Delving into the realm of household expenses, understanding what is the average cost for utilities per month is crucial for financial stability and sustainable living. This analysis aims to shed light on the intricacies of utility consumption, its contributing factors, and strategies for cost reduction, empowering individuals and families to make informed decisions about their energy usage.
From exploring the types of utilities and their impact on monthly bills to examining the influence of energy-efficient appliances and home insulation, this comprehensive guide provides a roadmap for navigating the complexities of utility costs. By delving into regional variations, seasonal fluctuations, and government assistance programs, we aim to equip readers with the knowledge and tools to optimize their energy consumption and minimize their financial burden.
Types of Utilities

Monthly utility costs encompass various services essential for modern living. These services can be broadly categorized into two types: essential and non-essential.
Essential Utilities
Essential utilities are indispensable for maintaining a basic standard of living and include:
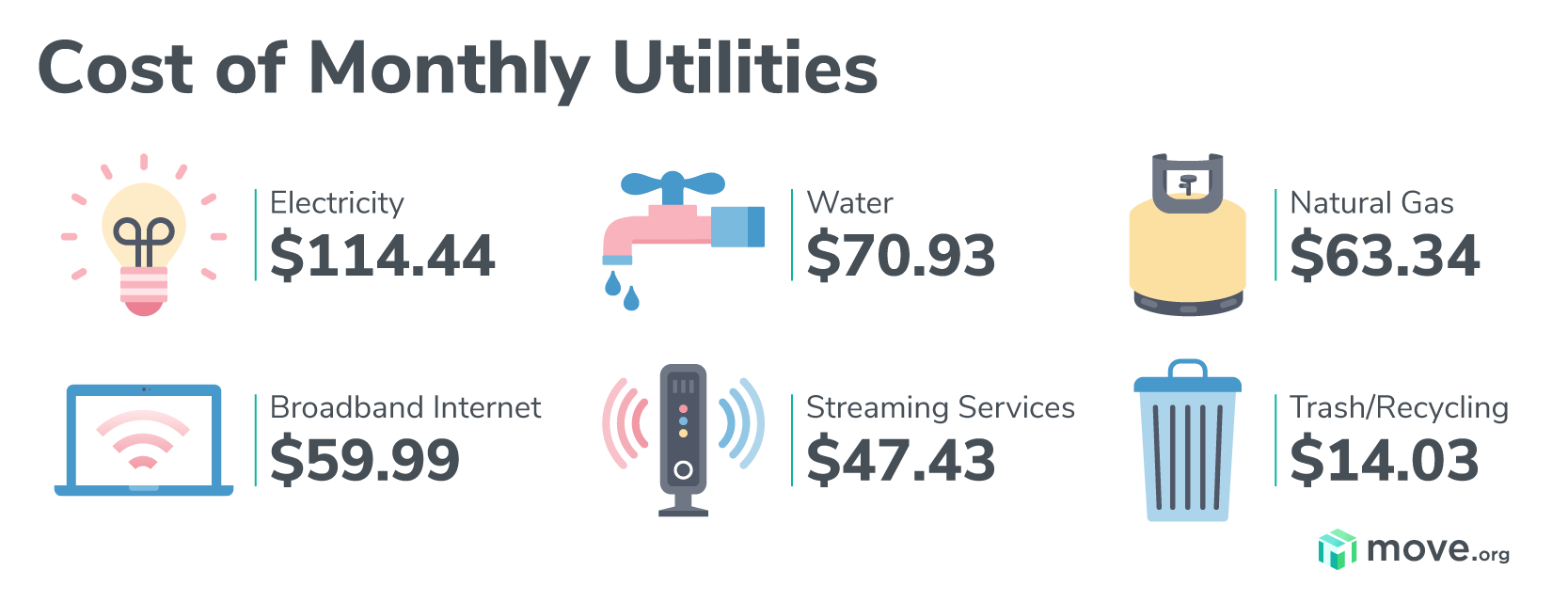
- Electricity:Powers appliances, lighting, and electronic devices.
- Gas:Provides heating, cooking, and hot water.
- Water:Essential for hydration, sanitation, and hygiene.
- Sewerage:Removes wastewater and sewage.
