What is pad printing – Pad printing, a versatile printing technique, has gained prominence in various industries due to its ability to print on complex shapes and curved surfaces. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of pad printing, exploring its intricacies, applications, and best practices, empowering you with a thorough understanding of this remarkable printing method.
Pad printing stands out as a unique and adaptable printing technique, capable of adorning a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, glass, and ceramics, with intricate designs and vibrant colors. Its applications span across diverse industries, from consumer electronics and automotive parts to medical devices and toys, making it a versatile solution for a multitude of printing needs.
Definition and Overview of Pad Printing
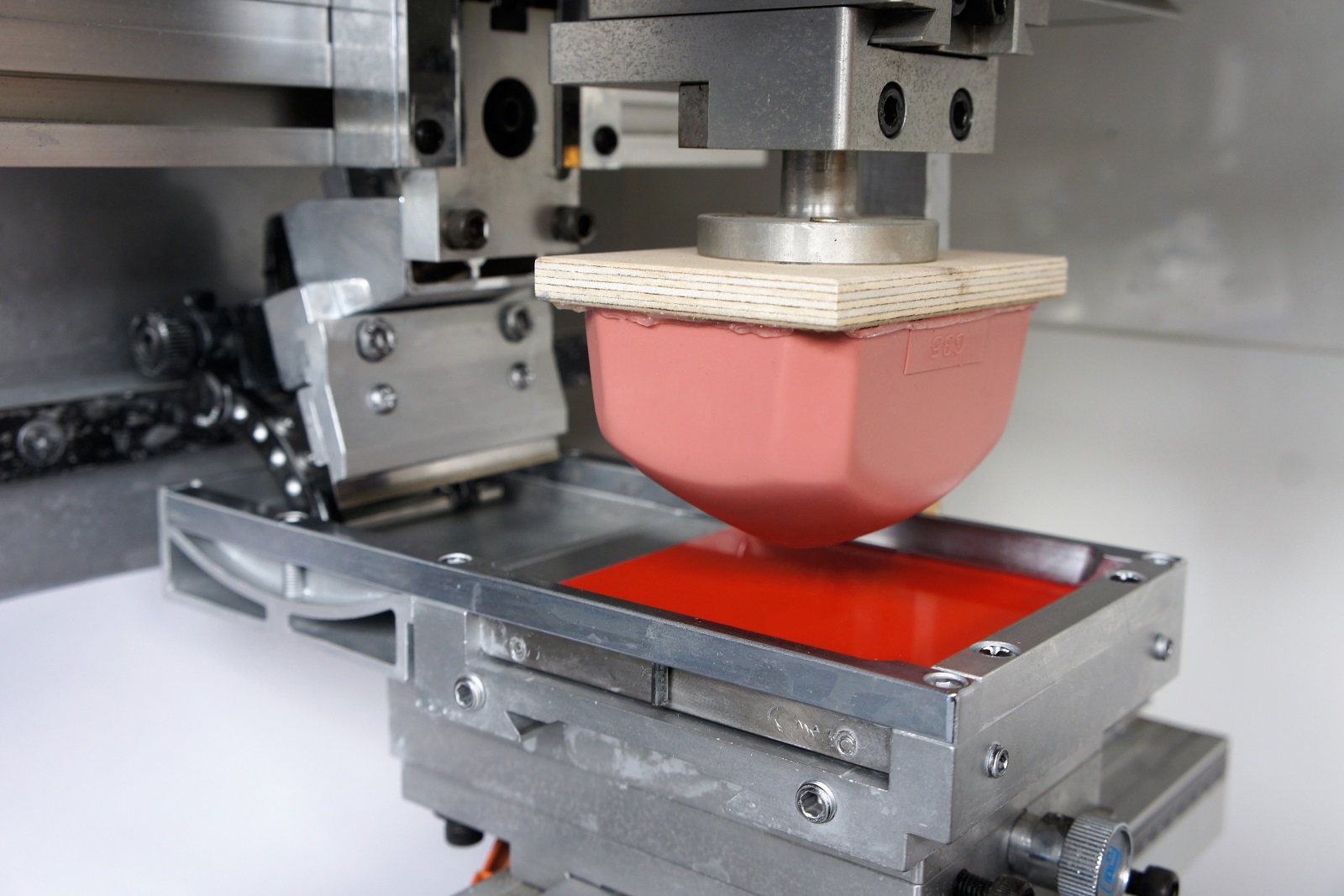
Pad printing, also known as tampography, is a printing technique that involves transferring a 2D image onto a 3D object. It uses a soft, silicone pad to pick up ink from an etched printing plate and then transfer it onto the substrate.
