What is printhead in printer – In the realm of printing technology, the printhead stands as a pivotal component, responsible for transferring digital data onto physical paper. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of printheads, exploring their functions, types, maintenance, and troubleshooting, providing a thorough understanding of these essential printing mechanisms.
Printheads serve as the heart of inkjet and laser printers, orchestrating the precise deposition of ink droplets or toner particles onto the printing surface. They play a crucial role in determining print quality, speed, and efficiency, making them a vital aspect of any printing system.
Definition of Printhead
A printhead, also known as a printer head, is a crucial component of a printer responsible for transferring ink onto paper to create printed images or text. It is the part of the printer that directly interacts with the paper and deposits ink droplets to form the desired output.
Printheads vary in design and technology, and the type used in a particular printer depends on factors such as the printer’s intended use, print quality, and speed requirements. The two main types of printheads commonly found in printers are:
Inkjet Printheads
Inkjet printheads utilize a technology where tiny ink droplets are ejected from nozzles onto the paper. These nozzles are controlled precisely to create high-resolution images and text. Inkjet printheads can be either thermal or piezoelectric, with thermal printheads using heat to create ink droplets and piezoelectric printheads using electrical pulses.
Laser Printheads
Laser printheads employ a different technology involving a laser beam and toner particles. The laser beam draws an electrostatic image on a photosensitive drum, which then attracts toner particles. The toner is then transferred to the paper and fused using heat and pressure to create a permanent image.
– Describe the function of the printhead in the printing process.
A printhead, also known as a print engine or print module, is a critical component in a printer that is responsible for transferring ink onto paper or other printable media to create an image or text. The printhead consists of a set of nozzles that precisely eject tiny droplets of ink onto the paper, forming the desired pattern.
The accuracy and precision of the printhead directly influence the quality and resolution of the printed output.
The printhead moves across the paper, depositing ink droplets to create the desired image or text. The printhead is controlled by the printer’s electronics, which determine the pattern and sequence of ink droplets to be ejected. The printhead also includes a heating element that helps to dry the ink droplets quickly, ensuring that they do not smudge or smear.
Printheads are available in various types, each with its own advantages and applications. The most common types of printheads include:
- Thermal printheadsuse heat to generate ink droplets. They are commonly used in inkjet printers and are known for their high resolution and affordability.
- Piezoelectric printheadsuse electrical signals to create ink droplets. They are typically found in high-end printers and offer excellent precision and durability.
- Laser printheadsuse a laser to create an electrostatic charge on the paper, which attracts toner particles. They are commonly used in laser printers and are known for their speed and reliability.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Printheads
Printheads require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Regular cleaning of the printhead nozzles is essential to prevent clogging, which can lead to poor print quality or even printer failure. The cleaning process typically involves using a special cleaning solution and running a cleaning cycle through the printer software.
The printhead is a crucial component in a printer, responsible for transferring ink or toner onto the paper. In the context of 3D printing, the printhead is equally important, determining the quality and precision of the printed objects. To learn more about the Ender 3 3D printer and its features, including the capabilities of its printhead, you can refer to this comprehensive review: is the ender 3 3d printer worth it.
The review delves into the specifics of the Ender 3’s printhead, providing valuable insights for potential buyers.
If print quality issues persist despite regular cleaning, the printhead may need to be replaced. Replacing the printhead is a more involved process that typically requires technical expertise. It is important to use genuine replacement printheads from the printer manufacturer to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
Resources for Further Research on Printheads
Printhead Technology
Printhead technology is the foundation of any modern printer, and it plays a crucial role in determining the print quality, speed, and cost of the printed output. Over the years, various printhead technologies have been developed, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages.
The three main printhead technologies used in modern printers are:
- Thermal Inkjet
- Piezoelectric Inkjet
- Laser
Thermal Inkjet Printheads
Thermal inkjet printheads are the most common type of printhead used in home and office printers. They work by heating ink droplets to create bubbles that propel the ink onto the paper. Thermal inkjet printheads are relatively inexpensive to manufacture, and they can produce high-quality prints at a reasonable speed.
