What is grayscale printing – Grayscale printing, a captivating technique that transforms shades of gray into visual masterpieces, offers a unique blend of art and science. By exploring the intricacies of grayscale, we uncover its remarkable applications and the profound impact it has on various industries.
Grayscale printing encompasses a spectrum of gray tones, ranging from pure white to deep black, creating a captivating visual language that transcends color. This monochromatic realm empowers designers, artists, and printers to convey emotions, enhance readability, and create striking designs.
Grayscale Printing Definition

Grayscale printing is a printing technique that utilizes various shades of gray to create images and text on paper or other substrates. It differs from color printing, which employs a combination of primary colors (cyan, magenta, yellow, and black) to produce a wider range of colors.
Technical Definition
Technically, grayscale printing involves the use of a single channel, where each pixel is assigned a value representing its shade of gray. The range of shades extends from pure black (value 0) to pure white (value 255), with intermediate values corresponding to varying degrees of gray.
This monochromatic approach allows for the reproduction of continuous tones and subtle gradations, creating a sense of depth and realism in images.
Grayscale Color Spectrum
The grayscale color spectrum encompasses a range of shades of gray, extending from pure black to pure white. These shades are created by varying the intensity of light or the amount of black ink used.
Grayscale printing utilizes a single color, typically black or gray, to produce images with varying shades of lightness and darkness. By controlling the amount of ink deposited on the paper, different tones of gray are achieved, creating a grayscale image.
Representation of Grayscale Shades
In digital grayscale printing, shades of gray are represented using a numerical value known as the “grayscale value.” This value ranges from 0 to 255, where 0 represents pure black and 255 represents pure white. Intermediate values represent various shades of gray, with lower values indicating darker shades and higher values indicating lighter shades.
Applications of Grayscale Printing
Grayscale printing finds applications in various areas, including:
- Photography:Grayscale printing is commonly used in black-and-white photography to create images with a wide range of tonal variations.
- Printing:Grayscale printing is employed in various printing techniques, such as offset printing and digital printing, to produce monochrome images or as a base for color printing.
- Textile Printing:Grayscale printing is used in textile printing to create designs with varying shades of gray, often used in t-shirt designs and other fabric applications.
- Medical Imaging:Grayscale imaging is used in medical imaging techniques such as X-rays and ultrasound to visualize internal structures and diagnose medical conditions.
Grayscale Printing Techniques
Grayscale printing techniques are methods used to create the illusion of continuous tones using a limited number of colors, typically black and white. These techniques manipulate the arrangement and distribution of ink droplets or toner particles to simulate the appearance of smooth transitions in tone and shade.
Halftoning
Halftoning is a grayscale printing technique that involves breaking down an image into a series of tiny dots. The size and spacing of these dots vary to create the illusion of different shades of gray. When viewed from a distance, the human eye blends these dots together, creating the perception of continuous tones.
Grayscale printing, a technique that employs shades of gray to create images, offers cost-effective printing solutions. When seeking printers with budget-friendly ink cartridges, discover the printers that boast the cheapest ink cartridges. By considering grayscale printing capabilities, you can potentially reduce ink consumption and save on printing expenses, making it a practical choice for various printing needs.
Dithering
Dithering is another grayscale printing technique that uses a pattern of small dots or lines to create the illusion of continuous tones. Unlike halftoning, dithering does not rely on the human eye’s ability to blend dots. Instead, it uses the varying densities of the dots or lines to create the perception of different shades of gray.
Error Diffusion
Error diffusion is a grayscale printing technique that involves distributing the error from one pixel to its neighboring pixels. This process creates a smooth transition in tone and shade, as the error is gradually diffused throughout the image. Error diffusion can produce high-quality grayscale prints with a wide range of tones.
Grayscale Printing Applications
Grayscale printing, utilizing shades of gray to create images and text, finds widespread applications across various industries. Its versatility and cost-effectiveness make it a popular choice for a range of printing needs.
Newspapers and Books
Grayscale printing is extensively used in the production of newspapers and books. Its ability to reproduce text and images with clarity and detail, even on low-quality paper, makes it suitable for mass printing. The use of grayscale also helps reduce printing costs compared to color printing.
Packaging
Grayscale printing plays a significant role in the packaging industry. It is commonly employed for printing on cardboard boxes, labels, and wrappers. The ability to create high-contrast images and text in grayscale ensures that essential information, such as product descriptions and branding, is easily readable and visually appealing.
