With the advent of 3D printing technology, the question of what program to use for 3D printing has become increasingly important. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, selecting the right software can make all the difference in the success of your 3D printing projects.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of 3D printing software, exploring the different types, features, and applications to help you make an informed decision.
From understanding the basics of CAD, slicing, and modeling software to discovering industry-specific programs and advanced options, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and insights you need to choose the perfect software for your 3D printing needs.
Introduction
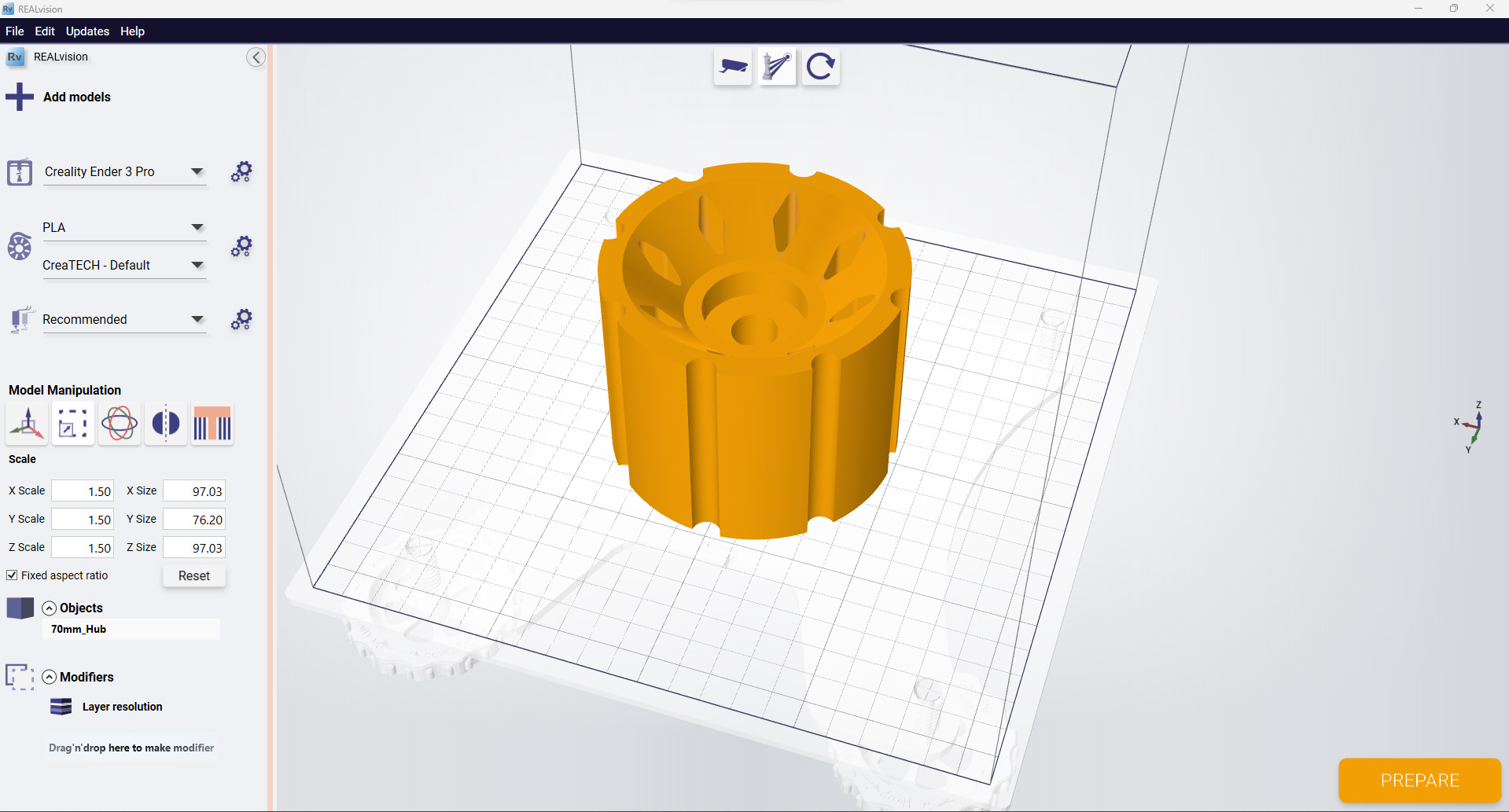
Choosing the right software for 3D printing is essential for achieving successful and efficient results. With a wide range of programs available, it’s crucial to consider various factors to select the one that best suits your needs and project requirements.