Advantages of thermal inkjet printheads:
- Low cost
- High print quality
- Reasonable speed
Disadvantages of thermal inkjet printheads:
- Can be susceptible to clogging
- May require frequent maintenance
- Not as durable as other printhead technologies
Examples of printers that use thermal inkjet printheads:
- HP DeskJet printers
- Canon Pixma printers
- Epson Expression printers
Piezoelectric Inkjet Printheads
Piezoelectric inkjet printheads use piezoelectric crystals to create vibrations that propel ink droplets onto the paper. Piezoelectric inkjet printheads are more expensive to manufacture than thermal inkjet printheads, but they offer several advantages.
Advantages of piezoelectric inkjet printheads:
- Less susceptible to clogging
- Require less maintenance
- More durable than thermal inkjet printheads
- Can produce higher-quality prints
Disadvantages of piezoelectric inkjet printheads:
- More expensive than thermal inkjet printheads
- Slower print speeds
Examples of printers that use piezoelectric inkjet printheads:
- Epson SureColor printers
- Canon imagePROGRAF printers
- HP DesignJet printers
Laser Printheads
Laser printheads use a laser beam to create an electrostatic image on a drum. The drum then transfers the image to the paper using toner particles. Laser printheads are the most expensive type of printhead, but they offer the highest print quality and the fastest print speeds.
Advantages of laser printheads:
- Highest print quality
- Fastest print speeds
- Durable
- Low maintenance
Disadvantages of laser printheads:
- Most expensive
- Not as versatile as inkjet printheads
Examples of printers that use laser printheads:
- HP LaserJet printers
- Canon imageCLASS printers
- Brother HL printers
Impact of Printhead Technology on Print Quality, Speed, and Cost
The type of printhead technology used in a printer has a significant impact on the print quality, speed, and cost of the printed output. Thermal inkjet printheads are the most affordable option, but they can produce lower-quality prints at slower speeds.
Piezoelectric inkjet printheads offer higher print quality and faster speeds, but they are more expensive. Laser printheads offer the highest print quality and the fastest speeds, but they are the most expensive type of printhead.
Evolution of Printhead Technology
Printhead technology is constantly evolving, and new innovations are being introduced all the time. One of the most recent advancements in printhead technology is the development of high-density printheads. High-density printheads have a higher number of nozzles than traditional printheads, which allows them to produce higher-quality prints at faster speeds.
Another recent advancement in printhead technology is the development of 3D printheads. 3D printheads can create three-dimensional objects by depositing layers of material onto a surface.
As printhead technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even higher print quality, faster print speeds, and lower costs in the future.
Printhead Maintenance

Proper printhead maintenance is essential to ensure optimal print quality and extend the lifespan of the printer. Regular cleaning and alignment procedures help prevent clogging, misalignment, and other issues that can affect print quality.
Cleaning the Printhead
- Use a soft, lint-free cloth or cotton swab moistened with isopropyl alcohol or a specialized printhead cleaning solution.
- Gently wipe the surface of the printhead, avoiding touching the nozzles.
- Repeat the process until no more ink residue is visible on the cloth or swab.
Aligning the Printhead
Printhead alignment ensures that the ink droplets are placed accurately on the paper, preventing blurry or misaligned prints.
- Most printers have a built-in printhead alignment utility that can be accessed through the printer’s control panel or software.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to print a test page with alignment patterns.
- Examine the test page and adjust the printhead alignment as needed using the printer’s controls.
Regular printhead maintenance helps prevent costly repairs and ensures that your printer delivers consistent, high-quality prints.
Common Printhead Problems and Troubleshooting
Printhead issues are a common cause of printing problems. Here is a comprehensive list of common printhead problems, their root causes, and troubleshooting steps to resolve them.