Non-Essential Utilities
Non-essential utilities provide additional comfort and convenience but are not essential for survival. These include:
- Internet:Provides access to information and entertainment.
- Cable TV:Offers entertainment and news.
- Landline phone:Provides communication services.
| Utility Type | Essential/Non-Essential | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Electricity | Essential | Lighting, appliances, heating |
| Gas | Essential | Heating, cooking, hot water |
| Water | Essential | Drinking, sanitation, hygiene |
| Sewerage | Essential | Wastewater removal |
| Internet | Non-Essential | Information, entertainment |
| Cable TV | Non-Essential | Entertainment, news |
| Landline phone | Non-Essential | Communication |
Factors Influencing Utility Costs

The cost of utilities can vary significantly depending on a number of factors, including location, size of dwelling, number of occupants, and energy efficiency of appliances and home insulation. Let’s delve into each of these factors and analyze their impact on utility consumption and costs.
Location
Location plays a crucial role in determining utility costs. Homes in colder climates typically have higher heating costs, while those in warmer climates have higher cooling costs. Additionally, the availability of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can also impact utility costs.
Homes in areas with abundant renewable energy sources may have lower utility costs compared to those in areas with limited access to these resources.
Size of Dwelling, What is the average cost for utilities per month
The size of a dwelling is another important factor that influences utility costs. Larger homes generally have higher utility costs than smaller homes. This is because larger homes require more energy to heat, cool, and light. The number of rooms, square footage, and overall layout of the home can all contribute to increased utility consumption.
Number of Occupants
The number of people living in a dwelling can also affect utility costs. Households with more occupants generally have higher utility costs than households with fewer occupants. This is because more occupants typically lead to increased energy consumption for activities such as cooking, laundry, and showering.
Energy-Efficient Appliances and Home Insulation
Energy-efficient appliances and home insulation can significantly reduce utility costs. Energy-efficient appliances consume less energy, resulting in lower utility bills. Home insulation helps to reduce heat loss and gain, which can lead to lower heating and cooling costs. Investing in energy-efficient appliances and proper home insulation can pay off in the long run by reducing utility expenses.
Regional Variations
Utility costs vary significantly across different regions due to a combination of geographic factors. These factors include climate, energy sources, and local regulations.