Industries Reliant on Grayscale Printing
Several industries heavily rely on grayscale printing for their operations:
- Publishing:Newspapers, magazines, and books utilize grayscale printing for cost-effective and high-quality reproduction of text and images.
- Packaging:Grayscale printing is essential for creating visually appealing and informative packaging designs.
- Medical Imaging:Medical imaging equipment, such as X-ray and ultrasound machines, produces grayscale images for diagnostic purposes.
- Security:Grayscale printing is used for printing security documents, such as passports and banknotes, where high-contrast and detailed images are crucial for authentication.
- Art and Photography:Grayscale printing is widely used in the art and photography industry for creating black-and-white prints, fine art reproductions, and photorealistic images.
Future of Grayscale Printing
Grayscale printing continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and changing market demands. Innovations in printing technology, such as high-resolution grayscale printers and improved ink formulations, are enhancing the quality and precision of grayscale printing.
In the future, grayscale printing is expected to play an increasingly important role in industries such as packaging, where the demand for sustainable and cost-effective printing solutions is growing. It is also likely to find new applications in areas such as medical imaging and digital art.
Grayscale Printing and Digital Imaging

Grayscale printing plays a crucial role in digital imaging and photography. It involves representing images using varying shades of gray, from pure white to pure black, to create a continuous tonal range without using colors.
Capture of Grayscale Images
Grayscale images are captured using digital cameras or scanners that convert the continuous tones of light into a digital grayscale representation. The camera’s sensor or scanner’s light-sensitive elements measure the intensity of light at each pixel, assigning a grayscale value to represent the brightness level.
Processing of Grayscale Images
After capture, grayscale images are processed to adjust brightness, contrast, and other parameters. Image editing software allows for various grayscale manipulations, such as tonal adjustments, noise reduction, and sharpening.
Reproduction of Grayscale Images
Grayscale images are reproduced using grayscale printers or digital displays. The printer or display interprets the grayscale values and produces a corresponding intensity of ink or light, creating a continuous range of tones.
Applications of Grayscale Digital Imaging
- Medical imaging: X-rays, MRI scans, and ultrasound images use grayscale to visualize internal structures.
- Black-and-white photography: Grayscale printing allows for the creation of high-quality black-and-white photographs with subtle tonal variations.
- Document reproduction: Grayscale printing is commonly used for copying and scanning documents, preserving the original’s tonal range.
Importance of Grayscale Printing and Digital Imaging
Grayscale printing and digital imaging have revolutionized the way we capture, process, and reproduce images. They enable the creation of high-quality black-and-white images, facilitate medical diagnostics, and enhance the preservation of historical documents.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Continuous tonal range | Limited color representation |
| Cost-effective compared to color printing | Less visually appealing than color images |
| Suitable for specific applications, such as medical imaging | Not suitable for reproducing full-color images |
Flowchart: Process of Capturing, Processing, and Reproducing Grayscale Images
- Capture: Camera or scanner measures light intensity and assigns grayscale values.
- Processing: Image editing software adjusts brightness, contrast, and other parameters.
- Reproduction: Grayscale printer or display interprets grayscale values and produces corresponding ink or light intensity.
Code Snippets
Python:
“`pythonimport cv2# Load a grayscale imageimage = cv2.imread(‘grayscale.jpg’, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)# Adjust brightness and contrastimage = cv2.addWeighted(image, 1.2, None, 0, 20)# Save the modified imagecv2.imwrite(‘modified_grayscale.jpg’, image)“`
Glossary of Terms
- Grayscale:A continuous range of shades from white to black.
- Digital imaging:The process of capturing, storing, and processing digital images.
- Tonal range:The range of brightness levels in an image.
- Image editing software:Software used to manipulate and enhance digital images.
- Grayscale printer:A printer that reproduces images using varying shades of gray.
Grayscale Printing and Graphic Design

Grayscale printing is a powerful tool in graphic design, allowing for the creation of sophisticated and visually appealing designs. By using a range of shades from black to white, designers can create subtle nuances, depth, and texture that enhance readability, evoke emotions, and convey messages effectively.
Readability and Visual Interest
Grayscale printing enhances readability by providing contrast between text and background. Light gray text on a dark gray background, for example, is easier to read than black text on a white background, reducing eye strain and improving comprehension. Grayscale also creates visual interest by breaking up large blocks of text, guiding the reader’s eye through the design, and highlighting important information.