Clogged Nozzles
Clogged nozzles occur when ink particles accumulate and obstruct the tiny nozzles on the printhead. This can be caused by:
- Infrequent printer use
- Using incompatible or expired ink
- Air bubbles in the ink cartridges
Troubleshooting:
- Run the printer’s built-in nozzle cleaning utility.
- Manually clean the printhead using a lint-free cloth dampened with isopropyl alcohol.
- Replace the ink cartridges if they are empty or expired.
Printhead Misalignment
Misaligned printheads can cause blurry or distorted prints. This can be caused by:
- Incorrect printhead installation
- Physical damage to the printer
Troubleshooting:
- Reinstall the printhead according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Inspect the printer for any visible damage. If damage is found, contact a qualified technician.
Electrical Faults
Electrical faults can prevent the printhead from receiving power or communicating with the printer. This can be caused by:
- Loose connections
- Faulty wiring
- Damaged printhead
Troubleshooting:
- Check all cable connections to ensure they are secure.
- Inspect the wiring for any visible damage. If damage is found, contact a qualified technician.
- Replace the printhead if it is damaged.
Error Messages
Printers often display error messages or codes to indicate printhead problems. Here are some common error messages and their interpretations:
- “Printhead not detected”: The printer cannot detect the printhead.
- “Printhead error”: A general error has occurred with the printhead.
- “Replace printhead”: The printhead has reached the end of its lifespan and needs to be replaced.
Preventive Measures
To minimize the occurrence of printhead problems, consider the following preventive measures:
- Use your printer regularly to prevent nozzles from clogging.
- Use high-quality ink cartridges from reputable manufacturers.
- Store ink cartridges properly to prevent air bubbles.
- Handle the printhead with care to avoid damage.
Printhead Replacement
When a printhead fails, it becomes necessary to replace it to restore the printer’s functionality. Several signs and symptoms indicate the need for printhead replacement, including:
- Deteriorated print quality, such as faded or streaked prints
- Missing or misaligned lines in printed documents
- Clogged or jammed nozzles, resulting in gaps or white lines in prints