When selecting a 3D printing software, consider the following factors:
User Interface and Ease of Use
The user interface should be intuitive and easy to navigate, allowing users to quickly learn the software and focus on their designs. Consider your experience level and the complexity of the models you plan to create.
Modeling Capabilities
Determine the types of models you need to create and choose software with the appropriate modeling capabilities. Consider the level of detail, precision, and customization required for your projects.
Slicing and Printing Features
Slicing software prepares the 3D model for printing by generating layer-by-layer instructions for the printer. Choose software with slicing features that optimize print quality, minimize material waste, and provide advanced options for controlling print parameters.
File Compatibility
Ensure the software is compatible with the file formats used by your 3D printer. This includes both the input file formats for importing models and the output file formats for generating print instructions.
Support and Community
Consider the availability of technical support, documentation, and online communities for the software. This can be invaluable for troubleshooting issues, accessing resources, and staying updated with the latest developments.
– Provide examples of each type of software, including open-source and commercial options.
3D printing software encompasses a wide range of applications, each tailored to specific aspects of the 3D printing process. These categories include CAD (Computer-Aided Design), slicing, and modeling software.
Open-source software, such as Blender and FreeCAD, offers a cost-effective alternative to commercial options, providing access to powerful features and a large community of users for support. Commercial software, like SolidWorks and CATIA, often includes advanced capabilities, comprehensive support, and industry-specific integrations.
CAD Software
CAD software empowers users to design and edit 3D models, featuring tools for precise geometric construction, parametric modeling, and assembly capabilities.
- Examples:SolidWorks, CATIA, AutoCAD
- Key Features:Parametric modeling, assembly tools, simulation capabilities
Slicing Software
Slicing software translates 3D models into instructions that 3D printers can understand, generating layers and optimizing print settings. It enables users to adjust parameters such as layer height, infill density, and support structure generation.
- Examples:Cura, Simplify3D, PrusaSlicer
- Key Features:Layer generation, print settings optimization, support structure generation
Modeling Software
Modeling software focuses on creating and manipulating 3D models, offering tools for sculpting, texture mapping, and organic shape design.
- Examples:Blender, Maya, ZBrush
- Key Features:3D modeling tools, sculpting, texture mapping
Features to Consider
When evaluating 3D printing software, it is crucial to consider key features that influence its usability, compatibility, and overall functionality. These features play a significant role in determining the software’s suitability for specific applications and user requirements.
The following are some of the key features to consider:
Ease of Use
Ease of use refers to the user-friendliness of the software. It encompasses factors such as the software’s interface design, learning curve, and availability of documentation and support resources. Intuitive software with a well-organized interface makes it easier for users to navigate and perform tasks efficiently, regardless of their experience level.
Compatibility
Compatibility ensures that the software can seamlessly interact with other software and hardware components involved in the 3D printing process. This includes compatibility with different operating systems, file formats, and 3D printers. Compatibility is crucial for ensuring smooth data transfer and error-free operation throughout the workflow.
Functionality
Functionality encompasses the range of features and capabilities offered by the software. This includes essential functions such as model creation, editing, slicing, and printing. Advanced software may offer additional features such as simulation tools, optimization algorithms, and support for multiple materials and technologies.
The specific functionality required depends on the user’s application and the complexity of the 3D models being processed.