Climate
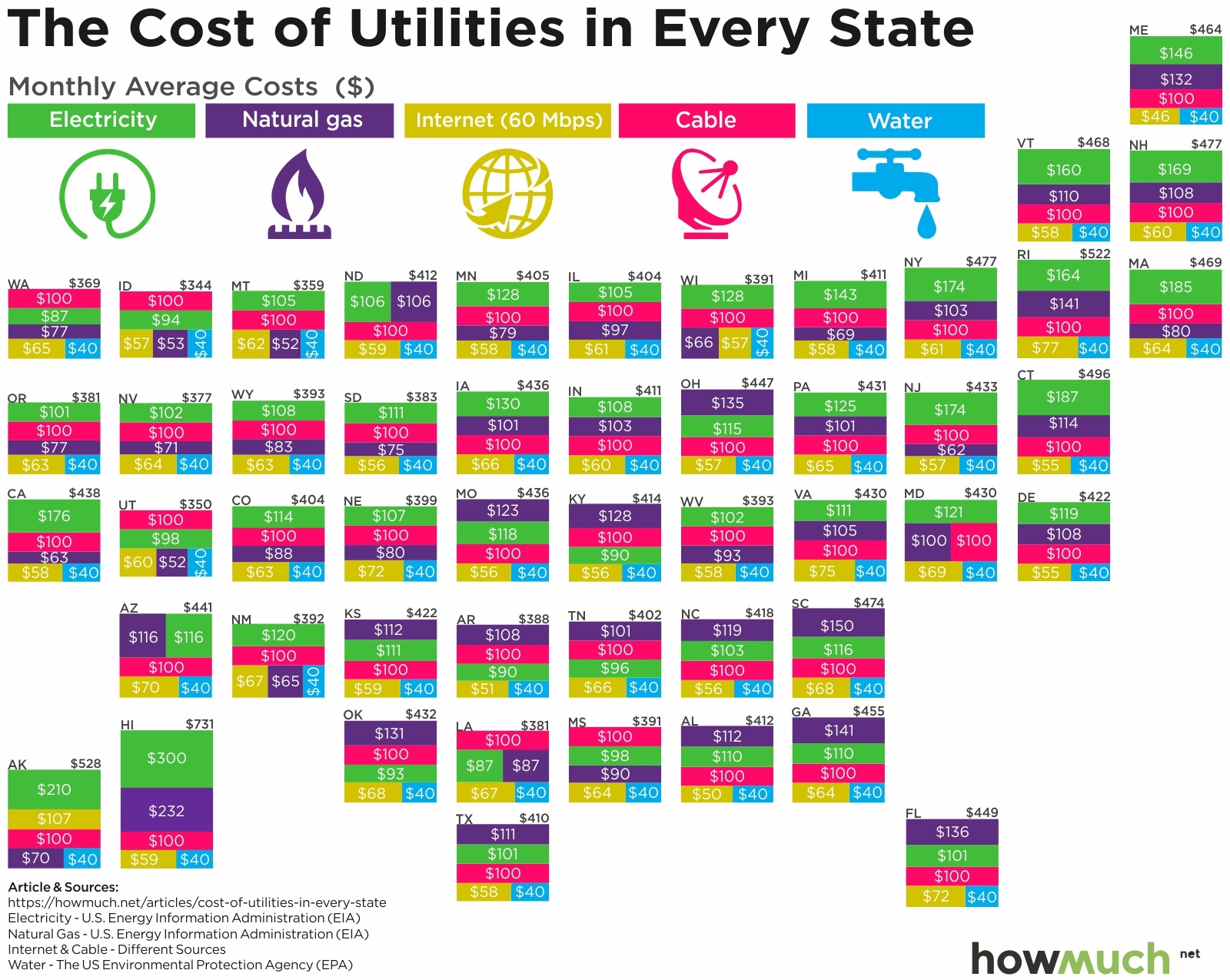
Climate plays a significant role in determining utility costs. Regions with colder climates typically have higher heating costs, while regions with warmer climates have higher cooling costs. For example, the average monthly utility bill in Maine, a state with a cold climate, is about $150, while the average monthly utility bill in Florida, a state with a warm climate, is about $100.
Energy Sources
The availability of energy sources also affects utility costs. Regions that have access to abundant and affordable energy sources, such as natural gas or hydroelectric power, typically have lower utility costs. For example, the average monthly utility bill in Texas, a state with abundant natural gas resources, is about $120, while the average monthly utility bill in California, a state that relies heavily on imported energy, is about $150.
Local Regulations
Local regulations can also impact utility costs. Some states and municipalities have implemented policies that promote energy efficiency or renewable energy, which can lead to lower utility costs for consumers. For example, the average monthly utility bill in Vermont, a state with a strong commitment to energy efficiency, is about $100, while the average monthly utility bill in Mississippi, a state with fewer energy efficiency programs, is about $130.
Table: Average Utility Costs by Region
The following table compares average utility costs across different regions in the United States:
| Region | Average Monthly Utility Cost |
|---|---|
| Northeast | $150 |
| Midwest | $120 |
| South | $100 |
| West | $150 |
Seasonal Fluctuations
Utility consumption and costs fluctuate throughout the year due to seasonal changes in weather and lifestyle. These fluctuations are primarily driven by the need for heating in winter and cooling in summer.
During winter months, energy consumption for heating purposes increases significantly. This is reflected in higher utility costs, as heating systems such as furnaces and boilers consume a substantial amount of energy. In contrast, during spring and fall, when temperatures are milder, heating requirements decrease, resulting in lower utility consumption and costs.
Summer Cooling
In summer months, the need for cooling becomes prominent, leading to increased consumption of electricity for air conditioning and fans. This surge in energy use results in higher utility costs. In regions with extreme summer temperatures, cooling costs can account for a significant portion of the annual utility budget.
Impact on Utility Budgets
Seasonal fluctuations in utility costs can impact household budgets. During peak seasons (winter and summer), when consumption and costs are higher, households may experience financial strain if they are not adequately prepared. It is essential to anticipate these seasonal changes and adjust budgets accordingly.