The basic components of a pad printing machine include the printing plate, ink cup, pad, and substrate holder. The printing plate is typically made of metal or ceramic and has the desired image etched into its surface. The ink cup holds the ink, and the pad is made of a soft, silicone material that conforms to the shape of the substrate.
Pad printing is a printing process that uses a silicone pad to transfer ink from an etched printing plate to a substrate. The silicone pad conforms to the shape of the substrate, allowing for printing on irregular surfaces. Is copy paper the same as printer paper ?
The answer is no. Copy paper is specifically designed for use in photocopiers, while printer paper is designed for use in inkjet and laser printers. Pad printing, on the other hand, is a versatile printing process that can be used on a wide variety of substrates, including metal, plastic, glass, and wood.
Pad printing is used in a wide variety of industries, including automotive, electronics, medical, and packaging. It is particularly well-suited for printing on curved or irregular surfaces, as well as on delicate or heat-sensitive materials.
Compared to other printing methods, pad printing offers several advantages. It is a relatively inexpensive process, and it can produce high-quality prints with fine detail. Pad printing is also versatile, and it can be used on a wide variety of materials.
Comparison with Other Printing Methods
- Screen printing:Screen printing is another common printing method that is used to create 2D images on 3D objects. However, screen printing is not as versatile as pad printing, and it is not as well-suited for printing on curved or irregular surfaces.
- Digital printing:Digital printing is a newer printing method that uses a computer to create a digital image that is then printed directly onto the substrate. Digital printing is more expensive than pad printing, but it can produce higher-quality prints with finer detail.
- Laser printing:Laser printing is a printing method that uses a laser to etch an image into a metal plate. The plate is then used to transfer the image onto the substrate. Laser printing is a high-quality printing method, but it is also more expensive than pad printing.
Applications of Pad Printing
Pad printing finds applications in diverse industries due to its versatility and ability to print on complex surfaces. Here are some examples:
- Automotive:Printing on dashboards, knobs, and dials for a variety of vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles.
- Electronics:Decorating keyboards, mice, and other electronic devices with intricate designs or logos.
- Medical:Printing on medical equipment, devices, and packaging, ensuring clarity and durability.
- Consumer products:Embellishing toys, sporting goods, and promotional items with colorful designs and graphics.
- Packaging:Printing on bottles, jars, and other packaging materials for branding and product identification.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pad Printing
Compared to other printing methods, pad printing offers several advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Versatility:Can print on a wide range of materials, including irregular or curved surfaces.
- Durability:Printed images are resistant to wear, abrasion, and chemicals.
- High-quality printing:Produces sharp and detailed images with precise color reproduction.
Disadvantages:
- Slower production speed:Compared to other methods like screen printing or digital printing.
- Limited printing area:The pad size limits the maximum printable area.
- Higher cost:Can be more expensive than other printing methods, especially for large-scale production.
Materials and Inks Used in Pad Printing

Pad printing is a versatile printing technique that can be used on a wide variety of materials. The most common materials used in pad printing include plastics, metals, glass, and ceramics.
The choice of materials for pad printing depends on a number of factors, including the desired print quality, the durability of the print, and the cost of the materials. Plastics are the most common material used in pad printing because they are relatively inexpensive, easy to print on, and durable.
Metals are also a popular choice for pad printing, as they provide a high-quality print that is resistant to wear and tear. However, metals are more expensive than plastics and can be more difficult to print on.
Pad printing is a printing process that uses a silicone pad to transfer ink from a metal plate to a substrate. This process is often used to print on irregular surfaces or on materials that are difficult to print on using other methods, such as polyester.
