What is flexographic printing – Flexographic printing, a captivating technique in the realm of printing, unveils its unique charm in this comprehensive exploration. Join us as we delve into its intricacies, unraveling the essence of this versatile and widely applicable method.
Flexographic printing, with its origins in the early 20th century, has evolved into a cornerstone of modern printing, gracing a vast array of products that touch our daily lives. Its versatility stems from its ability to print on a wide range of substrates, from flexible packaging to durable labels, making it an indispensable tool for industries worldwide.
Definition of Flexographic Printing
Flexographic printing, also known as flexo printing, is a printing technique that utilizes flexible relief plates to transfer ink onto a variety of substrates. Unlike offset printing, which employs a metal plate, flexographic printing uses a flexible polymer plate that conforms to the contours of the printing surface.
Flexographic printing is characterized by its high-quality printing capabilities, ability to print on various substrates, and cost-effectiveness for large print runs. The inks used in flexographic printing are typically water-based, solvent-based, or UV-curable, providing a wide range of options for different applications.
Plate Preparation and Printing Techniques
The plate preparation process involves creating a digital or photopolymer plate with the desired image or text. The plate is then mounted on a printing cylinder and inked. The printing process begins with the transfer of ink from the ink fountain to the plate cylinder.
The inked plate then comes into contact with the substrate, transferring the ink onto its surface.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages:
- High-quality printing
- Ability to print on various substrates
- Cost-effective for large print runs
- Fast printing speeds
- Environmentally friendly inks available
- Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for small print runs
- Requires skilled operators
- Can be susceptible to plate damage
- May require multiple passes for opaque colors
Printing Process
Flexographic printing is a relief printing technique that uses flexible printing plates to transfer ink to a substrate. The printing process involves several key steps, including prepress operations, plate preparation, ink selection, and substrate selection.
Prepress Operations
Prepress operations are essential for ensuring the accuracy and quality of the final printed product. These operations include creating the digital design, preparing the printing plates, and selecting the appropriate inks and substrates.
Plate Preparation
The printing plates used in flexographic printing are typically made of photopolymer, which is a light-sensitive material. The digital design is transferred to the printing plate using a laser engraving process, which creates raised and recessed areas on the plate.
The raised areas will transfer ink to the substrate, while the recessed areas will not.
Ink Selection
The choice of ink is critical in flexographic printing. The ink must be compatible with the substrate and the printing process. Inks are available in a variety of colors and finishes, and the appropriate ink will depend on the desired results.
Substrate Selection
The substrate is the material that the ink is printed on. Substrates can vary widely in terms of their composition, thickness, and surface texture. The appropriate substrate will depend on the intended use of the printed product.
Printing Process
The printing process itself involves several steps. First, the printing plate is mounted on a printing cylinder. The ink is then applied to the printing plate, and the substrate is fed through the printing press. The printing cylinder transfers the ink from the printing plate to the substrate, creating the printed image.
Quality Control
Quality control is essential in flexographic printing to ensure that the printed product meets the desired standards. Quality control measures include inspecting the printing plates, inks, and substrates before printing, as well as monitoring the printing process itself. If any defects are detected, the printing process can be adjusted to correct the problem.
Post-Press Operations
Once the printing process is complete, the printed product may undergo a variety of post-press operations. These operations can include cutting, folding, binding, and laminating. Post-press operations can enhance the appearance and durability of the printed product.
Plate Making
Flexographic printing plates are the heart of the flexographic printing process, transferring the desired image to the substrate. Several techniques are employed to create these plates, including laser engraving, thermal imaging, and water wash.
Laser Engraving
Laser engraving utilizes a laser beam to etch the image onto the plate material. This method offers high precision and resolution, enabling the production of fine details and complex designs. However, it can be time-consuming and expensive, especially for large-scale production.
Thermal Imaging
Thermal imaging involves exposing a photosensitive plate to ultraviolet light through a film positive. The exposed areas harden, while the unexposed areas remain soft and can be washed away. This method is relatively fast and cost-effective, making it suitable for medium- to large-scale production.