Strategies for Managing Costs
To manage utility costs during peak and off-peak seasons, households can implement various strategies:
- Energy-efficient appliances:Investing in energy-efficient appliances, such as ENERGY STAR-rated models, can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills.
- Thermostat adjustments:Adjusting thermostat settings during peak hours (e.g., raising the thermostat in summer or lowering it in winter) can help reduce energy use.
- Behavioral changes:Simple behavioral changes, such as turning off lights when leaving a room or unplugging electronics when not in use, can contribute to energy savings.
- Energy audits:Conducting an energy audit can help identify areas where energy efficiency can be improved, leading to potential cost savings.
- Time-of-use rates:In some areas, utility companies offer time-of-use rates, which charge different rates for electricity during peak and off-peak hours. Shifting energy consumption to off-peak hours can result in lower costs.
Energy Conservation Measures
Energy conservation measures are actions taken to reduce energy consumption and costs. These measures can be implemented in various sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial. By adopting energy conservation strategies, individuals and organizations can not only save money but also contribute to environmental sustainability.
Energy Audits
Energy audits are comprehensive assessments of a building’s energy use. They identify areas where energy is being wasted and provide recommendations for improvements. Energy audits can be conducted by qualified professionals and typically involve an inspection of the building, analysis of energy bills, and identification of energy-saving opportunities.
Weatherization
Weatherization involves making physical improvements to a building to reduce heat loss or gain. Common weatherization measures include insulation, air sealing, and energy-efficient windows. These measures can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs, especially in extreme climates.
Behavioral Changes
Behavioral changes, such as turning off lights when leaving a room or unplugging unused appliances, can also contribute to energy conservation. Encouraging energy-conscious behavior among building occupants can have a significant impact on overall energy consumption.
Case Studies of Successful Conservation Efforts
Numerous successful energy conservation efforts have been implemented worldwide. For example, the city of Portland, Oregon, has achieved significant energy savings through its “Portland Energy Challenge” program, which promotes energy efficiency in buildings and transportation.
The average cost for utilities per month varies depending on factors such as location, size of home, and usage habits. Understanding what is utilization can help you optimize your energy consumption and potentially reduce your utility bills. By tracking your energy usage and identifying areas where you can improve efficiency, you can make informed decisions to lower your average cost for utilities per month.
Table of Energy Audit Findings
| Building Type | Energy Savings | Key Findings ||—|—|—|| Residential | 15-25% | Improved insulation, air sealing, and energy-efficient appliances || Commercial | 10-20% | Lighting upgrades, HVAC optimization, and building automation || Industrial | 5-15% | Process optimization, energy-efficient equipment, and waste heat recovery |
Press Release: New Energy Conservation Program
City of San Francisco Launches New Energy Conservation Program
The City of San Francisco has announced the launch of a new energy conservation program aimed at reducing energy consumption and costs for residents and businesses. The program offers financial incentives, technical assistance, and educational resources to help participants implement energy-saving measures.
Blog Post: Tips for Homeowners
5 Tips to Reduce Your Energy Consumption and Save Money
1. Conduct an energy audit to identify areas of energy waste. 2. Make weatherization improvements, such as adding insulation and sealing air leaks. 3.
Replace old appliances with energy-efficient models. 4. Install energy-saving lighting, such as LED bulbs. 5. Encourage energy-conscious behavior among household members.
Government Assistance Programs
Government assistance programs play a crucial role in providing financial support and incentives to individuals and households facing financial constraints in managing utility costs. These programs aim to alleviate the burden of utility expenses and promote energy efficiency measures.
Eligibility criteria and application procedures vary depending on the specific program and the governing agency. Generally, income guidelines and household size are considered in determining eligibility. To apply for these programs, individuals can contact their local utility providers, community action agencies, or government websites.
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP)
LIHEAP is a federally funded program that provides financial assistance to low-income households for heating and cooling costs. The program offers grants to eligible households to help them pay for heating and cooling expenses, including fuel bills, natural gas, electricity, and propane.
Weatherization Assistance Program (WAP)
WAP is a federally funded program that provides energy efficiency improvements to low-income households. The program offers free or low-cost home weatherization services, such as insulation, air sealing, and energy-efficient appliances, to help reduce energy consumption and lower utility costs.
