitors:Track electricity consumption at the appliance level, identifying areas for energy reduction.
Benefits of Smart Utilities
Smart utilities offer a range of advantages, including:
- Cost savings:By optimizing energy consumption, smart utilities can significantly reduce utility bills.
- Environmental sustainability:Reduced energy consumption leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to environmental conservation.
- Improved user experience:Smart utility devices provide convenient control and monitoring of utilities, enhancing user comfort and convenience.
- Leak detection:Smart water meters can detect leaks in real-time, preventing costly water damage.
- Appliance monitoring:Smart energy monitors allow users to track energy consumption of individual appliances, identifying potential inefficiencies.
Key Features and Benefits of Smart Utility Devices
The table below summarizes the key features and benefits of different types of smart utility devices:
| Device | Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Smart thermostat | Temperature regulation, occupancy sensing, remote control | Energy savings, improved comfort, convenience |
| Smart lighting system | Dimming, scheduling, remote control | Energy savings, convenience, ambiance enhancement |
| Smart water meter | Real-time monitoring, leak detection, consumption tracking | Water conservation, leak prevention, cost savings |
| Smart energy monitor | Appliance-level energy tracking, consumption analysis | Energy savings, appliance optimization, cost control |
Process of Implementing a Smart Utility System
Implementing a smart utility system typically involves the following steps:
- Assessment:Determine the specific utility needs and goals.
- Device selection:Choose smart utility devices that align with the identified needs.
- Installation:Install the devices according to manufacturer instructions.
- Configuration:Set up and configure the devices to meet specific preferences.
- Monitoring:Track utility usage and device performance through a centralized platform.
- Optimization:Analyze data and adjust device settings to maximize efficiency and cost savings.
Code Snippet for Integrating a Smart Utility Device
The following code snippet demonstrates how to integrate a smart thermostat with a home automation system using an API:
“`pythonimport requests# Thermostat API endpointendpoint = ‘https://api.thermostat.com/thermostat’# Create a function to set the thermostat temperaturedef set_temperature(temperature): # Prepare the request data data = ‘temperature’: temperature # Send a PUT request to the API endpoint response = requests.put(endpoint, data=data) # Check the response status code if response.status_code == 200: print(‘Temperature set successfully.’) else: print(‘Error setting temperature.’)# Example usageset_temperature(22)“`
Utility Security
Ensuring the security of utilities is paramount to maintain the smooth functioning of our daily lives and prevent potential hazards. Common threats to utilities include theft, vandalism, and natural disasters. Understanding the importance of utility security and implementing measures to protect them is crucial for both individuals and utility companies.
To safeguard utilities from theft or damage, individuals should consider the following tips:
- Install security devices such as alarms, motion sensors, and security cameras around utility areas.
- Keep utility areas well-lit and free from obstructions to deter potential intruders.
- Regularly inspect utility equipment and report any suspicious activity or damage to the utility company.
Utility companies play a vital role in ensuring utility security by implementing comprehensive measures:
- Investing in advanced security technologies to monitor and protect critical infrastructure.
- Establishing partnerships with law enforcement agencies to enhance surveillance and response capabilities.
- Conducting regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and mitigate potential threats.
Utility Contracts
Utility contracts Artikel the terms and conditions for the provision of utility services to a specific property or individual. These contracts vary based on the type of utility service, the provider, and the location. Understanding the different types of utility contracts and their key terms is essential for making informed decisions and securing the best possible rates and services.
Types of Utility Contracts
There are several types of utility contracts available, each with its own unique characteristics:
- Fixed-rate contracts:Lock in a fixed price for a specified period, typically one to three years. This provides stability and predictability in utility costs but may not be the most cost-effective option if utility rates fluctuate significantly.
- Variable-rate contracts:The price of utilities fluctuates based on market conditions. This can lead to lower costs during periods of low demand but also higher costs during periods of high demand.
- Tiered-rate contracts:Charge different rates for different levels of usage. For example, a tiered-rate electricity contract may charge a lower rate for the first 500 kilowatt-hours used each month and a higher rate for usage above that threshold.