Other Considerations
In addition to the core features discussed above, other factors to consider include:
- Cost:The cost of the software can vary significantly, depending on its features and licensing model.
- Support:The availability of technical support and documentation is essential for troubleshooting and resolving issues.
- Updates:Regular software updates ensure that the software remains compatible with the latest technologies and operating systems.
Top Software Options

There are numerous 3D printing software options available, each with its own set of features and capabilities. To help you choose the best software for your needs, we have compiled a table comparing the top three options.
For 3D printing, choosing the right program is crucial. Factors to consider include the model’s complexity, desired print quality, and printer compatibility. Once the model is ready, printing can commence. However, post-processing steps may be necessary, such as mounting a canvas print to enhance its durability and presentation.
Subsequently, returning to the topic of 3D printing, selecting the appropriate software for the specific printing task remains essential to achieve optimal results.
The table includes columns for features, pricing, and compatibility. We have also included a brief overview of each software option.
Table of Top Software Options
| Software | Features | Pricing | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autodesk Fusion 360 | – Comprehensive suite of design and manufacturing tools
| – Free for hobbyists and startups
| – Windows, macOS, Linux |
| SolidWorks | – Industry-leading 3D modeling software
| – $3,995 per year | – Windows |
| Siemens NX | – Powerful CAD/CAM/CAE software
| – $20,000 per year | – Windows |
Open Source vs. Commercial Software
In the realm of 3D printing software, the choice between open source and commercial options presents distinct advantages and drawbacks. Open source software, freely available and modifiable, offers flexibility and customization. Commercial software, on the other hand, typically provides comprehensive features and dedicated support.
Open source software grants users access to the underlying code, enabling them to tailor the software to their specific needs. This flexibility allows for customization and integration with other tools. Additionally, open source software often benefits from a vibrant community of developers who contribute to its ongoing improvement.
However, open source software may lack the comprehensive features and dedicated support found in commercial offerings. Commercial software, developed and maintained by dedicated teams, typically offers a wider range of features and functionality. Additionally, commercial software often comes with dedicated support, ensuring users have access to technical assistance and updates.
Deciding on the appropriate software for 3D printing can be a crucial step. Factors such as the complexity of the model, the desired output quality, and the compatibility with your printer should be considered. Additionally, specialized software may be required for specific materials, such as how to print on acrylic.
Understanding the capabilities and limitations of different software programs can help you make an informed choice and optimize your 3D printing experience.
Examples
- Open source:Cura, Slic3r, PrusaSlicer
- Commercial:Simplify3D, Ultimaker Cura, Autodesk Fusion 360
– Identify 3D printing software specifically designed for different industries, such as engineering, medical, and art.
Industry-specific 3D printing software offers tailored features and capabilities that cater to the unique requirements of various industries. These specialized programs enhance efficiency, precision, and compliance within their respective domains.
Engineering
Engineering software enables the design, simulation, and manufacturing of complex 3D models. It integrates with CAD software, supports advanced materials, and provides tools for simulating structural integrity and performance.
- Autodesk Fusion 360:Integrated design, simulation, and manufacturing platform with support for generative design and cloud collaboration.
- Siemens NX:Comprehensive software for product design, simulation, and manufacturing, with a focus on complex assemblies and large-scale projects.
- Dassault Systèmes SOLIDWORKS:User-friendly software for mechanical design, simulation, and data management, widely used in engineering and manufacturing.
Medical
Medical software specializes in creating medical devices, prosthetics, and anatomical models. It integrates with medical imaging software, ensures compliance with regulatory standards, and supports advanced biomaterials.
- 3D Systems Mimics:Software for medical image segmentation, 3D modeling, and surgical planning, used in orthopedics, cardiology, and dentistry.
- Materialise Magics:Comprehensive software for medical device design, simulation, and manufacturing, with a focus on patient-specific implants and prosthetics.
- Stratasys J750 Digital Anatomy Printer:Specialized printer for creating high-resolution anatomical models, used in medical education, surgical planning, and patient communication.