- Printer error messages or alerts specifically mentioning printhead issues
Step-by-Step Printhead Replacement Guide
Replacing a printhead requires careful handling and attention to safety precautions. Before proceeding, ensure the printer is unplugged from the power source and cooled down if it has been in use. Gather the necessary tools, including a replacement printhead, gloves, and a clean cloth or paper towels.
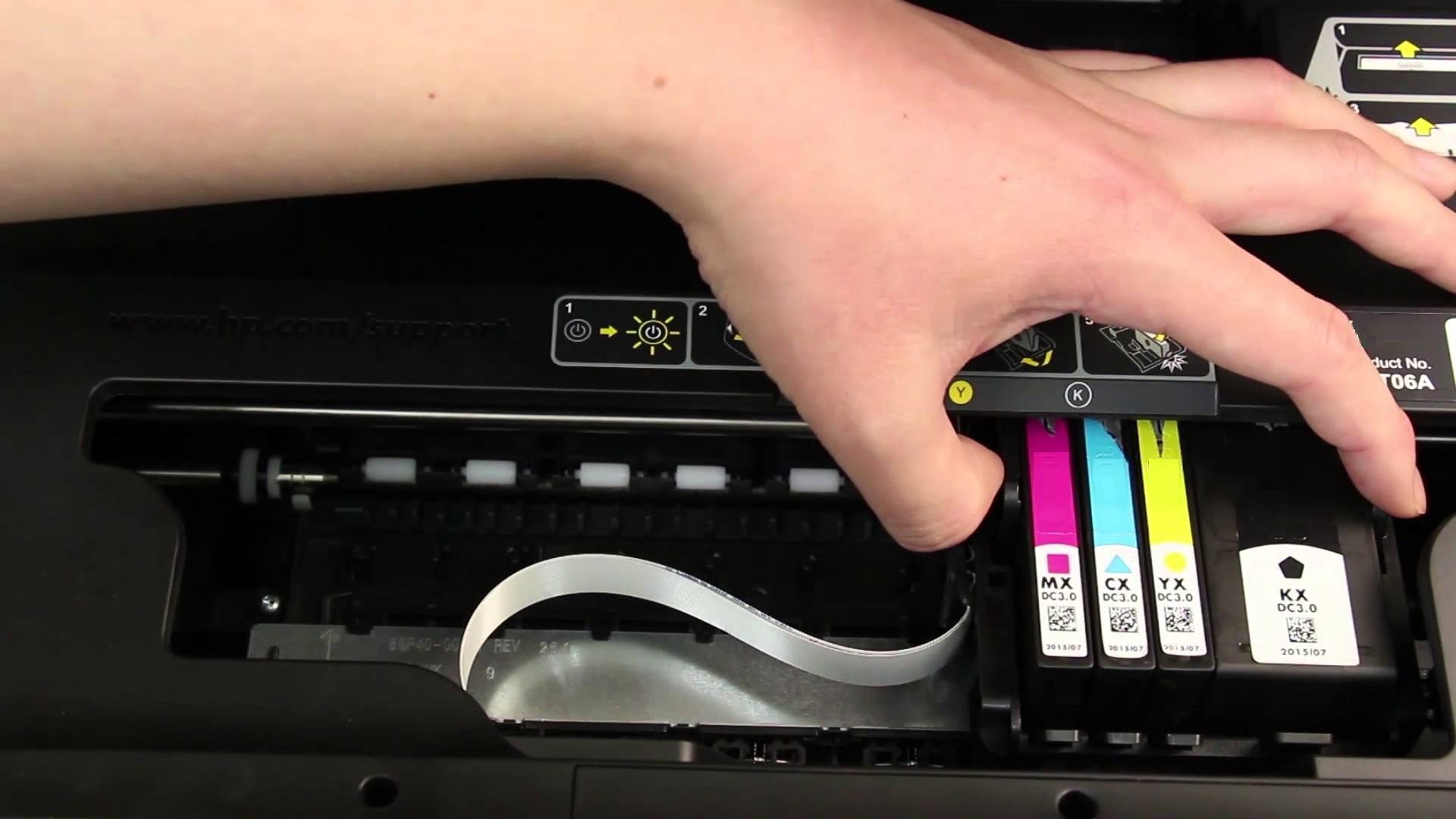
1. Locate the Printhead
Open the printer’s cover and identify the printhead. It is typically located at the front of the printer, behind the ink cartridges.
2. Remove the Old Printhead
Depending on the printer model, there may be a release button or latch to unseat the printhead. Gently press the release mechanism and lift the old printhead straight up to remove it.
3. Clean the Printhead Seat
Use a clean cloth or paper towels to wipe away any ink or debris from the printhead seat. This ensures proper contact and alignment of the new printhead.
4. Install the New Printhead
Carefully align the new printhead with the seat and gently lower it into place. Press down firmly until it clicks or locks into position.
5. Reconnect Cables
If any cables or connectors were disconnected during the process, reconnect them securely.
6. Power On and Test
Plug the printer back into the power source and turn it on. The printer will automatically initialize the new printhead and run a test print.
Printhead Replacement Procedures for Different Types of Printheads
Printheads vary in design and technology, and their replacement procedures may differ. Here is a table summarizing the different types of printheads and their corresponding replacement methods:| Printhead Type | Replacement Procedure ||—|—|| Piezoelectric | Similar to the steps Artikeld above, with variations in release mechanisms.
|| Thermal Inkjet | May require additional steps for priming or cleaning before installation. || Laser Printer | Typically replaced as a single unit along with the toner cartridge. |
Troubleshooting Printhead Replacement Issues
During printhead replacement, you may encounter certain issues. Here are some common problems and their potential solutions:
Printhead Not Recognized
Ensure the printhead is properly installed and making good contact with the seat. Check for any debris or obstructions.
