Were mass produced using a woodblock printing process, a groundbreaking technique that revolutionized the dissemination of knowledge and art.
This ancient printing method, with its intricate carvings and vibrant colors, left an enduring mark on history and continues to inspire contemporary artists and designers.
Woodblock Printing Process
Woodblock printing, a historical printing technique, played a significant role in the mass production of texts, images, and other materials. Originating in China during the 7th century, it became a widely used method for printing in East Asia, Europe, and beyond.
Materials and Techniques
Woodblock printing involves carving a design or text onto a block of wood, usually made from cherry, pear, or other close-grained woods. The carved areas are then inked, and a sheet of paper is pressed onto the inked block, transferring the design or text onto the paper.
The process can be repeated to create multiple copies of the same image or text.
Advantages and Limitations
Woodblock printing offers several advantages over other printing methods of its time. It is a relatively simple and inexpensive process, making it accessible to a wide range of users. Additionally, woodblocks are durable and can withstand repeated use, allowing for the production of large quantities of printed materials.
However, woodblock printing also has limitations. The carving process can be time-consuming and requires skilled artisans. The size of the woodblock limits the size of the printed image or text, and the level of detail that can be achieved is limited by the grain of the wood.
Despite its limitations, woodblock printing remains an important historical printing technique that played a significant role in the dissemination of knowledge and the development of printing technology.
Mass Production Techniques

Woodblock printing revolutionized the mass production of printed materials, enabling the dissemination of knowledge and ideas on an unprecedented scale. The technique, which involves carving text or images onto a wooden block and then transferring them to paper using ink, allowed for the rapid and cost-effective production of large quantities of printed matter.
Examples of Mass-Produced Products
Woodblock printing was widely used to produce a variety of printed materials, including:
- Books:The Diamond Sutra (868 CE), the oldest known printed book, was produced using woodblock printing. This technology facilitated the mass production of books, making them more widely available and contributing to the spread of literacy.
- Newspapers:The Peking Gazette (1343), one of the earliest known newspapers, was printed using woodblocks. Woodblock printing allowed for the rapid production and distribution of news and information, fostering a more informed public.
- Religious texts:The Lotus Sutra (1057), a sacred Buddhist text, was disseminated through woodblock printing. This technique enabled the widespread distribution of religious teachings and promoted the growth of religious practices.
Economic Implications
The mass production of printed materials through woodblock printing had significant economic implications:
- Creation of new industries:The printing and publishing industries emerged as a result of woodblock printing, providing new employment opportunities and stimulating economic growth.
- Expansion of markets:Woodblock printing expanded the markets for printed materials, making them more accessible to a wider audience. This led to increased demand for books, newspapers, and other printed goods.
- Lower production costs:Woodblock printing reduced the costs of producing printed materials compared to traditional methods, making them more affordable for consumers.
Social Implications
The mass production of printed materials through woodblock printing also had profound social implications:
- Increased literacy:The availability of printed materials led to increased literacy rates, as more people had access to books and other educational resources.
- Dissemination of ideas:Woodblock printing facilitated the spread of ideas and information, contributing to intellectual and cultural exchange. This dissemination of knowledge played a crucial role in shaping societies and fostering progress.
- Promotion of cultural and religious practices:The printing of religious texts and cultural works promoted the preservation and dissemination of cultural and religious traditions, strengthening communal identities and fostering a sense of belonging.
Artistic Considerations
Woodblock prints possess distinct aesthetic qualities that have profoundly influenced popular culture. Their unique visual language, characterized by bold lines, vibrant colors, and intricate patterns, has captivated audiences for centuries.
Woodblock printing played a pivotal role in the development of various art styles, including Ukiyo-e in Japan and the European woodcut movement. Artists like Katsushika Hokusai and Albrecht Dürer utilized the medium’s versatility to create iconic works that showcased the interplay of line, form, and composition.
Techniques for Visual Appeal
To create visually appealing woodblock prints, artists employ a range of techniques:
- Linework:Precise carving and printing techniques produce sharp, expressive lines that define forms and create a sense of movement.
- Coloration:The use of multiple woodblocks, each inked with a different color, allows for complex and vibrant color combinations.
- Texture:The grain of the wood and the pressure applied during printing impart a unique texture to the prints, adding depth and interest.
- Composition:Artists carefully arrange elements within the print’s space to create balance, harmony, and a sense of narrative.
– Cultural Impact
Woodblock prints have played a significant role in various societies worldwide, serving as a means of artistic expression, religious dissemination, educational dissemination, and political commentary. Their accessibility and versatility have made them a powerful tool for cultural preservation and transmission.
Religious Context
In many cultures, woodblock prints have been used to depict religious figures, scenes, and narratives. In Japan, for instance, ukiyo-e prints often featured Buddhist and Shinto deities, while in China, woodblock prints were used to illustrate Buddhist sutras and Confucian teachings.
These prints served as devotional objects, educational tools, and a means of spreading religious beliefs.
Educational Context
Woodblock prints have also been used for educational purposes. In the Edo period of Japan, for example, woodblock prints known as “kusazoshi” depicted historical events, folktales, and moral lessons. These prints were widely distributed and played a significant role in educating the populace.
Political Context
Woodblock prints have also been used as a means of political expression. In Europe during the Reformation, woodcuts were used to spread Protestant ideas and criticize the Catholic Church. Similarly, in Japan during the Meiji period, woodblock prints were used to promote modernization and Westernization.