Art
Art software focuses on creating digital sculptures, models, and high-resolution prints. It supports sculpting tools, high-polygon modeling, and integration with 3D scanning software.
- ZBrush:Industry-leading software for digital sculpting, with powerful tools for creating detailed models and textures.
- Blender:Open-source software for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering, widely used in the art and entertainment industries.
- Autodesk Maya:Professional software for 3D animation, modeling, and rendering, used in film, television, and video game production.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Industry-Specific Software
While general-purpose software offers versatility, industry-specific software provides tailored solutions with the following advantages:
- Optimized features:Specialized tools and workflows designed for specific industry requirements.
- Enhanced efficiency:Streamlined processes and automation reduce development time.
- Compliance and accuracy:Adherence to industry standards and regulations ensures reliability.
However, industry-specific software may also have limitations:
- Limited flexibility:Tailored features may restrict usage outside the intended industry.
- Higher cost:Specialized software can be more expensive than general-purpose options.
- Learning curve:Industry-specific software often requires specialized knowledge and training.
Software for Beginners
For beginners just starting their 3D printing journey, user-friendly software is crucial. These programs prioritize ease of use, allowing novices to quickly grasp the basics of 3D printing and begin creating their own designs.
To help beginners choose the best software for their needs, we’ve compiled a table comparing the features of several popular options. These include ease of use, cost, and compatibility with different 3D printers.
Ease of Use
- Cura: Known for its intuitive interface and user-friendly features, Cura is a great choice for beginners. It offers a range of presets and customization options, making it easy to get started with 3D printing.
- PrusaSlicer: Another beginner-friendly option, PrusaSlicer is known for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive documentation. It provides a variety of features and settings, allowing users to fine-tune their prints.
- Simplify3D: While not specifically designed for beginners, Simplify3D offers a user-friendly interface and a range of features that can be helpful for beginners. It provides a variety of presets and customization options, making it easy to get started with 3D printing.
Cost
- Cura: Free and open-source, Cura is a great option for beginners on a budget.
- PrusaSlicer: Also free and open-source, PrusaSlicer is another great option for beginners who want to save money.
- Simplify3D: A paid software, Simplify3D offers a range of features and customization options that may be worth the investment for some users.
Compatibility
- Cura: Cura is compatible with a wide range of 3D printers, making it a great choice for beginners who may not yet have a specific printer in mind.
- PrusaSlicer: PrusaSlicer is primarily designed for use with Prusa 3D printers, but it can also be used with other printers with some additional configuration.
- Simplify3D: Simplify3D is compatible with a wide range of 3D printers, including both FDM and SLA printers.
In addition to the software listed above, there are several other 3D printing software options available for beginners. These include:
- Tinkercad: A free and browser-based 3D modeling software, Tinkercad is a great option for beginners who want to learn the basics of 3D modeling and printing.
- 3D Builder: A free and easy-to-use 3D modeling and printing software, 3D Builder is a good choice for beginners who want to create simple 3D models.
- Meshmixer: A free and open-source 3D modeling and printing software, Meshmixer is a more advanced option that offers a range of features and customization options.
For beginners who are just getting started with 3D printing, using open-source software can be a great way to save money and learn the basics of 3D printing. Cura and PrusaSlicer are both excellent open-source options that offer a range of features and customization options.
They are also well-supported by the 3D printing community, so there are plenty of resources available to help beginners get started.
In addition to the software listed above, there are several other resources available to help beginners learn more about 3D printing. These include:
- 3D Printing for Beginners: A free online course from Udemy that teaches the basics of 3D printing.
- The 3D Printing Handbook: A free ebook that covers everything you need to know about 3D printing.
- The 3D Printing subreddit: A community of 3D printing enthusiasts who are always willing to help beginners get started.
Identify 3D Printing Software Designed for Advanced Users
D printing software designed for advanced users offers a range of advanced features and capabilities, including:
- Advanced slicing algorithms:These algorithms can generate more accurate and efficient toolpaths, resulting in higher-quality prints.