Print Quality Issues
Run a printhead alignment or cleaning cycle to resolve any nozzle clogging or misalignment.
Printer Error Messages
Refer to the printer’s user manual or contact the manufacturer for specific troubleshooting steps related to the error message.
Visual Guide to Printhead Replacement
[Insert a flowchart or diagram illustrating the printhead replacement process step-by-step, with clear labels and arrows.]
Printhead Design
Printhead design plays a crucial role in determining the capabilities and performance of a printer. Several factors influence printhead design, including:
Nozzle Size
The diameter of the nozzle determines the size of the ink droplets produced. Smaller nozzles produce finer droplets, resulting in higher printing resolution.
Spacing
The distance between nozzles affects the density of printed dots and the overall image quality. Closer spacing allows for more precise printing.
Droplet Size
A printhead is a critical component of a printer responsible for transferring ink onto paper. It contains tiny nozzles that precisely eject ink droplets to create the desired image or text. If you’re interested in finding a location to print edible images near you, click here.
Returning to our discussion of printheads, they play a crucial role in ensuring high-quality prints and are often specific to the type of printer they are used in.
The size of the ink droplets influences the printing speed and resolution. Smaller droplets enable faster printing but may compromise resolution.
Printhead Technology
Advancements in printhead technology have significantly improved printing capabilities. Two widely used technologies are:
Piezoelectric
Piezoelectric printheads use electrical pulses to create pressure waves that eject ink droplets. They offer high precision and low noise but are relatively expensive and slow.
Thermal Inkjet
Thermal inkjet printheads heat ink to create bubbles that propel ink droplets. They are low-cost and fast but have lower precision and produce more noise.
Impact on Printing Capabilities
Printhead design directly affects printing resolution, speed, and cost:
Resolution
Smaller nozzle size and closer spacing contribute to higher printing resolution.
Speed
Larger nozzle size and fewer nozzles enable faster printing.
Cost
Piezoelectric printheads are generally more expensive than thermal inkjet printheads.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite advancements, printhead design faces ongoing challenges:
Clogging
Ink can clog nozzles, affecting print quality.
Durability
Printheads can degrade over time, requiring replacement.Future directions in printhead design include:
Improved Precision
Developing printheads with smaller nozzles and closer spacing for even higher printing resolution.
Enhanced Durability
Designing printheads with longer lifespans and resistance to clogging.
Multi-functionality
Integrating printheads with other printing technologies, such as 3D printing, to expand printing capabilities.
Printhead Manufacturing
The manufacturing of printheads involves a complex series of processes that require precision and quality control to ensure optimal performance.
The process typically begins with the fabrication of the printhead’s substrate, which is the base material on which the printhead’s components are mounted. The substrate is usually made of a durable material such as ceramic or silicon, and it is carefully designed to provide a stable and reliable foundation for the printhead’s components.
Quality Control
Throughout the manufacturing process, rigorous quality control measures are implemented to ensure that each printhead meets the required performance standards. These measures include:
- Dimensional inspection to verify the accuracy of the printhead’s physical dimensions.
- Electrical testing to ensure that the printhead’s electrical components are functioning properly.
- Functional testing to evaluate the printhead’s ability to produce high-quality prints.
Printhead Applications: What Is Printhead In Printer

Beyond traditional printing, printheads have found applications in various fields, enabling innovative technologies and solutions.
The versatility of printheads allows them to be integrated into diverse devices and systems, expanding their functionality and creating new possibilities.
Emerging Technologies
- 3D Printing:Printheads are used in 3D printers to deposit molten material layer by layer, creating three-dimensional objects.
- Textile Printing:Printheads are employed in digital textile printing machines to print intricate designs and patterns directly onto fabrics.
- Bioprinting:Printheads are utilized in bioprinting systems to create living tissue structures for medical research and regenerative medicine.