Can you screen print on polyester ? Yes, you can screen print on polyester, but it requires special inks and techniques. Pad printing is a versatile printing process that can be used to create high-quality prints on a variety of materials.
Glass and ceramics are less common materials for pad printing, but they can be used to create high-quality prints that are resistant to heat and chemicals.
Inks Used in Pad Printing, What is pad printing
The inks used in pad printing are typically solvent-based, water-based, UV-curable, or silicone-based.
- Solvent-based inksare the most common type of ink used in pad printing. They are relatively inexpensive and easy to use, but they can be harmful to the environment.
- Water-based inksare a more environmentally friendly option than solvent-based inks. They are also less expensive than solvent-based inks, but they can be more difficult to use.
- UV-curable inksare cured using ultraviolet light. They are more expensive than solvent-based and water-based inks, but they provide a high-quality print that is resistant to wear and tear.
- Silicone-based inksare used for printing on silicone substrates. They are resistant to heat and chemicals, but they can be more difficult to use than other types of inks.
The choice of ink for pad printing depends on a number of factors, including the desired print quality, the durability of the print, and the cost of the ink.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Materials and Inks
When selecting materials and inks for pad printing, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The desired print quality
- The durability of the print
- The cost of the materials and inks
- The environmental impact of the materials and inks
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the right materials and inks for your pad printing application.
Safety Precautions
When working with pad printing materials and inks, it is important to take the following safety precautions:
- Wear gloves and eye protection.
- Use a well-ventilated area.
- Avoid contact with skin and eyes.
- Dispose of materials and inks properly.
By following these safety precautions, you can help to protect yourself from the harmful effects of pad printing materials and inks.
– Equipment and Machinery

Pad printing utilizes a specialized set of equipment to achieve its unique printing capabilities. These components work together to transfer ink from an engraved printing plate to a variety of surfaces.
The primary equipment used in pad printing includes printing presses, ink cups, and pads. Each component plays a crucial role in the printing process, ensuring precise ink transfer and high-quality results.
Printing Presses