- Support for multiple materials and print profiles:This allows users to print with a variety of materials and create complex multi-material prints.
- Advanced model editing and manipulation tools:These tools allow users to make precise modifications to their models, including adding or removing features, scaling, and rotating.
- Integration with CAD software:This allows users to import and export models from CAD software, making it easier to create and modify 3D models for printing.
- Scripting and automation capabilities:These capabilities allow users to automate repetitive tasks and create custom scripts to extend the functionality of the software.
Top Software Options
Several software options are available for advanced 3D printing users, including:
- Ultimaker Cura:Open-source software with a wide range of features and support for multiple printers.
- Simplify3D:Commercial software with advanced slicing algorithms and support for multiple materials.
- PrusaSlicer:Open-source software with a focus on ease of use and customization.
- Ideamaker:Commercial software with advanced features and integration with CAD software.
- Kisslicer:Commercial software with a focus on speed and accuracy.
Open Source vs. Commercial Software
Open-source software is freely available and can be modified by users, while commercial software is typically licensed and requires payment. Open-source software often has a larger community of users and developers, which can lead to more frequent updates and a wider range of features.
However, commercial software often offers more polished features and better support.
Best Practices for Using Advanced 3D Printing Software
When using advanced 3D printing software, it is important to:
- Start with the basics:Learn the basics of 3D printing and the software’s interface before attempting advanced features.
- Use the right tools for the job:Choose the right slicing algorithm and print settings for the specific material and print quality you need.
- Experiment with different settings:Experiment with different slicing settings to find the optimal combination for your needs.
- Use automation:Use scripting and automation capabilities to streamline repetitive tasks and save time.
- Stay updated:Keep your software up to date to take advantage of new features and bug fixes.
By following these best practices, you can get the most out of your advanced 3D printing software and create high-quality prints.
Tips for Choosing Software
Choosing the right 3D printing software is crucial for successful printing projects. Here are some factors to consider when selecting software:
Experience Level
* Beginners: Opt for user-friendly software with intuitive interfaces and guided tutorials.
Advanced users
Choose software with advanced features, customization options, and support for complex designs.
Budget, What program to use for 3d printing
* Open-source software: Free to use, suitable for hobbyists and small-scale projects.
Commercial software
Typically paid, offers a wider range of features and support.
Printing Requirements
* Printing quality: Choose software that supports high-resolution printing and detailed models.
Speed and efficiency
Consider software that optimizes slicing algorithms for faster and more efficient printing.
Compatibility
Ensure the software is compatible with your 3D printer and operating system.
Software for Specific Materials
Different 3D printing materials require specific software to optimize their properties and achieve desired results. Each software is tailored to the unique characteristics of the material, ensuring optimal printing parameters, layer adhesion, and surface quality.
Let’s explore the advantages and limitations of 3D printing software for common materials like PLA, ABS, and resin.
PLA
- Advantages:PLA-specific software provides precise temperature control, ensuring minimal warping and optimal layer adhesion. It also offers customizable print profiles for different PLA grades and colors.
- Limitations:Limited compatibility with other materials and lower temperature resistance compared to other materials.
ABS
- Advantages:ABS-optimized software manages the material’s shrinkage and warping tendencies, resulting in dimensionally accurate prints. It also allows for higher printing temperatures, enabling stronger and more durable parts.
- Limitations:Requires a heated build chamber to prevent warping and may release fumes during printing.
Resin
- Advantages:Resin-specific software enables precise control over layer thickness and UV exposure time, resulting in high-resolution prints with smooth surfaces. It also supports various resin types and colors.
- Limitations:Requires post-processing steps such as curing and cleaning, and may have limited material compatibility compared to other materials.