- Food Decoration:Printheads are integrated into food printers to decorate pastries, cakes, and other food items with edible inks.
- Electronic Circuit Fabrication:Printheads are used in the production of printed electronics, enabling the direct printing of conductive inks onto substrates.
Printhead Specifications

Printhead specifications vary depending on the type of printhead used. The key specifications include:
- Resolution:Measured in dots per inch (dpi), resolution determines the sharpness and detail of printed images.
- Speed:Measured in pages per minute (ppm), speed indicates the number of pages that can be printed per minute.
- Ink compatibility:Printheads are designed to work with specific types of ink, such as water-based, solvent-based, or UV-curable inks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Printhead Types
Different printhead types offer unique advantages and disadvantages:
- Thermal printheads:Low cost, high speed, but limited resolution.
- Piezoelectric printheads:High resolution, accurate ink placement, but slower and more expensive.
- Electrostatic printheads:High speed, low cost, but lower resolution and ink compatibility.
- Laser printheads:High speed, high resolution, but expensive and limited to black and white printing.
Printhead Comparison
Different printhead technologies offer unique advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these variations helps in selecting the optimal printhead for specific printing applications.
Technology Comparison
| Technology | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Inkjet | – High-quality prints
| – Limited durability
|
| Piezoelectric Inkjet | – Precise ink droplet control
| – Higher cost
|
| Laser | – High print speed
| – Expensive
|
| Solid Ink | – Vibrant colors
| – Slower printing speed
|
| Dye-Sublimation | – Exceptional color accuracy
| – Expensive
|
Printhead Optimization

Printhead optimization is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of a printer. By following specific techniques and addressing factors that impact printhead performance, users can maximize print quality and minimize downtime.
Factors Affecting Printhead Efficiency
Several factors influence printhead efficiency, including:
- Ink viscosity and type
- Printhead temperature
- Print speed and resolution
- Paper quality and type
- Environmental conditions
Optimization Techniques
To optimize printhead efficiency, consider the following techniques:
| Factor | Optimization Technique |
|---|---|
| Ink viscosity and type | Use high-quality inks specifically designed for the printer model and printhead technology. |
| Printhead temperature | Maintain an optimal printhead temperature according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. |
| Print speed and resolution | Adjust print settings to balance print speed and resolution to minimize printhead strain. |
| Paper quality and type | Use high-quality paper compatible with the printer and printhead technology to prevent nozzle clogging. |
| Environmental conditions | Control environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and dust to minimize printhead corrosion and clogging. |
Printhead Optimization Guide
- Identify the factors affecting printhead efficiency in your specific printing environment.
- Implement the optimization techniques mentioned above.
- Monitor print quality regularly and make adjustments as needed.
- Perform regular printhead maintenance, including cleaning and alignment.
Importance of Printhead Maintenance
Regular printhead maintenance is essential for optimal print quality and printhead longevity. Proper maintenance includes:
- Cleaning the printhead to remove ink buildup and clogs
- Aligning the printhead to ensure accurate ink placement
- Inspecting the printhead for damage or wear
Consequences of Neglecting Optimization and Maintenance
Neglecting printhead optimization and maintenance can lead to:
- Poor print quality
- Clogged nozzles and printhead failure
- Increased downtime and repair costs
Troubleshooting Common Printhead Issues
Common printhead issues and their solutions include:
- Clogged nozzles:Perform a printhead cleaning cycle or use a specialized cleaning solution.
- Misaligned printhead:Run a printhead alignment procedure from the printer’s control panel.
- Damaged printhead:Contact the printer manufacturer or a qualified technician for replacement.
Advancements in Printhead Technology, What is printhead in printer
Advancements in printhead technology include:
- High-density printheads:Enable higher print resolutions and finer detail.
- Variable droplet printheads:Produce prints with smoother gradients and transitions.
- 3D printheads:Used in additive manufacturing for creating three-dimensional objects.