Emotional Impact
Different shades of gray can convey a range of emotions. Darker shades create a sense of seriousness, mystery, or sophistication, while lighter shades evoke feelings of lightness, airiness, or tranquility. Designers can use grayscale to set the mood of a design, create a specific atmosphere, or evoke a desired response from the viewer.
Examples of Grayscale Designs
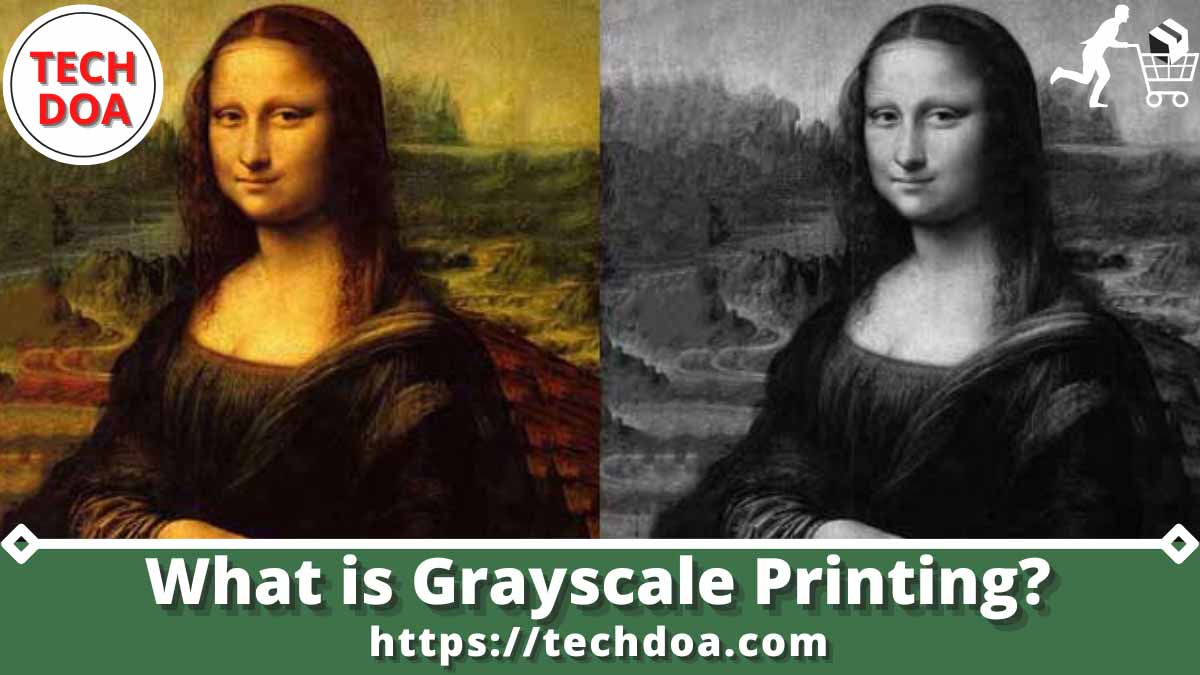
Grayscale printing has been used in iconic designs throughout history. The Mona Lisa, for example, is known for its subtle grayscale shading, which creates a sense of depth and realism. Modern designers also use grayscale to create stunning effects, such as the grayscale photography of Ansel Adams, which captures the beauty of the natural world in shades of gray.
Technical Considerations
Grayscale printing requires careful consideration of ink selection, paper quality, and printing techniques. The choice of ink affects the range of shades and the overall contrast of the design. Paper quality influences the absorption and reflection of light, affecting the appearance of the grayscale image.
Printing techniques, such as offset lithography or digital printing, determine the precision and consistency of the grayscale reproduction.
Combining Grayscale with Other Techniques
Grayscale printing can be combined with other printing techniques to create visually striking effects. Spot colors, for example, can be added to grayscale designs to create pops of color and highlight specific elements. Metallic inks can add a touch of elegance and sophistication, enhancing the overall impact of the design.
Benefits of Grayscale in Graphic Design
Using grayscale in graphic design offers several benefits. It allows for the creation of sophisticated and visually appealing designs that enhance readability, create visual interest, and convey emotions effectively. Grayscale printing is versatile, allowing for combination with other techniques to create unique and memorable designs.
Furthermore, it is a cost-effective option that can be used to produce high-quality prints with a wide range of shades and tones.