Water Wash
Water wash is a variation of thermal imaging where a water-based solution is used to wash away the unexposed areas of the plate. This method produces plates with a high level of detail and is particularly suited for printing on absorbent substrates.
Plate Materials
The choice of plate material significantly impacts the quality and durability of the printing plates. Common materials include:
Rubber
Natural or synthetic rubber plates offer flexibility and conformability, making them ideal for printing on uneven surfaces.
Photopolymer
Photopolymer plates are highly durable and resistant to wear, suitable for high-volume printing applications.
Metal
Metal plates, such as copper or steel, provide exceptional durability and image quality but are more expensive and require specialized equipment.
Factors Affecting Plate Quality
Several factors influence the quality of flexographic printing plates, including:
Plate Thickness
Plate thickness determines the amount of ink transferred to the substrate, affecting print density and opacity.
Resolution
Resolution refers to the number of dots per inch (dpi) on the plate, which influences the sharpness and detail of the printed image.
Surface Roughness
Surface roughness affects the ink transfer efficiency and can impact the overall print quality.
Plate Making Process, What is flexographic printing
The plate making process typically involves the following steps:
1. Image Preparation
The desired image is converted into a digital format and edited to meet the specific requirements of the printing process.
2. Plate Creation
The chosen plate making technique is used to create the printing plate based on the prepared image.
Flexographic printing is a versatile printing process that uses flexible printing plates to transfer ink to a wide range of substrates. It is commonly used for packaging, labels, and other high-volume printing applications. To connect a Canon printer to a Mac computer, follow these steps: how to connect to a canon printer on a mac.
Flexographic printing offers advantages such as high print quality, fast production speeds, and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for various industries.
3. Plate Mounting
The plate is mounted onto the printing cylinder or press, ensuring proper alignment and tension.
4. Plate Conditioning
Flexographic printing, a process using flexible relief plates to transfer ink onto non-porous surfaces, is commonly used for packaging and labeling. If you encounter printing issues with your Epson printer, consider checking for common problems such as why is my epson printer not printing.
Flexographic printing’s versatility extends to various substrates, making it suitable for applications where durability and high-speed printing are essential.
The plate is conditioned to optimize its performance and ensure consistent print quality throughout the print run.
Inks and Substrates

Flexographic printing utilizes various ink types to cater to different substrate requirements. These inks are specially formulated to adhere to the specific properties of the substrate being printed on.
Ink Types
- Solvent-based Inks:These inks are characterized by their fast drying time and excellent adhesion to non-porous substrates such as plastic, metal, and glass.
- Water-based Inks:Environmentally friendly and cost-effective, water-based inks are suitable for printing on absorbent substrates like paper and cardboard.
- UV-curable Inks:UV-curable inks undergo rapid curing under ultraviolet light, resulting in high-quality prints with excellent durability.
- Electron Beam Inks:These inks cure through exposure to an electron beam, providing high-speed printing and excellent adhesion to various substrates.
Substrate Compatibility
The compatibility of inks with substrates is crucial for successful flexographic printing. The ink’s properties, such as viscosity, surface tension, and drying time, must be compatible with the substrate’s surface characteristics and porosity. Proper ink-substrate compatibility ensures optimal ink transfer, adhesion, and print quality.