Energy Star Rebate Programs
Energy Star Rebate Programs are offered by utilities and government agencies to incentivize the purchase of energy-efficient appliances and equipment. These programs provide rebates or discounts on the purchase of Energy Star-certified appliances, such as refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners, which can lead to long-term savings on utility bills.
Comparison of Utility Providers
Comparing different utility providers can help consumers make informed decisions and choose the best option for their needs. This comparison takes into account factors such as rates, services offered, customer service, billing options, and renewable energy offerings.
The following table provides a comparison of rates and services offered by different utility providers in a specific region:
| Provider | Electricity Rate (kWh) | Gas Rate (therm) | Water Rate (gallon) | Services Offered | Customer Service | Billing Options | Renewable Energy Offerings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provider A | $0.12 | $1.20 | $0.005 | Electricity, gas, water | 24/7 support | Online, mail, phone | Solar, wind |
| Provider B | $0.15 | $1.10 | $0.006 | Electricity, gas | 8am-5pm weekdays | Online, mail | None |
| Provider C | $0.10 | $1.30 | $0.004 | Electricity, water | 24/7 support | Online, phone | Solar |
Key Differences
The key differences between the providers are as follows:
- Provider A offers the lowest electricity rate but the highest gas rate.
- Provider B offers the highest electricity rate but the lowest gas rate.
- Provider C offers the lowest water rate.
- Provider A and C offer 24/7 customer support, while Provider B only offers support during business hours.
- Provider A offers the most renewable energy offerings, including solar and wind.
Utility Cost Forecasting
Utility cost forecasting is a crucial aspect of financial planning for both individuals and organizations. Accurate forecasting enables budgeting and decision-making to manage future utility expenses effectively.
Forecasting utility costs involves various methods, including:
- Historical Data Analysis:Examining past utility consumption patterns, identifying trends, and projecting future costs based on historical data.
- Energy Market Trends:Monitoring fluctuations in energy prices, supply and demand dynamics, and regulatory changes to predict potential impacts on utility costs.
- Econometric Models:Utilizing statistical models that incorporate economic indicators, weather patterns, and other factors to forecast future utility costs.
Accurate utility cost forecasting is essential for:
- Budgeting:Establishing realistic budgets for utility expenses, avoiding unexpected financial burdens.
- Financial Planning:Allocating resources effectively, making informed decisions about investments and financial strategies.
- Risk Management:Identifying potential fluctuations in utility costs and developing strategies to mitigate financial risks.
Emerging Technologies

The utility industry is undergoing a significant transformation driven by the emergence of new technologies. These technologies have the potential to reshape the way utilities operate, deliver services, and interact with customers. This section explores the key emerging technologies that are expected to impact utility consumption and costs.
Smart Meters
Smart meters are advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) devices that provide real-time data on energy consumption. They enable utilities to monitor and manage the grid more efficiently, reduce energy waste, and provide customers with detailed information about their energy usage.
- Benefits:
- Improved grid efficiency
- Reduced energy consumption
- Enhanced customer engagement
- Challenges:
- Cost of implementation
- Data security concerns
- Customer acceptance
Renewable Energy Systems
Renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power, are becoming increasingly cost-effective and are playing a growing role in the utility industry. These systems can help utilities reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, generate clean energy, and meet increasing demand for electricity.
- Benefits:
- Reduced carbon emissions
- Diversification of energy sources
- Increased energy independence
- Challenges:
- Intermittency of renewable energy sources
- Cost of storage
- Grid integration issues
Energy Storage Systems
Energy storage systems, such as batteries, can help utilities store excess energy generated from renewable sources and release it during periods of high demand. This can help balance the grid, reduce the need for fossil fuel generation, and improve the reliability of the electricity supply.
The average cost of utilities per month can vary greatly depending on factors such as location, size of the home, and usage habits. However, the average cost for utilities such as electricity, gas, and water typically falls within a certain range.
Understanding the average cost for utilities per month can provide a basis for comparison when evaluating how much is a utility easement worth , as the cost of utilities can impact the value of the easement. Furthermore, understanding the average cost for utilities per month can assist in budgeting and managing household expenses.