Grayscale Printing and Art
Grayscale printing finds artistic expression in various mediums, notably photography, painting, and beyond. Its ability to convey emotions, create atmospheres, and evoke symbolism makes it a powerful tool for artistic expression.
Photography
In photography, grayscale captures the essence of light and shadow, revealing details and textures often obscured in color images. Black-and-white photography has a long and rich history, from the iconic works of Ansel Adams to the evocative street photography of Henri Cartier-Bresson.
Grayscale allows photographers to focus on composition, form, and emotion, evoking a sense of nostalgia, mystery, or surrealism.
Painting
Grayscale painting, also known as monochrome or grisaille, has been used for centuries to create stunning works of art. Artists like Rembrandt and Caravaggio employed grayscale to achieve dramatic chiaroscuro effects, enhancing the illusion of depth and form. In contemporary painting, grayscale continues to be a popular choice for its ability to convey subtle nuances of tone and mood.
Other Mediums
Grayscale printing extends beyond photography and painting. It finds application in printmaking, graphic design, and even digital art. Artists use grayscale to create intricate textures, patterns, and illusions that would be difficult to achieve with color. In graphic design, grayscale is often used to create a sense of sophistication and elegance.
– Grayscale Printing and Technology
Grayscale printing has undergone significant advancements due to technological innovations. Digital printing, inkjet technology, and laser printing have revolutionized the capabilities of grayscale printing.
– Digital Printing
Digital printing involves creating a digital image that is directly transferred to a printing surface. This technology has improved grayscale printing by providing:
- Precise control over ink droplets, resulting in smoother transitions and finer details.
- Variable data printing, allowing for customization and personalization of printed materials.
- Increased speed and efficiency, making it suitable for high-volume printing.
– Inkjet Technology
Inkjet technology uses tiny droplets of ink to create images. It has impacted grayscale printing by:
- Producing high-quality grayscale prints with sharp edges and smooth gradients.
- Enabling printing on various substrates, including paper, canvas, and fabric.
- Offering a wide color gamut, allowing for more accurate and realistic grayscale reproduction.
– Laser Printing
Laser printing uses a laser to create an electrostatic image on a photosensitive drum. This technology has influenced grayscale printing by:
- Providing fast and efficient printing, suitable for large print runs.
- Producing high-resolution grayscale prints with precise dot placement.
- Reducing operating costs compared to other printing methods.
– Future Trends and Innovations
Grayscale printing technology continues to evolve, with emerging trends and innovations including:
- Development of new inks and substrates to enhance print quality and durability.
- Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize printing processes and improve color accuracy.
- Advancements in 3D printing, enabling the creation of grayscale objects with complex geometries.
Grayscale Printing and Environmental Considerations
Grayscale printing, employing a single color in varying shades, presents unique environmental considerations compared to color printing. Understanding these differences is crucial for sustainable printing practices.
Grayscale printing generally consumes less ink and energy than color printing, reducing waste and greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, grayscale printing allows for the use of eco-friendly materials such as soy-based inks and recycled paper.
Eco-Friendly Materials, What is grayscale printing
Soy-based inks, derived from renewable resources, offer a more environmentally friendly alternative to petroleum-based inks. They are biodegradable, reduce air pollution, and minimize the impact on ecosystems.
Recycled paper, produced from post-consumer waste, conserves natural resources, reduces landfill waste, and lowers energy consumption compared to virgin paper production.
Sustainable Practices
To promote sustainable grayscale printing, consider the following recommendations:
- Use soy-based inks and recycled paper whenever possible.
- Optimize print settings to minimize ink and energy consumption.
- Consider using digital printing technologies that reduce waste and emissions.
- Implement a waste management system to properly dispose of printing materials.
Grayscale Printing and Color Theory: What Is Grayscale Printing
Grayscale printing, despite its monochromatic nature, plays a significant role in color theory by manipulating shades of gray to create visual harmony and contrast. Grayscale can be effectively employed to evoke specific emotions, set the tone of an image, and guide the viewer’s attention.
Grayscale Color Schemes
- Monochromatic:Comprises different shades of a single color, from pure black to pure white, creating a harmonious and sophisticated look.
- Analogous:Utilizes colors adjacent to each other on the color wheel, producing a cohesive and visually pleasing effect.
- Complementary:Employs colors opposite each other on the color wheel, generating a high level of contrast and visual impact.