Printing presses are the heart of the pad printing system. They provide the mechanical force necessary to transfer ink from the printing plate to the pad and subsequently to the substrate. Presses come in various sizes and configurations, ranging from manual to fully automated models.
The main components of a printing press include:
- Printing plate holder: Secures the printing plate in place
- Ink cup holder: Supports the ink cup
- Pad holder: Holds the silicone pad
- Impression adjustment mechanism: Controls the pressure applied to the substrate
- Drive system: Powers the press and controls its speed and movement
Ink Cups
Ink cups hold the ink used in pad printing. They are typically made of metal or ceramic and are designed to minimize ink evaporation and contamination. Ink cups come in various sizes and shapes to accommodate different ink volumes and printing requirements.
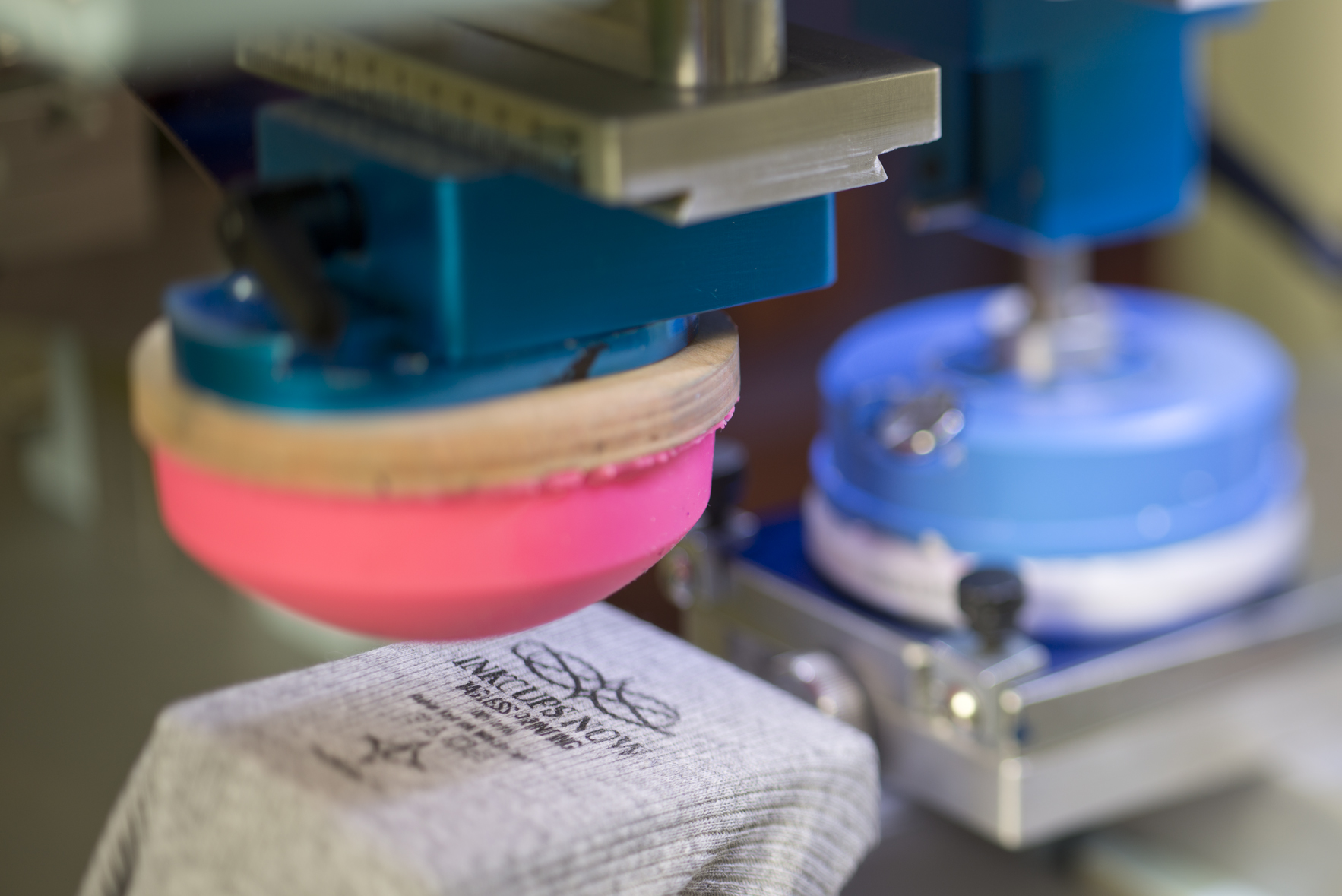
Pads
Pads are the key component that transfers ink from the printing plate to the substrate. They are made of soft, flexible silicone and are shaped to conform to the surface of the substrate being printed. Pads come in a range of sizes, shapes, and hardness levels to suit different printing applications.
Pre-Treatment and Post-Treatment Processes
Pre-treatment and post-treatment processes play crucial roles in ensuring the adhesion, durability, and quality of pad printed images. These processes involve preparing the substrate’s surface before printing and enhancing the printed image’s properties afterward.
Pre-treatment methods are employed to improve the surface’s receptivity to ink, while post-treatment techniques aim to protect and enhance the printed image’s longevity and resistance to environmental factors.
Surface Preparation
Prior to pad printing, the substrate’s surface must be properly prepared to ensure optimal ink adhesion and image quality. This involves removing contaminants, activating the surface, and enhancing its wettability.
- Surface Cleaning Techniques:Degreasing, solvent cleaning, and ultrasonic cleaning are commonly used to remove dirt, oils, and other contaminants from the substrate’s surface.
- Etching and Priming Methods:Etching involves using chemical or mechanical means to create a roughened surface, increasing the surface area for ink adhesion. Priming involves applying a thin layer of adhesive to the substrate, improving the ink’s bonding strength.
- Corona Treatment:This process utilizes high-voltage electrical discharge to modify the surface’s chemical composition, making it more receptive to ink.
Post-Treatment Techniques
After pad printing, post-treatment techniques are employed to enhance the printed image’s durability, resistance to wear and tear, and overall quality.
- Curing Methods:UV curing, heat curing, and infrared curing are commonly used to solidify and cross-link the printed ink, improving its adhesion and resistance to solvents and chemicals.