- Benefits:
- Increased grid flexibility
- Reduced reliance on fossil fuels
- Improved reliability of electricity supply
- Challenges:
- Cost of storage
- Limited lifespan of batteries
- Environmental concerns associated with battery disposal
Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular, and their adoption is expected to have a significant impact on the utility industry. EVs can help reduce air pollution, reduce dependence on fossil fuels, and increase the demand for electricity.
- Benefits:
- Reduced air pollution
- Reduced dependence on fossil fuels
- Increased demand for electricity
- Challenges:
- Cost of EVs
- Range anxiety
- Availability of charging infrastructure
Environmental Impact
The consumption of utilities, particularly energy, has significant environmental implications. The generation and distribution of electricity, heating, and transportation fuels contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and water depletion.
Energy conservation measures and the adoption of renewable energy sources play a crucial role in reducing these environmental impacts. By reducing energy consumption, we can lower the demand for fossil fuels and the associated emissions.
Renewable Energy Sources
- Solar Energy:Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, providing a clean and renewable source of power.
- Wind Energy:Wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of wind to generate electricity, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Hydroelectric Energy:Dams and turbines use the flow of water to generate electricity, providing a sustainable and reliable source of power.
Case Studies
Several case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of various strategies in reducing utility costs for households and businesses.
These case studies provide valuable insights into the practical implementation and outcomes of energy conservation measures, showcasing the potential savings that can be achieved.
Residential Case Study
A household in California implemented a comprehensive energy efficiency plan that included:
- Installing energy-efficient appliances
- Upgrading insulation and windows
- Adopting smart home technologies
As a result, their monthly utility bills were reduced by 30%, with annual savings of over $500.
Commercial Case Study
A small business in New York implemented a lighting retrofit program that replaced traditional incandescent bulbs with energy-efficient LEDs.
This single measure reduced their lighting costs by 50%, resulting in monthly savings of $200.
Online Resources
Finding comprehensive and reliable information on utility costs, energy conservation measures, and government assistance programs can be challenging. To assist our readers, we have compiled a comprehensive list of reputable online resources that provide detailed information on these topics.
The resources are categorized by type, including websites, databases, and industry publications. Each resource provides a brief description and a direct link for easy access.
Websites
| Resource | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| ENERGY STAR | Provides information on energy-efficient products, homes, and businesses. | https://www.energystar.gov/ |
| U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) | Provides data and analysis on energy production, consumption, and prices. | https://www.eia.gov/ |
| Utility Database | Provides a searchable database of utility providers and their rates. | https://www.utilitydatabase.com/ |
Databases
| Resource | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| National Energy Data Center (NEDC) | Provides access to a vast collection of energy-related data. | https://www.nedc.org/energy-data/ |
| EIA Electricity Data Browser | Provides interactive data on electricity generation, consumption, and prices. | https://www.eia.gov/electricity/data/browser/ |
| Utility Dive Reports Database | Provides access to a collection of utility-related reports and studies. | https://www.utilitydive.com/utility-reports-database |
Industry Publications
| Resource | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Utility Week | Provides news, analysis, and commentary on the utility industry. | https://www.utilityweek.co.uk/ |
| Energy Central | Provides a platform for energy professionals to share knowledge and insights. | https://www.energycentral.com/ |
| GreenTech Media | Provides coverage of the clean energy industry. | https://www.greentechmedia.com/ |
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and managing utility costs is crucial for financial stability and environmental sustainability. By considering the various factors that influence utility costs, including regional variations, seasonal fluctuations, and energy conservation measures, consumers can make informed decisions to reduce their utility expenses and minimize their environmental impact.
Government assistance programs and utility cost forecasting tools can further support consumers in managing their utility costs. By staying informed about emerging technologies and environmental impact, consumers can actively participate in shaping the future of the utility industry and contribute to a more sustainable energy landscape.
Q&A: What Is The Average Cost For Utilities Per Month
What are the primary factors that affect utility costs?
Usage, location, seasonality, size of dwelling, number of occupants, energy efficiency of appliances and home insulation.
How can I reduce my utility consumption?
Conduct energy audits, implement weatherization measures, adopt energy-efficient appliances, and make behavioral changes.
Are there any government programs available to assist with utility costs?
Yes, various programs offer financial assistance or incentives for energy efficiency and utility cost reduction.