Applications of Grayscale Color Schemes
Grayscale color schemes find application in various design fields, including:
- Photography:Black-and-white photography captures the essence of a scene by emphasizing textures, shapes, and light.
- Graphic Design:Grayscale printing is used in logos, typography, and illustrations to create a timeless and elegant aesthetic.
- Art:Grayscale drawings and paintings explore the nuances of light and shadow, conveying depth and emotion.
– Elaborate on the importance of grayscale printing for accessibility and inclusivity.
Grayscale printing plays a crucial role in enhancing accessibility and inclusivity in the realm of design and printing. It offers a valuable solution for individuals with visual impairments, enabling them to access and engage with printed materials more effectively.
By converting color images and text into shades of gray, grayscale printing eliminates the potential barriers posed by color vision deficiencies, such as color blindness. Additionally, it improves readability for individuals with low vision, as the absence of distracting colors allows for better focus and clarity.
Grayscale and Dyslexia
For individuals with dyslexia, grayscale printing can alleviate the challenges associated with reading. The reduced visual complexity of grayscale documents minimizes distractions and visual noise, creating a more legible and coherent reading experience.
Guidelines for Accessible Grayscale Documents
To ensure the accessibility of grayscale documents and designs, it is essential to adhere to specific guidelines:
- Color Conversion Techniques:Utilize color conversion tools that accurately translate colors into grayscale shades, preserving the contrast and clarity of the original.
- Contrast Ratios:Maintain sufficient contrast ratios between text and background colors to enhance readability, especially for individuals with low vision.
- Font Size and Spacing:Choose legible font sizes and ensure adequate spacing between lines and characters to reduce visual clutter and improve readability.
Examples of Accessible Grayscale Designs
Numerous examples demonstrate the effectiveness of grayscale printing in enhancing accessibility. From grayscale textbooks for students with visual impairments to accessible signage in public spaces, grayscale designs have proven their ability to cater to diverse user needs.
Table: Benefits and Best Practices of Grayscale Printing for Accessibility
| Benefits | Best Practices |
|---|---|
| Improved readability for individuals with color blindness | Accurate color conversion techniques |
| Enhanced clarity for individuals with low vision | Sufficient contrast ratios |
| Reduced distractions for individuals with dyslexia | Minimal visual complexity |
| Legible font sizes and spacing | Clear and coherent reading experience |
“Accessibility in design and printing is not merely a matter of compliance but a fundamental ethical obligation. By embracing grayscale printing and adhering to accessibility guidelines, we can create inclusive environments that empower individuals with visual impairments to fully participate in society.”
Checklist for Ensuring the Accessibility of Grayscale Documents and Designs
- Convert colors accurately to grayscale shades.
- Maintain a contrast ratio of at least 4.5:1 between text and background.
- Use legible font sizes (minimum 12pt) and ensure adequate spacing.
- Avoid using distracting colors or patterns.
- Test the document or design with individuals with visual impairments to gather feedback.
Grayscale Printing and Historical Significance
Grayscale printing has a rich and diverse history, spanning from the early days of woodcuts to the modern era of digital printing. Throughout this journey, it has played a pivotal role in the development of visual arts, photography, and other visual media.
One of the earliest forms of grayscale printing can be traced back to woodcuts, where artists used chisels to carve images into wooden blocks. These blocks were then inked and pressed onto paper, creating grayscale prints with bold lines and high contrast.
Woodcuts were widely used for centuries, particularly in the production of books and religious imagery.
The Invention of the Halftone Screen
A significant milestone in grayscale printing was the invention of the halftone screen in the 19th century. This technique involved breaking down continuous-tone images into a series of dots of varying sizes. When viewed from a distance, these dots create the illusion of grayscale tones, allowing for more detailed and nuanced prints.
Digital Imaging and Grayscale Printing
The advent of digital imaging in the late 20th century revolutionized grayscale printing. Digital cameras and scanners captured images as electronic signals, which could be processed and printed using digital printing technologies. This enabled the creation of high-quality grayscale prints with precise control over tone and contrast.
Grayscale Printing in Photography and Cinema
Grayscale printing played a crucial role in the development of photography. Early photographs were produced in grayscale, capturing the subtleties of light and shadow in a way that color photography could not. Grayscale photography became a popular art form, and it continues to be used by photographers today.
In cinema, grayscale films were commonly used in the early days of the medium. These films created a distinct and evocative atmosphere, often used to convey a sense of nostalgia or drama. Grayscale films continue to be produced today, often as a stylistic choice or for artistic effect.