Software for Large-Scale Printing: What Program To Use For 3d Printing

Large-scale printing projects require specialized software that can handle large file sizes, slice models efficiently, and manage multiple printers. These software programs offer advanced features such as adaptive slicing, support generation, and automation capabilities to ensure successful large-scale prints.
Features and Capabilities
The key features and capabilities to consider when choosing software for large-scale printing include:
- File size management:Ability to handle large file sizes (e.g., over 1 GB)
- Slicing performance:Fast and efficient slicing algorithms
- Support for multiple printers:Ability to control multiple printers simultaneously
- Job management:Features for managing and monitoring print jobs
- Advanced slicing options:Advanced slicing features such as adaptive slicing and support generation
- Material profiles:Pre-defined profiles for different materials
- Automation:Scripting and automation capabilities
Top Software Options
Several software programs are available for large-scale printing, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some popular options include:
- Simplify3D:Known for its advanced slicing capabilities, including adaptive slicing and support generation.
- Cura:An open-source software with a user-friendly interface and support for multiple printers.
- PrusaSlicer:Another open-source software with a focus on quality and reliability.
- IdeaMaker:A commercial software with advanced features such as real-time print monitoring and remote control.
- MatterControl:A software designed specifically for large-scale printing, with features such as job management and automated bed leveling.
Table of Features and Capabilities
The following table compares the features and capabilities of different software programs for large-scale printing:| Feature | Simplify3D | Cura | PrusaSlicer | IdeaMaker | MatterControl ||—|—|—|—|—|—|| File size management | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes || Slicing performance | Excellent | Good | Good | Excellent | Excellent || Support for multiple printers | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes || Job management | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes || Advanced slicing options | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes || Material profiles | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes || Automation | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Summary
The key findings of this research are as follows:
- There are a number of software programs available that are suitable for large-scale printing projects.
- The most important features and capabilities to consider when choosing a software program include file size management, slicing performance, support for multiple printers, job management, advanced slicing options, material profiles, and automation.
- The specific software program that is best for a particular project will depend on the specific requirements of the project.
Software for 3D Scanning

D printing software that integrates with 3D scanning technology offers a comprehensive solution for capturing, processing, and printing physical objects. This integration streamlines the workflow, enabling users to seamlessly create 3D models from real-world objects.
Benefits and Applications of 3D Scanning Software for 3D Printing
The benefits of using 3D scanning software for 3D printing include:
- Accurate Capture:3D scanning technology accurately captures the geometry and details of physical objects, creating highly detailed 3D models.
- Rapid Prototyping:The integration of 3D scanning and 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping, enabling users to quickly create physical models from digital scans.
- Customization and Repair:3D scanning can be used to customize existing objects or repair damaged ones, creating precise replacements.
- Cultural Heritage Preservation:3D scanning plays a vital role in preserving cultural artifacts and historical sites, enabling the creation of digital archives and replicas.
- Medical Applications:3D scanning is used in medical applications, such as creating custom prosthetics, surgical planning, and patient-specific medical devices.
Comparison Table of 3D Scanning Software for 3D Printing
| Software | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artec Studio | – High-resolution scanning
| – Accurate and detailed scans
| – Expensive
|
| EinScan-Pro | – Portable and handheld scanner
| – Convenient for on-site scanning
| – Lower resolution than some other scanners
|
| 3D Systems Geomagic Design X | – Advanced mesh editing and manipulation tools
| – Comprehensive and powerful software
| – Complex and may have a steep learning curve
|
| MeshLab | – Open-source and free to use
| – Cost-effective
| – Can be complex for beginners
|
Examples of Successful Use Cases
Successful use cases of 3D scanning software for 3D printing include:
- Custom Prosthetics:3D scanning is used to create custom-fit prosthetics that are tailored to the individual patient’s anatomy.
- Historical Artifact Preservation:The Smithsonian Institution uses 3D scanning to preserve and digitize historical artifacts, making them accessible to a wider audience.
- Rapid Prototyping for Automotive:Automotive manufacturers use 3D scanning to rapidly prototype new parts and components, reducing development time.