- Prepaid contracts:Require customers to pay for utilities in advance. This can help manage utility costs but may not be suitable for everyone.
Key Terms and Conditions
When signing a utility contract, it is crucial to pay attention to the following key terms and conditions:
- Term length:The duration of the contract.
- Rates:The price charged for the utility service.
- Usage limits:Any restrictions on the amount of utility service that can be used.
- Cancellation fees:Penalties for terminating the contract early.
- Payment options:The methods available for paying utility bills.
Negotiating the Best Utility Contract
To negotiate the best utility contract for your needs, consider the following tips:
- Compare offers from multiple providers:Get quotes from several utility providers to compare rates and terms.
- Consider your usage patterns:Choose a contract that aligns with your typical usage to avoid paying higher rates for excess usage.
- Negotiate rates and terms:Don’t be afraid to negotiate with utility providers to secure the best possible deal.
- Read the contract carefully:Before signing a utility contract, read it thoroughly to understand all the terms and conditions.
Utility Providers: What Utilities Do You Pay For In An Apartment

Utility providers are companies that supply essential services such as electricity, gas, water, and sewage to residential and commercial customers. There are different types of utility providers, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Commonly in an apartment, utilities like electricity, water, gas, and trash removal are covered by the tenant. Additionally, there may be a fee for access to shared amenities such as laundry facilities or parking. For those using Adobe software, understanding the Adobe GC Invoker Utility is also essential.
This utility, described in detail at what is adobe gc invoker utility , is a background process that runs when Adobe applications are launched. It helps manage licensing and ensures that the software is running properly. Therefore, tenants in apartments may encounter various utilities that require payment or understanding, including Adobe GC Invoker Utility.
Types of Utility Providers
Municipal Utilities:These are owned and operated by local governments. They often offer lower rates than private utilities, but may have limited service areas and may not be as responsive to customer needs. Investor-Owned Utilities:These are owned by private companies and are regulated by state or federal agencies.
They often offer more competitive rates and a wider range of services, but may be more profit-driven. Cooperatives:These are non-profit organizations owned by their customers. They typically offer lower rates than investor-owned utilities, but may have limited service areas and may require members to participate in maintenance and operations.
Choosing a Utility Provider
When choosing a utility provider, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Rates:Compare the rates of different providers to find the most affordable option.
- Services:Consider the range of services offered by each provider, such as energy efficiency programs, renewable energy options, and customer support.
- Reliability:Check the provider’s track record for outages and customer satisfaction.
- Customer Service:Consider the provider’s reputation for responsive and helpful customer service.
- Location:Some providers may not offer service in all areas.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the utility provider that best meets your needs and budget.
Utility Rebates and Incentives
Utility rebates and incentives are financial rewards offered by utility companies, government agencies, and non-profit organizations to encourage energy efficiency, renewable energy adoption, and affordability for low-income households.
These programs provide financial assistance to offset the costs of energy-saving upgrades, renewable energy installations, and energy bill assistance.
Eligibility Requirements and Application Process
Eligibility for utility rebates and incentives typically depends on factors such as income, property type, and the specific program guidelines. To apply for these programs, individuals or businesses must meet the eligibility criteria and submit an application, which may include documentation of income, energy usage, or equipment specifications.
Maximizing Benefits
- Research available programs: Explore various utility and government websites to identify programs that align with your needs.
- Bundle multiple rebates: Some programs allow for combining multiple rebates to maximize savings.
- Utilize professional assistance: Energy auditors or contractors can help identify eligible upgrades and assist with the application process.
Successful Programs
Many utilities and government agencies have implemented successful rebate and incentive programs:
- The US Department of Energy’s Weatherization Assistance Program provides grants to low-income households for energy efficiency upgrades.
- California’s Self-Generation Incentive Program offers rebates for installing solar panels and other renewable energy systems.