Printing Machines
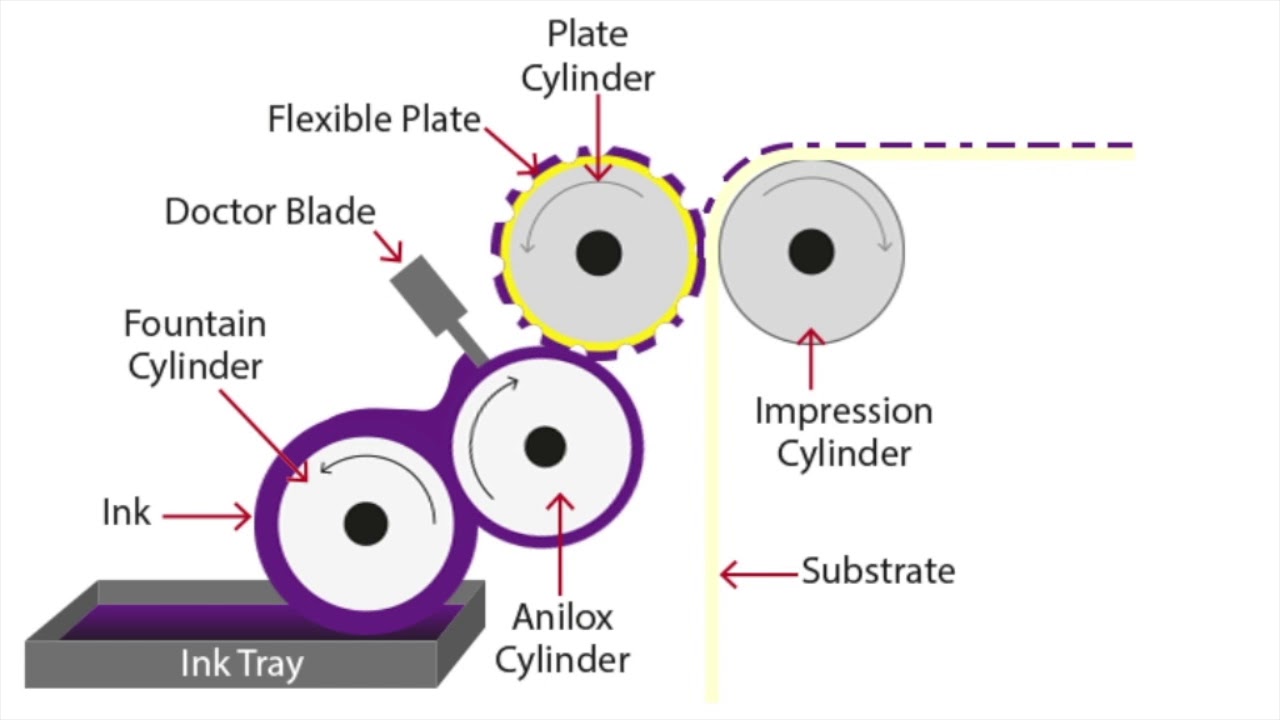
Flexographic printing machines are available in various types, each with its own capabilities and limitations. The main types of flexographic printing machines include:
- Central impression
- Stack-type
- In-line
- Common impression
Central Impression
Central impression printing machines are characterized by a central impression cylinder that supports the substrate. The printing plates are mounted on individual plate cylinders, which rotate around the impression cylinder. Central impression machines offer high print quality and are suitable for printing on a wide range of substrates.
However, they can be more expensive and complex to operate than other types of flexographic printing machines.
Stack-type
Stack-type printing machines have multiple printing units stacked vertically. The substrate passes through each printing unit in sequence, with each unit applying a different color or layer of ink. Stack-type machines are compact and efficient, and they can produce high-quality prints.
However, they can be limited in terms of the number of colors that can be printed in a single pass.
In-line
In-line printing machines combine multiple printing units into a single, continuous line. The substrate passes through all of the printing units in one pass, which can significantly increase productivity. In-line machines are suitable for high-volume printing applications, but they can be more expensive and complex to operate than other types of flexographic printing machines.
Common Impression
Common impression printing machines have multiple printing units that share a common impression cylinder. The substrate passes through all of the printing units in one pass, which can increase productivity. Common impression machines are less expensive and complex than in-line machines, but they may not offer the same level of print quality.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Flexographic Printing Machine
When choosing a flexographic printing machine, several factors should be considered, including:
- Print quality
- Speed
- Substrate compatibility
- Cost
The specific requirements of the printing application will determine the most suitable type of printing machine. For example, if high print quality is required, a central impression machine may be the best choice. If speed is a priority, an in-line machine may be more suitable.