- Medical Device Development:3D scanning is used to create patient-specific medical devices, such as surgical implants and dental crowns.
- Art and Design:3D scanning is used by artists and designers to create unique and intricate sculptures and objects.
Future Trends and Advancements
Future trends and advancements in 3D scanning software for 3D printing include:
- Improved Accuracy and Resolution:Advancements in scanning technology will lead to higher accuracy and resolution, enabling the capture of even finer details.
- Automated Processing and Optimization:Software will become more automated, reducing the need for manual intervention in the processing and optimization of scanned data.
- Integration with AI:Artificial intelligence (AI) will play a significant role in enhancing the capabilities of 3D scanning software, enabling automatic object recognition and feature extraction.
- Cloud-Based Solutions:Cloud-based solutions will provide greater accessibility and scalability for 3D scanning and processing, allowing users to access software and resources from anywhere.
- Haptic Feedback:Haptic feedback will be integrated into 3D scanning systems, providing users with a more immersive and intuitive scanning experience.
Software for Post-Processing

Post-processing in 3D printing refers to the steps taken after the printing process to refine and enhance the final product. Software designed for post-processing plays a crucial role in these tasks, enabling users to slice, edit, and finish their 3D models efficiently.
Post-processing software typically offers a range of features and capabilities, including:
- Slicing: Dividing the 3D model into thin layers for printing
- Editing: Modifying the model’s geometry, orientation, and support structures
- Finishing: Applying textures, colors, and other enhancements to the printed object
Examples of popular post-processing software include:
- Cura (open-source)
- Simplify3D (commercial)
- PrusaSlicer (open-source)
- Slic3r (open-source)
Slicing Software
Slicing software is essential for preparing 3D models for printing. It generates a set of instructions that guide the printer in building the object layer by layer. Key features of slicing software include:
- Automatic layer generation
- Control over layer height and infill density
- Support structure generation
- Preview of the sliced model
Editing Software
Editing software allows users to modify the 3D model before slicing. This can involve adjusting the geometry, rotating or scaling the object, and adding or removing support structures. Editing software typically offers:
- Mesh manipulation tools
- Boolean operations (union, intersection, subtraction)
- Support for different file formats
- Integration with slicing software
Finishing Software
Finishing software is used to apply textures, colors, and other enhancements to the printed object. This can improve the appearance and durability of the finished product. Finishing software typically includes:
- Texture mapping
- Color mixing
- Post-processing effects (e.g., smoothing, sharpening)
- Support for different materials
Emerging Trends in 3D Printing Software

D printing software is rapidly evolving, with new trends and developments emerging all the time. These trends are shaping the future of 3D printing, making it more accessible, efficient, and versatile than ever before.One of the most significant trends in 3D printing software is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI).
AI can be used to automate many of the tasks involved in 3D printing, such as design, slicing, and printing. This can free up users to focus on more creative aspects of the process.Another trend is the development of software that is specifically designed for different industries.
For example, there is now software that is optimized for engineering, medical, and art applications. This software includes features that are tailored to the specific needs of each industry.
Key Trends in 3D Printing Software| Trend | Potential Implications ||—|—|| Use of AI | Automation of tasks, increased efficiency || Industry-specific software | Improved performance, tailored features || Cloud-based software | Accessibility, collaboration || Open-source software | Lower costs, increased customization || Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) | Improved visualization, remote collaboration |
Questions and Answers
What are the key factors to consider when choosing 3D printing software?
Ease of use, compatibility with your 3D printer, available features, and cost are all important factors to consider when selecting 3D printing software.
What are the different types of 3D printing software?
There are three main types of 3D printing software: CAD software for designing 3D models, slicing software for preparing models for printing, and modeling software for creating and editing 3D models.
Which software is best for beginners?
For beginners, user-friendly software with a simple interface and clear instructions is recommended. Some popular options include Cura, PrusaSlicer, and Tinkercad.