- Coating and Sealing Techniques:Applying a protective coating or sealant over the printed image can enhance its resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and environmental factors.
- Inspection and Quality Control Procedures:Thorough inspection and quality control measures are essential to ensure the printed images meet the desired specifications and standards.
Design and Artwork Preparation
Designing for pad printing requires attention to specific guidelines to ensure optimal results. The artwork preparation process involves creating a high-quality design and converting it into a format suitable for pad printing.
Artwork Preparation Process
- Create the design:Design software like Adobe Illustrator or CorelDRAW is used to create the artwork. Consider factors such as print size, color accuracy, and detail level.
- Choose the file format:Vector-based file formats like EPS, AI, or SVG are preferred as they maintain image quality when scaled.
- Set the resolution:High-resolution artwork (300-600 dpi) is necessary for sharp and detailed prints.
- Convert to bitmap:For printing, the vector artwork is converted to a bitmap image using specialized software.
- Optimize for pad printing:The artwork may need adjustments to account for the pad printing process, such as adjusting line weights or removing fine details.
Color Management
Color management is crucial in pad printing to ensure accurate reproduction of the desired colors in the final printed product. Slight variations in color can significantly impact the overall appearance and quality of the print. Therefore, it is essential to implement effective color management techniques throughout the pad printing process.One of the primary techniques used in color management for pad printing is color calibration.
This involves using specialized equipment to measure and adjust the color output of the printing machine to match the desired color standards. Color calibration ensures that the colors printed on the substrate accurately represent the intended design.Additionally, the use of color profiles is essential for color management in pad printing.
Color profiles are mathematical descriptions of the color characteristics of a specific printing system, including the ink, substrate, and printing machine. By incorporating color profiles into the printing process, the accuracy of color reproduction can be further enhanced.
Quality Control and Troubleshooting

Ensuring consistency and accuracy in pad printing is crucial for high-quality results. Quality control measures involve regular monitoring of print quality, equipment performance, and adherence to established standards. This includes visual inspections, dimensional measurements, and color matching to ensure that prints meet the desired specifications.
Troubleshooting common pad printing problems is essential for maintaining optimal production efficiency. Some common issues and their potential solutions include:
Troubleshooting Common Pad Printing Problems
- Blurred or smeared prints:This can be caused by excessive ink viscosity, improper pad hardness, or inadequate pre-treatment of the printing surface. Solutions include adjusting ink viscosity, selecting a pad with the appropriate hardness, and ensuring proper surface preparation.
- Incomplete or missing prints:This may be due to insufficient ink transfer, improper pad alignment, or substrate defects. Possible solutions include increasing ink flow, adjusting pad pressure and alignment, and inspecting the substrate for any imperfections.
- Color variations:Inconsistent color reproduction can result from variations in ink formulation, printing conditions, or substrate properties. To address this, ensure proper ink mixing, control printing parameters, and consider the compatibility of the ink with the substrate.
- Poor adhesion:Prints that peel or flake off indicate insufficient adhesion between the ink and the substrate. This can be remedied by optimizing pre-treatment processes, selecting the appropriate ink type, and ensuring proper curing conditions.
- Equipment malfunctions:Mechanical or electrical issues can lead to print quality problems. Regular maintenance, proper calibration, and prompt repairs are essential to minimize equipment-related downtime and ensure consistent printing results.
Safety and Environmental Considerations: What Is Pad Printing
Pad printing involves the use of chemicals and equipment that can pose potential hazards to health and the environment. Therefore, it is crucial to adhere to safety precautions and implement sustainable practices to minimize risks.
Proper ventilation is essential to prevent exposure to harmful fumes and solvents used in pad printing. Protective clothing, including gloves, aprons, and eye protection, should be worn to prevent contact with chemicals and inks. Additionally, proper handling and storage of chemicals are necessary to avoid spills, leaks, and fires.
Environmental Impact
Pad printing can have an environmental impact due to the use of solvents and inks. Solvents used in cleaning and degreasing processes can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution. Inks used in pad printing may contain hazardous substances that require proper disposal to prevent contamination of soil and water.