Advantages of Flexographic Printing

Flexographic printing offers numerous benefits compared to other printing methods, making it a versatile and cost-effective choice for a wide range of applications.Flexographic printing excels in printing on non-absorbent substrates such as plastic, metal, and cellophane, which are commonly used in packaging and labeling industries.
The raised ink dots in flexographic printing provide excellent adhesion and durability on these surfaces, ensuring high-quality and long-lasting prints.Compared to offset printing, flexographic printing offers faster production speeds and lower setup costs. The flexible printing plates used in flexographic printing allow for quick changeovers between jobs, making it suitable for short-run and variable data printing.Flexographic printing is also more cost-effective than gravure printing, especially for shorter print runs.
Gravure printing requires expensive copper cylinders for plate making, while flexographic printing uses relatively inexpensive photopolymer plates. This cost advantage makes flexographic printing a viable option for applications where high-quality printing is required at a lower cost.
Applications of Flexographic Printing
Flexographic printing finds extensive applications across various industries, offering high-quality and cost-effective printing solutions for a wide range of products.
- Packaging Industry:Flexography is the dominant printing method for flexible packaging, including food wrappers, labels, bags, and pouches. Its ability to print on various substrates, such as paper, plastic, and foil, makes it suitable for packaging diverse products, from food and beverages to pharmaceuticals and consumer goods.
- Paper and Board Products:Flexographic printing is widely used in the production of corrugated cardboard boxes, paper bags, and other paperboard products. Its high speed and ability to print on rough surfaces make it an efficient and economical choice for these applications.
- Labels and Tags:Flexographic printing is ideal for producing high-quality labels and tags for a variety of products, including food, beverages, cosmetics, and industrial goods. Its ability to print on pressure-sensitive materials and various substrates allows for the creation of durable and eye-catching labels.
- Newspapers and Magazines:Flexography is increasingly used in the printing of newspapers and magazines, offering cost-effective and high-speed production. Its ability to print on large rolls of paper makes it suitable for long print runs.
- Other Applications:Flexographic printing is also used in various other applications, including wallpaper, gift wrap, lottery tickets, and security documents. Its versatility and ability to print on a wide range of substrates make it a valuable tool for producing a diverse range of printed materials.
Environmental Considerations
Flexographic printing, like any industrial process, has an environmental impact. However, the industry has made significant strides in recent years to minimize its ecological footprint.One of the key environmental concerns with flexographic printing is the use of solvents. Solvents are used to clean printing plates and rollers, and they can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere.
VOCs can contribute to smog and other air pollution problems.To reduce VOC emissions, flexographic printers have adopted a number of measures, including:
- Using water-based inks
- Using low-VOC solvents
- Installing VOC abatement equipment
Another environmental concern with flexographic printing is the generation of waste. Flexographic printing plates are typically made of photopolymer, which is a non-biodegradable plastic. In the past, these plates were often disposed of in landfills. However, today there are a number of recycling programs for flexographic plates.In addition to reducing VOC emissions and waste generation, flexographic printers are also working to reduce their energy consumption.
This can be achieved by using energy-efficient printing presses and by installing solar panels or other renewable energy sources.Overall, the flexographic printing industry is committed to minimizing its environmental impact. By adopting a number of measures, flexographic printers are helping to protect the environment and reduce their carbon footprint.
Waste Reduction
Waste reduction is an important environmental consideration for flexographic printing. Flexographic printing plates are typically made of photopolymer, which is a non-biodegradable plastic. In the past, these plates were often disposed of in landfills. However, today there are a number of recycling programs for flexographic plates.One of the most effective ways to reduce waste is to recycle flexographic printing plates.
Photopolymer plates can be recycled into a variety of products, including new printing plates, plastic lumber, and roofing tiles.In addition to recycling printing plates, flexographic printers can also reduce waste by using water-based inks and by reducing the amount of solvent used in the printing process.
Energy Conservation
Energy conservation is another important environmental consideration for flexographic printing. Flexographic printing presses can consume a significant amount of energy, especially when they are running at high speeds.One of the most effective ways to conserve energy is to use energy-efficient printing presses.