Table of Key Features
| Program | Eligibility | Application Process | Potential Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency Rebate | Homeowners, renters | Submit application with proof of income and energy usage | Up to 50% of upgrade costs |
| Solar Panel Rebate | Homeowners | Submit application with system specifications and proof of ownership | Up to $10,000 per system |
| Low-Income Energy Assistance | Low-income households | Contact local utility or government agency | Bill payment assistance, weatherization upgrades |
Frequently Asked Questions
- Who is eligible for utility rebates and incentives?
Eligibility varies by program, but typically includes homeowners, renters, and low-income households.
- How do I apply for a utility rebate or incentive?
Contact your utility company or visit their website for application details.
- What are the benefits of participating in these programs?
Reduced energy costs, increased energy efficiency, and environmental sustainability.
Call to Action
Explore available utility rebates and incentives to reduce your energy costs and contribute to environmental sustainability. Visit your utility’s website or contact local government agencies for more information and application details.
Utility Outages
Utility outages are a major inconvenience and can have a significant impact on our lives. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including natural disasters, equipment failures, and intentional acts. It is important to be prepared for utility outages and to know how to respond in the event of one.
Causes of Utility Outages
- Natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods, can damage power lines and other utility infrastructure, causing outages.
- Equipment failures, such as downed power lines or broken transformers, can also cause outages.
- Intentional acts, such as vandalism or sabotage, can also lead to utility outages.
Preparation for Utility Outages
There are a number of things you can do to prepare for utility outages, including:
- Creating an emergency kit that includes food, water, first aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
- Having a plan for communication in the event of an outage, such as a designated meeting place or a list of contact numbers.
- Knowing how to turn off your utilities in the event of an emergency.
Responding to Utility Outages
If you experience a utility outage, there are a number of things you can do to respond, including:
- Checking to see if your neighbors are also experiencing an outage.
- Calling your utility company to report the outage.
- Following the instructions of your utility company regarding safety and restoration.
Role of Utility Companies in Restoring Service
Utility companies have a responsibility to restore service to their customers as quickly and safely as possible. They will typically follow a process that includes:
- Assessing the damage and determining the cause of the outage.
- Repairing the damage and restoring service.
- Communicating with customers throughout the process.
Types of Utility Outages
There are three main types of utility outages:
- Power outages occur when there is a disruption in the flow of electricity.
- Water outages occur when there is a disruption in the flow of water.
- Gas outages occur when there is a disruption in the flow of gas.
Staying Informed During Utility Outages
It is important to stay informed during utility outages. You can do this by:
- Listening to local news and weather reports.
- Following your utility company on social media.
- Checking your utility company’s website.
Role of Government Agencies and Community Organizations
Government agencies and community organizations can play a role in assisting with utility outages. They can provide:
- Financial assistance to low-income families who are affected by outages.
- Emergency shelters and cooling centers during heat waves.
- Information and resources to help people prepare for and respond to outages.
Utility Regulations
Utility regulations are a set of rules and guidelines established by government agencies to oversee the operation of utility companies. These regulations aim to protect consumers, ensure fair competition, and promote investment in infrastructure.
There are three main types of utility regulations: rate regulation, service standards, and safety regulations.
Rate Regulation
Rate regulation involves setting the prices that utility companies can charge consumers for their services. The purpose of rate regulation is to ensure that consumers are paying fair and reasonable rates for the services they receive.
Rate regulation is typically implemented through a cost-of-service approach, in which the utility company is allowed to charge rates that cover its costs of providing service, plus a reasonable profit.
Service Standards
Service standards are regulations that establish the minimum level of service that utility companies must provide to their customers.
Service standards may include requirements for reliability, quality, and customer service. For example, a utility company may be required to maintain a certain level of reliability, such as a minimum number of outages per year.
Safety Regulations
Safety regulations are designed to protect consumers from the hazards associated with utility services.
Safety regulations may include requirements for the safe operation of equipment, the proper handling of hazardous materials, and the training of employees.
| Type of Regulation | Purpose | Impact on Consumers |
|---|---|---|
| Rate Regulation | To ensure that consumers are paying fair and reasonable rates for the services they receive | Sets the prices that utility companies can charge consumers |
| Service Standards | To establish the minimum level of service that utility companies must provide to their customers | Ensures that consumers receive reliable, high-quality service |
| Safety Regulations | To protect consumers from the hazards associated with utility services | Ensures that utility companies operate their equipment safely and handle hazardous materials properly |
History of Utility Regulation
The history of utility regulation in the United States dates back to the late 19th century, when the rapid growth of the electric and gas industries led to concerns about monopoly power and unfair pricing.