Sustainable Practices
To minimize the environmental impact of pad printing, sustainable practices can be implemented. Using water-based inks reduces VOC emissions and eliminates the need for solvents in cleaning processes. Recycling materials, such as ink cups and pads, helps conserve resources and reduce waste.
Additionally, proper disposal of waste materials, including inks, solvents, and contaminated rags, is essential to prevent environmental contamination.
| Safety Precautions | Environmental Considerations |
|---|---|
| Proper ventilation | Use of water-based inks |
| Protective clothing | Recycling of materials |
| Proper handling and storage of chemicals | Proper disposal of waste materials |
Safety Manual for Pad Printing Operators
This safety manual Artikels the safety precautions and emergency procedures for pad printing operators to ensure a safe working environment.
Safety Precautions
- Wear appropriate protective clothing, including gloves, aprons, and eye protection.
- Ensure proper ventilation to prevent exposure to harmful fumes and solvents.
- Handle and store chemicals properly to avoid spills, leaks, and fires.
- Follow all operating instructions for pad printing equipment.
- Keep work areas clean and free of clutter.
Emergency Procedures
- In case of a chemical spill, immediately contain the spill and notify a supervisor.
- In case of a fire, evacuate the area and call the fire department.
- In case of an injury, seek medical attention immediately.
Waste Management and Disposal
Proper waste management and disposal are essential to minimize the environmental impact of pad printing. Inks, solvents, and contaminated rags should be disposed of according to local regulations. Recycling programs should be implemented to conserve resources and reduce waste.
Trends and Innovations in Pad Printing

Pad printing is continuously evolving, with ongoing advancements in technology and materials. These innovations drive the expansion of pad printing applications and enhance its efficiency and versatility.
One significant trend is the integration of digital printing technologies with pad printing. This combination enables high-quality, full-color printing with precise control over ink deposition and curing. Digital pad printing systems offer greater flexibility in design and customization, opening up new possibilities for product decoration and branding.
Advancements in Ink and Curing Systems
Innovations in ink formulations and curing systems contribute to the improved performance and durability of pad printed products. Water-based inks, UV-curable inks, and solvent-based inks have been developed with enhanced adhesion, colorfastness, and resistance to wear and chemicals. Advanced curing technologies, such as LED and laser curing, provide faster curing times, reduced energy consumption, and improved environmental sustainability.
Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics play an increasingly important role in pad printing, improving efficiency and productivity. Automated pad printing machines can perform multiple printing cycles with precision and speed, reducing labor costs and minimizing errors. Robotic systems can be integrated into production lines for seamless integration with other manufacturing processes, enabling high-volume production and consistent quality.
Case Studies and Examples

Pad printing finds applications in various industries, showcasing its versatility and capabilities. Here are some real-world examples:
Medical Devices
- Printing precise markings and scales on medical instruments, such as syringes and surgical tools, for clear visibility and accuracy.
- Decorating and branding medical equipment, such as CPAP machines and infusion pumps, for enhanced aesthetics and recognition.
Consumer Products
- Applying logos and designs on electronic devices, such as smartphones and laptops, for branding and personalization.
- Printing intricate patterns on toys, sporting goods, and home appliances, adding aesthetic appeal and value.
Industrial Applications
- Marking and identifying automotive parts, such as engine components and dashboards, for traceability and quality control.
- Printing instructions and safety warnings on industrial machinery and equipment for clear communication and safe operation.
Glossary of Pad Printing Terms
The following is a glossary of key terms and definitions related to pad printing, providing a comprehensive understanding of the technical and industry-specific terminology used in the field.
Organized alphabetically, this glossary offers clear and concise explanations, ensuring easy comprehension of the concepts. Examples and illustrations are included to further clarify the terms and their applications in pad printing.
Technical Terms
- Anvil:A rigid surface on which the substrate is placed during printing, providing support and preventing deformation.
- Cliché:The printing plate used in pad printing, typically made of metal or photopolymer, containing the desired image or design.
- Doctor blade:A blade used to spread ink evenly across the cliché, ensuring a consistent ink transfer.
- Etching:A process used to create the desired design on the cliché by chemically removing material from the non-printing areas.
- Ink cup:A container that holds the printing ink and is attached to the printing machine.