Energy-efficient printing presses are designed to use less energy without sacrificing print quality.In addition to using energy-efficient printing presses, flexographic printers can also conserve energy by:
- Installing solar panels or other renewable energy sources
- Turning off printing presses when they are not in use
- Using energy-efficient lighting in the printing plant
Quality Control

Quality control in flexographic printing is crucial to ensure consistent and high-quality prints. It involves a comprehensive set of measures to monitor and control various aspects of the printing process.
One important aspect of quality control is the inspection of printing plates before and after printing. This includes checking for defects, such as scratches, dents, or missing dots, which can affect the quality of the final print. Regular maintenance and calibration of printing machines are also essential to maintain optimal performance and prevent potential issues.
Prepress
In the prepress stage, quality control measures include:
- Checking the accuracy of digital files to ensure they match the intended design.
- Calibrating the platemaking equipment to produce plates with consistent quality and dimensions.
- Inspecting plates for defects before mounting them on the printing press.
Press
During the printing process, quality control measures include:
- Monitoring ink density and viscosity to ensure consistent ink transfer.
- Adjusting press settings, such as impression pressure and plate-to-cylinder gap, to optimize print quality.
- Regularly inspecting the printing plates for wear or damage.
- Performing color matching to ensure accurate reproduction of colors.
Postpress
In the postpress stage, quality control measures include:
- Inspecting the final prints for defects, such as smudging, misregistration, or color variations.
- Measuring print quality using densitometers or spectrophotometers to ensure it meets the desired specifications.
- Storing printed materials under controlled conditions to prevent fading or damage.
By implementing these quality control measures throughout the flexographic printing process, printers can ensure consistent and high-quality prints that meet the expectations of customers.
Recent Advancements in Flexographic Printing

Flexographic printing has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, revolutionizing the industry and enhancing the efficiency and quality of the printing process. These advancements have transformed the way flexible packaging, labels, and other products are printed, offering numerous benefits to manufacturers and consumers alike.
High-Definition Flexography (HDF)
HDF is a cutting-edge technology that utilizes advanced platemaking techniques and high-resolution inks to produce exceptional print quality. It enables printers to achieve fine lines, sharp details, and vibrant colors, rivaling the quality of offset printing. HDF has opened up new possibilities for flexographic printing, particularly in high-end packaging and label applications.
Computer-to-Plate (CTP) Systems
CTP systems have streamlined the platemaking process, eliminating the need for film and reducing lead times. These systems directly transfer digital images to printing plates, ensuring accuracy and consistency. CTP has significantly improved efficiency and reduced waste, making it a valuable tool for modern flexographic printing operations.
Automated Print Inspection
Automated print inspection systems use advanced sensors and cameras to monitor print quality in real-time. These systems detect and identify defects such as color variations, registration errors, and missing elements. By automating the inspection process, printers can minimize waste, improve quality control, and enhance overall productivity.
Impact on Efficiency and Print Quality
These advancements have had a profound impact on the efficiency and print quality of flexographic printing. HDF and CTP systems have enabled printers to produce high-quality prints with greater precision and speed. Automated print inspection systems have further improved quality control, reducing waste and ensuring consistent results.
Cost Implications
While these advancements offer significant benefits, they also come with cost implications. HDF systems require specialized equipment and materials, which can increase initial investment costs. CTP systems can also be expensive, but they offer long-term cost savings by eliminating film and reducing waste.
Automated print inspection systems are typically used in high-volume production environments, where the cost savings from reduced waste can offset the investment.
Challenges in Adoption
Despite the advantages, some challenges are associated with adopting these advancements. HDF requires skilled operators and careful calibration to achieve optimal results. CTP systems require a significant investment and may not be suitable for all print shops. Automated print inspection systems can be complex and require specialized training to operate effectively.
Real-World Applications
These advancements have been successfully implemented in various real-world applications. HDF is widely used in high-end packaging for products such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and luxury goods. CTP systems have become the standard for platemaking in large-scale flexographic printing operations. Automated print inspection systems are employed in high-volume production environments, ensuring quality and reducing waste.