In 1885, the Massachusetts legislature created the first state utility commission, which was tasked with regulating the rates and services of electric and gas companies.
The federal government began regulating utilities in the early 20th century, with the passage of the Hepburn Act of 1906, which gave the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) authority to regulate the rates and services of railroads and other interstate transportation companies.
The Public Utility Holding Company Act of 1935 gave the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) authority to regulate the holding companies that controlled many of the nation’s utilities.
Current Challenges and Future Trends in Utility Regulation
Utility regulation is facing a number of challenges today, including the impact of new technologies, the changing energy landscape, and the increasing demand for affordable and reliable energy.
New technologies, such as distributed generation and smart meters, are changing the way that electricity is generated and consumed.
The changing energy landscape, with the increasing use of renewable energy sources, is also putting pressure on traditional utility business models.
The increasing demand for affordable and reliable energy is also a challenge for utility regulators.
Utility regulators are working to address these challenges by developing new regulatory frameworks that are more flexible and adaptable to the changing energy landscape.
Utility Trends

The utility industry is undergoing a period of rapid transformation, driven by a number of emerging trends. These trends include distributed generation, smart grids, energy storage, electric vehicles, and blockchain technology. These trends have the potential to significantly impact consumers, including reducing energy costs, increasing energy independence, improving reliability and resilience, and creating new job opportunities.
Distributed Generation
Distributed generation refers to the generation of electricity from small, decentralized sources, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and combined heat and power (CHP) systems. Distributed generation is becoming increasingly popular as a way to reduce energy costs, increase energy independence, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Smart Grids
Smart grids are electrical grids that use information and communication technologies to improve the efficiency, reliability, and resilience of the grid. Smart grids can help to integrate distributed generation into the grid, reduce energy costs, and improve customer service.
Energy Storage, What utilities do you pay for in an apartment
Energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro storage, can help to store excess electricity from renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power. Energy storage can help to integrate renewable energy into the grid, reduce energy costs, and improve reliability.
Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular as a way to reduce transportation costs and emissions. EVs can help to reduce energy costs, improve air quality, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger technology that can be used to create secure, transparent, and efficient systems for managing energy transactions. Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the utility industry by reducing costs, improving efficiency, and increasing transparency.
The Future of Utilities
The future of utilities is likely to be characterized by a number of key trends, including:
- The increasing adoption of distributed generation and renewable energy sources.
- The development of smart grids and energy storage technologies.
- The increasing popularity of electric vehicles.
- The use of blockchain technology to create more efficient and transparent energy markets.
- The need for new business models and regulatory frameworks to support the transition to a decarbonized energy system.
These trends are likely to have a significant impact on the role of utilities in society. Utilities will need to become more customer-centric and provide a wider range of services, such as energy efficiency programs, distributed generation support, and electric vehicle charging.
Utility Comparison
Utility comparison is the process of evaluating different utility providers and plans to find the best option for your needs. There are many factors to consider when comparing utilities, including cost, reliability, customer service, and environmental impact.
Table of Utility Providers
One of the most important factors to consider when comparing utilities is cost. The cost of utilities can vary significantly depending on the provider, the plan you choose, and your usage. It is important to compare the costs of different providers before making a decision.Another important factor to consider is reliability.
You want to choose a utility provider that is reliable and can provide you with consistent service. You should research the reliability of different providers before making a decision.Customer service is also an important factor to consider. You want to choose a utility provider that has good customer service.
This means that they are responsive to your needs and are willing to help you resolve any problems.Finally, you may also want to consider the environmental impact of different utility providers. Some providers use renewable energy sources, while others use fossil fuels.
If you are concerned about the environment, you may want to choose a provider that uses renewable energy sources.