Printhead Future Trends
The future of printhead technology holds exciting advancements that promise to revolutionize the printing industry. New materials, designs, and technologies are emerging, leading to enhanced print quality, increased productivity, and novel applications.
New Materials and Designs for Printheads
Advanced materials, such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, offer improved durability, conductivity, and precision. These materials enable the development of smaller, more efficient printheads with increased nozzle density.
Advancements in Drop-on-Demand and Continuous Inkjet Technologies
Drop-on-demand (DOD) technology is expected to witness advancements in nozzle design and ink droplet control, resulting in finer droplets and higher resolution prints. Continuous inkjet (CIJ) technology may incorporate new ink formulations and nozzle configurations for faster printing speeds and wider color gamuts.
Integration of Sensors and Electronics into Printheads
The integration of sensors and electronics into printheads will enhance print quality and productivity. Sensors can monitor ink levels, nozzle performance, and printhead temperature, enabling real-time adjustments and predictive maintenance. Embedded electronics can provide advanced image processing capabilities, color management, and data analytics.
Impact on the Printing Industry
These advancements will significantly impact the printing industry:
- Improved Print Quality and Resolution:New materials and technologies will lead to sharper, more vibrant, and detailed prints.
- Increased Productivity and Efficiency:Faster printing speeds, reduced maintenance, and predictive analytics will enhance overall productivity.
- New Applications and Markets:Novel printhead designs and capabilities will open up new markets and applications, such as flexible electronics, 3D printing, and personalized manufacturing.
Printhead Glossary

To facilitate a comprehensive understanding of printhead technology, it is essential to define the key terms and concepts associated with this critical component of printers.
This glossary provides a concise explanation of technical jargon, enabling readers to navigate the complexities of printhead technology with clarity and confidence.
Resolution
Resolution refers to the number of dots per inch (dpi) that a printhead can produce, directly influencing the sharpness and detail of printed images and text. Higher resolution printheads produce finer dots, resulting in higher quality prints.
Drop Size
Drop size denotes the volume of ink droplets ejected by the printhead. Smaller drop sizes enable precise placement of ink, leading to smoother gradients and more accurate color reproduction.
Nozzle
Nozzles are tiny orifices on the printhead through which ink is expelled. The size, shape, and number of nozzles impact the printhead’s resolution and drop size.
Firing Frequency
Firing frequency refers to the rate at which ink droplets are ejected from the printhead. Higher firing frequencies allow for faster printing speeds, but may compromise print quality.
Dot Gain
Dot gain is the phenomenon where ink droplets spread and enlarge on the paper surface, affecting the accuracy of printed colors and details. Printheads with precise drop placement and control minimize dot gain.
Pass
A pass refers to a single sweep of the printhead across the paper. Multiple passes are often required to achieve desired print quality and color depth.
Swath
Swath width refers to the area covered by the printhead in a single pass. Wider swaths enable faster printing speeds, while narrower swaths provide higher precision and detail.
Capping Station
The capping station is a component of the printhead that stores and maintains the printhead when not in use. It prevents ink from drying out and ensures proper printhead performance.
Printhead Resources
The following resources provide further information on printheads, including technical articles, user forums, and industry publications:
Technical Articles
User Forums
Industry Publications
FAQ Compilation
What is the primary function of a printhead?
The primary function of a printhead is to transfer digital data onto physical paper by precisely depositing ink droplets or toner particles onto the printing surface.
What are the different types of printheads?
The two main types of printheads are inkjet printheads and laser printheads. Inkjet printheads use liquid ink, while laser printheads use toner powder.
How do I maintain my printhead?
Regular cleaning and alignment are essential for maintaining optimal print quality. You should also avoid using low-quality ink or toner, as this can clog the printhead.
What are some common printhead problems?
Common printhead problems include clogged nozzles, misalignment, and fading colors. These problems can often be resolved by cleaning or replacing the printhead.