Future Trends
The future of flexographic printing holds exciting prospects. Continuous advancements in platemaking technology, inks, and press design are expected to further enhance print quality and efficiency. Integration with digital printing technologies is also anticipated, enabling hybrid printing solutions that combine the strengths of both processes.
Key Players and Research
Key players driving innovation in flexographic printing include major press manufacturers such as Bobst, Mark Andy, and Nilpeter. Research institutions and industry associations are actively involved in developing new technologies and improving existing processes. The Flexographic Technical Association (FTA) is a prominent organization dedicated to promoting and advancing flexographic printing worldwide.
Future Trends

Flexographic printing continues to evolve, with new technologies and innovations emerging regularly. Some potential future trends include:
Increased automation:Automation is already playing a major role in flexographic printing, and this trend is expected to continue. Automated systems can improve efficiency, reduce waste, and improve quality. For example, automated prepress systems can streamline the plate-making process, while automated press controls can help to maintain consistent print quality.
Digital printing:Digital printing is a rapidly growing technology that is starting to make inroads into the flexographic printing market. Digital printing offers a number of advantages over traditional flexographic printing, including the ability to print variable data and short runs. As digital printing technology continues to improve, it is likely to become more widely adopted for flexographic printing.
Sustainability:Sustainability is becoming increasingly important to businesses and consumers alike. Flexographic printing is a relatively sustainable printing process, but there are still opportunities for improvement. For example, flexographic printers can reduce their environmental impact by using water-based inks and recycling waste.
New materials:The development of new materials is also expected to have a significant impact on the future of flexographic printing. For example, new substrates are being developed that are more durable and resistant to wear and tear. This will open up new opportunities for flexographic printing in a variety of applications.
Comparison with Other Printing Methods

Flexographic printing stands out among various printing techniques due to its unique characteristics and cost-effectiveness. To gain a comprehensive understanding, it is essential to compare flexographic printing with other prominent methods, such as offset printing, gravure printing, and digital printing.
This comparison will highlight the strengths and limitations of each method, enabling informed decision-making based on specific printing requirements.
The following table provides a detailed comparison of flexographic printing with other printing methods, considering factors such as cost, quality, speed, durability, environmental impact, and suitability for different substrates:
| Printing Method | Cost | Quality | Speed | Durability | Environmental Impact | Substrate Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexographic Printing | Low to moderate | Good to excellent | High | Moderate | Moderate | Wide range, including flexible substrates |
| Offset Printing | Moderate to high | Excellent | Moderate | Good | High | Paper and paperboard |
| Gravure Printing | High | Excellent | High | Excellent | Low | Non-absorbent substrates |
| Digital Printing | High | Good to excellent | Low to moderate | Moderate | Low | Wide range, including specialty substrates |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Printing Method:
- Flexographic Printing:Advantages include low to moderate cost, high speed, and versatility in substrate selection. Disadvantages include moderate durability and environmental impact.
- Offset Printing:Advantages include excellent quality and good durability. Disadvantages include higher cost and limited substrate range.
- Gravure Printing:Advantages include excellent quality, high durability, and low environmental impact. Disadvantages include high cost and limited substrate range.
- Digital Printing:Advantages include low environmental impact and versatility in substrate selection. Disadvantages include high cost and lower speed.
Emerging Trends and Future Prospects:
Flexographic printing continues to evolve with advancements in technology. These include the adoption of digital technologies, such as computer-to-plate (CTP) and digital front ends (DFEs), which enhance efficiency and reduce waste. Additionally, the development of new inks and coatings improves print quality and durability.
Flexographic printing is expected to maintain its competitiveness in the future due to its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ongoing technological advancements.
Examples of Flexographic Printing
Flexographic printing is a versatile and adaptable printing method, capable of producing high-quality prints on various substrates. Here are some examples that showcase its capabilities:
Flexible Packaging
- Plastic bags and wraps: Flexographic printing is widely used in the production of flexible packaging for food, beverages, and other products. It offers excellent print quality, flexibility, and resistance to moisture and abrasion.