Tips for Comparing Utilities
Here are a few tips for comparing utilities:* Start by gathering information from different providers.You can do this by visiting their websites or calling their customer service departments.
- Compare the costs of different providers.Be sure to compare the costs of different plans as well as the costs of different providers.
- Consider the reliability of different providers.You can research the reliability of different providers by reading online reviews or by talking to your friends and neighbors.
- Compare the customer service of different providers.You can do this by calling their customer service departments or by reading online reviews.
- Consider the environmental impact of different providers.You can find information about the environmental impact of different providers on their websites or by calling their customer service departments.
Utility Resources

Utility-related resources can provide valuable information and assistance to consumers. These resources include utility providers, government agencies, consumer advocacy groups, industry associations, and research institutions.The following table provides a comprehensive list of utility resources, categorized by type:
| Resource Name | Website | Phone Number | Email Address | Social Media Handle | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Utility Providers | |||||
| American Electric Power | www.aep.com | 1-800-672-2231 | [email protected] | @AmericanElectricPower | Provides electricity to 11 states in the Midwest and East Coast. |
| Consolidated Edison | www.coned.com | 1-800-752-6633 | [email protected] | @ConsolidatedEd | Provides electricity, gas, and steam to New York City and Westchester County. |
| Duke Energy | www.duke-energy.com | 1-800-777-9090 | [email protected] | @DukeEnergy | Provides electricity, gas, and renewable energy to customers in six states. |
Government Agencies | |||||
| Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) | www.ferc.gov | 1-866-208-3372 | [email protected] | @FERC | Regulates the interstate transmission of electricity, natural gas, and oil. |
| National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners (NARUC) | www.naruc.org | 1-202-898-2200 | [email protected] | @NARUC | Represents state public utility commissions and provides resources for consumers. |
| U.S. Department of Energy | www.energy.gov | 1-800-953-4636 | [email protected] | @ENERGY | Provides information and resources on energy efficiency, renewable energy, and other energy-related topics. |
Consumer Advocacy Groups | |||||
| Citizens Utility Board | www.citizensutilityboard.org | 1-800-669-5556 | [email protected] | @CUBIllinois | Advocates for consumers in Illinois on utility issues. |
| National Consumer Law Center | www.nclc.org | 1-617-542-8010 | [email protected] | @NatConsumerLaw | Provides legal assistance and resources to consumers on a variety of issues, including utilities. |
| Utility Consumers’ Action Network (UCAN) | www.ucan.org | 1-415-441-1100 | [email protected] | @UtilityConsumers | Advocates for consumers on utility issues in California. |
Industry Associations | |||||
| American Gas Association (AGA) | www.aga.org | 1-703-841-8600 | [email protected] | @AGA | Represents the natural gas industry in the United States. |
| Edison Electric Institute (EEI) | www.eei.org | 1-202-508-5000 | [email protected] | @EdisonElectric | Represents the investor-owned electric utility industry in the United States. |
| National Rural Electric Cooperative Association (NRECA) | www.nreca.coop | 1-703-907-5500 | [email protected] | @NRECA | Represents the electric cooperatives in the United States. |
Research Institutions | |||||
| Center for Energy Studies | www.energy.rice.edu | 1-713-348-5737 | [email protected] | @EnergyRice | Conducts research on energy policy, economics, and technology. |
| Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Energy Initiative | energy.mit.edu | 1-617-253-5411 | [email protected] | @MITEnergy | Conducts research on energy efficiency, renewable energy, and other energy-related topics. |
| National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) | www.nrel.gov | 1-303-275-3000 | [email protected] | @NREL | Conducts research on renewable energy and energy efficiency technologies. |
Quick FAQs
What are the most common essential utilities included in apartment rent?
Essential utilities typically include water, electricity, gas (for heating or cooking), and trash removal.
Can I negotiate with my landlord to exclude certain utilities from the rent?
Negotiating utility exclusions may be possible, but it depends on the landlord’s policies and local rental market conditions.
How can I reduce my utility costs in an apartment?
Consider energy-efficient appliances, practice responsible water usage, and explore utility assistance programs if eligible.