Current State of Grayscale Printing Technology
Today, grayscale printing technology continues to advance, with new techniques and applications emerging. High-resolution digital printing presses produce stunning grayscale prints with exceptional detail and color accuracy. Grayscale printing is also used in various fields, including graphic design, fine art, and industrial printing.
– Include historical examples of grayscale printing techniques and their cultural significance.

Grayscale printing has a rich history dating back centuries, with various techniques and cultural influences shaping its development. One notable example is the use of chiaroscuro in Renaissance art, where artists employed contrasting light and dark shades to create depth and realism in their paintings.
In East Asia, grayscale printing flourished during the Edo period in Japan, where ukiyo-e prints showcased intricate grayscale compositions depicting scenes from everyday life and folklore. These prints gained immense popularity and influenced Western art movements such as Impressionism.
Woodblock printing
Woodblock printing, a technique originating in China during the Tang dynasty, played a significant role in the development of grayscale printing. Artists carved designs onto wooden blocks, which were then inked and pressed onto paper. This technique allowed for the mass production of grayscale images, contributing to the spread of knowledge and cultural exchange.
Grayscale printing utilizes shades of gray to produce images, providing a cost-effective alternative to color printing. If you encounter connectivity issues with your Canon printer, consider following a comprehensive guide like how do i get my canon printer back online for troubleshooting and re-establishing connectivity.
Once your printer is operational, you can continue exploring the capabilities of grayscale printing, which offers a wide range of applications in art, photography, and document reproduction.
Grayscale Printing and Education
Grayscale printing has found significant applications in the educational sector, particularly in the production of textbooks and visual aids. The use of grayscale offers several advantages that enhance comprehension and engagement among learners.
Benefits of Grayscale in Education
Grayscale printing reduces visual clutter and distractions, allowing learners to focus on the essential information presented in textbooks and visual aids. The absence of color helps eliminate unnecessary visual stimuli, enabling students to concentrate better on the content and comprehend the concepts more effectively.Additionally, grayscale printing can improve accessibility for learners with visual impairments or color blindness.
By removing color variations, grayscale materials can make it easier for these individuals to distinguish between different elements and understand the information presented.
Examples of Effective Grayscale Educational Materials
One notable example of effective grayscale educational materials is the textbook “Understanding Physics” by Isaac Asimov. This book uses grayscale illustrations and diagrams to explain complex scientific concepts in a clear and concise manner. The absence of color allows students to focus on the underlying principles and relationships without being distracted by unnecessary visual details.Another example is the use of grayscale in educational videos and presentations.
By eliminating color variations, educators can create more engaging and accessible visual aids that cater to a wider range of learners. Grayscale videos and presentations can help students with visual impairments better understand the concepts being taught and improve their overall learning experience.
Grayscale Printing and Marketing
Grayscale printing plays a significant role in marketing and advertising, offering a sophisticated and professional aesthetic that can enhance brand perception. By utilizing shades of gray, grayscale printing creates a timeless and elegant look that appeals to a wide audience.
The cost-effectiveness of grayscale printing compared to color printing makes it an attractive option for businesses seeking to optimize their marketing budget. Additionally, grayscale printing has environmental benefits, as it requires less ink and energy than color printing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Grayscale Printing
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Sophisticated and professional appearance | Limited color range |
| Cost-effective | May not be suitable for all types of products or services |
| Environmentally friendly | Can appear less vibrant than color printing |
Guidelines for Using Grayscale Effectively in Marketing Materials
- Choose high-quality grayscale images with good contrast and detail.
- Use grayscale to create a sense of nostalgia or timelessness.
- Combine grayscale with spot colors for a unique and eye-catching effect.
- Experiment with different grayscale gradients to create depth and texture.
Key Questions Answered
What are the advantages of grayscale printing?
Grayscale printing offers several advantages, including enhanced readability, cost-effectiveness, environmental friendliness, and the ability to convey emotions and create visual interest.
How is grayscale printing used in graphic design?
In graphic design, grayscale printing is employed to create visual harmony, enhance readability, convey emotions, and achieve a sophisticated and professional aesthetic.
What is the role of grayscale printing in photography?
Grayscale printing plays a crucial role in photography, allowing photographers to capture and reproduce images with subtle tonal variations, evoking mood, atmosphere, and symbolism.