- Labels and tags: Flexographic printing is commonly used to create labels and tags for a variety of products, including food, beverages, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. It provides high-quality printing with vibrant colors and sharp details.
Corrugated Cardboard
- Boxes and cartons: Flexographic printing is used to print on corrugated cardboard boxes and cartons, providing durable and eye-catching packaging for a wide range of products.
Paper and Board
- Newspapers and magazines: Flexographic printing is employed in the production of newspapers and magazines, offering high-speed printing with excellent ink coverage and consistency.
- Books and catalogs: Flexographic printing is used to print books and catalogs, producing high-quality images and text with precise registration.
Other Applications
- Wallpapers and home décor: Flexographic printing is utilized to create decorative wallpapers and home décor items, offering vibrant colors and intricate designs.
- Textiles and apparel: Flexographic printing is used to print on fabrics and garments, producing high-quality graphics and patterns for clothing, sportswear, and home textiles.
Glossary of Flexographic Printing Terms: What Is Flexographic Printing
The flexographic printing industry utilizes a specialized vocabulary to describe its processes and materials. This glossary provides clear and concise definitions of common terms, organized in a table format for easy reference.
Each term is accompanied by a brief description to enhance understanding. This glossary serves as a valuable resource for professionals and students alike, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of flexographic printing terminology.
Terms and Definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Anilox roll | A cylindrical roller with a precisely engraved surface that transfers ink to the printing plate. |
| Doctor blade | A flexible blade that removes excess ink from the anilox roll, ensuring a controlled ink transfer. |
| Flexographic plate | A flexible printing plate made of photopolymer or rubber that transfers the image to the substrate. |
| Impression cylinder | A cylinder that presses the printing plate against the substrate, transferring the ink. |
| Inking system | The mechanism that supplies and circulates ink throughout the printing press. |
| Print run | The total number of copies printed in a single production cycle. |
| Proofing | The process of creating a sample print to verify the accuracy and quality of the final product. |
| Substrate | The material on which the print is produced, such as paper, plastic, or film. |
| Web | A continuous roll of substrate that is fed through the printing press. |
Case Studies of Successful Flexographic Printing Applications

Flexographic printing has been adopted by businesses across various industries, achieving notable success. Here are a few case studies highlighting the challenges faced and benefits gained by companies that have implemented flexographic printing:
Flexible Packaging Industry
- Challenge:A leading flexible packaging manufacturer faced challenges with conventional printing methods, resulting in inconsistent print quality and high waste rates.
- Solution:The company invested in advanced flexographic printing equipment and implemented a comprehensive quality control system. This enabled them to achieve superior print quality, reduce waste, and improve production efficiency.
- Benefits:The company experienced significant cost savings due to reduced waste, enhanced customer satisfaction through improved print quality, and increased production capacity.
Label Printing Industry
- Challenge:A label printing company struggled to meet the increasing demand for high-volume, short-run label printing.
- Solution:The company adopted flexographic printing technology, which offered faster printing speeds and reduced setup times. They also implemented automated processes to streamline production.
- Benefits:The company significantly increased its production capacity, reduced lead times, and improved overall efficiency, enabling them to meet the growing market demand.
FAQ Corner
What are the key advantages of flexographic printing?
Flexographic printing offers a multitude of advantages, including its ability to print on various substrates, its cost-effectiveness compared to other printing methods, and its high-quality printing results.
What types of inks are used in flexographic printing?
Flexographic printing utilizes liquid inks that are specifically designed for this technique. These inks are typically water-based, solvent-based, or UV-curable, offering a wide range of options to suit different printing requirements.
How does flexographic printing compare to other printing methods?
Flexographic printing offers unique advantages compared to other printing methods. It is particularly well-suited for printing on flexible packaging and labels due to its ability to handle a wide range of substrates and its cost-effectiveness for large print runs.