- Pad:A soft, flexible material, typically made of silicone rubber, that transfers the ink from the cliché to the substrate.
- Pre-treatment:Processes applied to the substrate before printing to improve ink adhesion and print quality.
- Post-treatment:Processes applied to the printed substrate to enhance durability, resistance, or appearance.
- Printing cycle:The sequence of steps involved in pad printing, including cliché preparation, ink transfer, and substrate printing.
- Squeegee:A blade used to apply pressure to the pad, forcing the ink onto the substrate.
- Substrate:The material being printed on, such as plastic, metal, glass, or fabric.
Industry-Specific Terms
- CMYK:The four primary colors used in color printing (cyan, magenta, yellow, and black).
- Pantone Matching System (PMS):A standardized color matching system used in printing to ensure consistent color reproduction.
- Registration:The alignment of multiple colors or images on the substrate during printing.
- Screen printing:A printing technique that uses a mesh screen to transfer ink onto the substrate.
- Spot color:A single, specific color used in printing, as opposed to a mixture of colors.
- Transfer printing:A printing method that involves transferring an image or design from a carrier material to the substrate.
Table of Terms and Definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Anvil | A rigid surface on which the substrate is placed during printing. |
| Cliché | The printing plate used in pad printing, containing the desired image or design. |
| Doctor blade | A blade used to spread ink evenly across the cliché. |
| Etching | A process used to create the desired design on the cliché by chemically removing material. |
| Ink cup | A container that holds the printing ink. |
| Pad | A soft, flexible material that transfers the ink from the cliché to the substrate. |
| Pre-treatment | Processes applied to the substrate before printing to improve ink adhesion and print quality. |
| Post-treatment | Processes applied to the printed substrate to enhance durability, resistance, or appearance. |
| Printing cycle | The sequence of steps involved in pad printing, including cliché preparation, ink transfer, and substrate printing. |
| Squeegee | A blade used to apply pressure to the pad, forcing the ink onto the substrate. |
| Substrate | The material being printed on, such as plastic, metal, glass, or fabric. |
Resources and References
Explore additional resources and references to delve deeper into the world of pad printing. These include industry associations, online forums, and comprehensive technical articles that provide valuable insights into the techniques and applications of pad printing.
The following table provides a curated list of resources for your reference:
Industry Associations
- Pad Printing Associationhttps://www.padprinting.org The Pad Printing Association is a global industry association dedicated to advancing the art and science of pad printing. It provides a platform for professionals to connect, share knowledge, and promote the industry.
- European Pad Printing Associationhttps://www.europeanpadprinting.org The European Pad Printing Association represents the interests of pad printing companies and professionals across Europe. It fosters collaboration, promotes technical advancements, and organizes industry events.
Online Forums
- Pad Printing Forumhttps://www.padprintingforum.com The Pad Printing Forum is an active online community where pad printers from around the world connect to ask questions, share experiences, and discuss the latest industry trends.
- Pad Printing Hubhttps://www.padprintinghub.com The Pad Printing Hub provides a comprehensive online forum for pad printers to connect, access resources, and engage in discussions related to all aspects of pad printing.
Technical Articles
- “The Ultimate Guide to Pad Printing”https://www.padprintingguide.com This comprehensive technical article provides an in-depth overview of pad printing techniques, applications, and best practices. It covers everything from setup to troubleshooting, making it a valuable resource for both beginners and experienced pad printers.
- “Pad Printing: A Step-by-Step Guide”https://www.makeitfrom.com/pad-printing-a-step-by-step-guide This practical guide offers a step-by-step approach to pad printing, covering the entire process from design to production. It includes detailed instructions and helpful tips for achieving optimal results.
Popular Questions
What are the advantages of pad printing?
Pad printing offers several advantages, including the ability to print on complex shapes and curved surfaces, high precision and detail, durability, and versatility in terms of materials and inks.
What industries use pad printing?
Pad printing finds applications in a wide range of industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, toys, and promotional products.
What are the different types of pad printing inks?
Pad printing inks come in various types, including solvent-based, water-based, UV-curable, and silicone-based, each with its own characteristics and applications.