Preservation of Cultural Heritage
Woodblock prints have played a crucial role in preserving cultural heritage and traditions. By depicting traditional customs, beliefs, and historical events, these prints have served as a valuable record of past societies. For example, in China, woodblock prints have been used to preserve traditional Chinese opera costumes and performances.
Timeline of Significant Events in the History of Woodblock Printing: Were Mass Produced Using A Woodblock Printing Process

Woodblock printing has a long and rich history, dating back to ancient times. The following is a timeline of some of the most significant events in its development:
7th century AD:The earliest known woodblock prints are produced in China. These prints are used for religious purposes, and depict Buddhist images and texts.
8th century AD:Woodblock printing is introduced to Japan from China. Japanese artists quickly adopt the technique, and use it to produce a wide variety of prints, including religious images, landscapes, and portraits.
12th century AD:Woodblock printing is used to produce the first illustrated books in China. These books are widely distributed, and help to spread knowledge and ideas throughout the country.
14th century AD:Woodblock printing is introduced to Europe from China. European artists quickly adopt the technique, and use it to produce a wide variety of prints, including religious images, maps, and scientific illustrations.
16th century AD:The development of the printing press in Europe leads to a decline in the use of woodblock printing for book production. However, woodblock printing continues to be used for the production of prints, and is particularly popular in Japan.
19th century AD:The development of new printing technologies, such as lithography and photography, leads to a further decline in the use of woodblock printing. However, woodblock printing continues to be used by artists as a means of artistic expression.
20th century AD:Woodblock printing experiences a revival in popularity, as artists rediscover the unique qualities of the medium. Contemporary artists continue to use woodblock printing to create a wide variety of prints, from traditional Japanese ukiyo-e to abstract and experimental works.
Contemporary Applications
Woodblock printing continues to be practiced in contemporary art and design, finding new applications and interpretations in various fields.
Modern woodblock printing techniques involve the use of traditional carving tools and materials, such as woodblocks made from cherry, pear, or maple, and ink made from pigments and binders. However, contemporary artists also experiment with unconventional materials and techniques, such as using acrylic paints, power tools, and digital processes.
Challenges and Opportunities
Contemporary woodblock printers face challenges in balancing traditional techniques with modern sensibilities, as well as in finding ways to market and promote their work in an increasingly competitive art market.
Despite these challenges, there are also opportunities for woodblock printers to explore new creative possibilities and connect with audiences through the unique qualities of the medium. The versatility of woodblock printing allows artists to create both traditional and experimental works, appealing to a wide range of collectors and enthusiasts.
Printing Methods
Woodblock printing involves transferring an image from a carved wooden block to paper or fabric. Different printing methods can be used to achieve varying effects and results. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the desired outcome and the specific requirements of the project.
Hand Printing
Hand printing is the traditional method of woodblock printing, where the artist manually applies ink to the carved block and then presses it onto paper. This method allows for great control over the pressure and placement of the block, resulting in a more nuanced and expressive print.
However, it can be time-consuming and requires a high level of skill and experience.
Press Printing
Press printing uses a press to apply pressure to the inked block, transferring the image to paper. This method is more efficient than hand printing and allows for more consistent results. However, it can be more difficult to control the pressure and placement of the block, which can affect the quality of the print.
Relief Printing
Relief printing is a type of printing method where the image is raised above the surface of the block. The inked block is pressed onto paper, and the raised areas transfer the ink to the paper, creating a raised image.
Relief printing is commonly used for woodblock printing and can produce bold and striking prints.
Intaglio Printing
Intaglio printing is a type of printing method where the image is carved into the surface of the block. The block is inked, and the excess ink is wiped away, leaving ink only in the recessed areas. The inked block is then pressed onto paper, and the paper is forced into the recessed areas, transferring the ink to create an image.
Intaglio printing is less commonly used for woodblock printing but can produce very detailed and subtle prints.
Comparison Table
The following table summarizes the different printing methods used in woodblock printing, their advantages, and disadvantages:
| Printing Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Hand Printing |
|
|
| Press Printing |
|
|
| Relief Printing |
|
|
| Intaglio Printing |
|
|
Examples of Woodblock Prints Created Using Different Printing Methods
The following are examples of woodblock prints created using different printing methods:
- Hand Printing:Katsushika Hokusai’s “The Great Wave off Kanagawa” (1831)
- Press Printing:Utagawa Hiroshige’s “The Fifty-Three Stations of the Tokaido” (1833-1834)
- Relief Printing:Albrecht Dürer’s “The Knight, Death, and the Devil” (1513)
- Intaglio Printing:Rembrandt van Rijn’s “The Three Trees” (1643)
Impact of Different Printing Methods on the Overall Appearance and Quality of Woodblock Prints
The choice of printing method can significantly impact the overall appearance and quality of woodblock prints. Hand printing allows for greater control over the pressure and placement of the block, resulting in more nuanced and expressive prints. Press printing produces more consistent results but may result in less control over the pressure and placement of the block.
Relief printing is commonly used for woodblock printing and can produce bold and striking prints, while intaglio printing can produce very detailed and subtle prints.
The choice of printing method should be based on the desired outcome and the specific requirements of the project. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the artist should carefully consider the effects that each method will have on the final print.
Woodblock Design
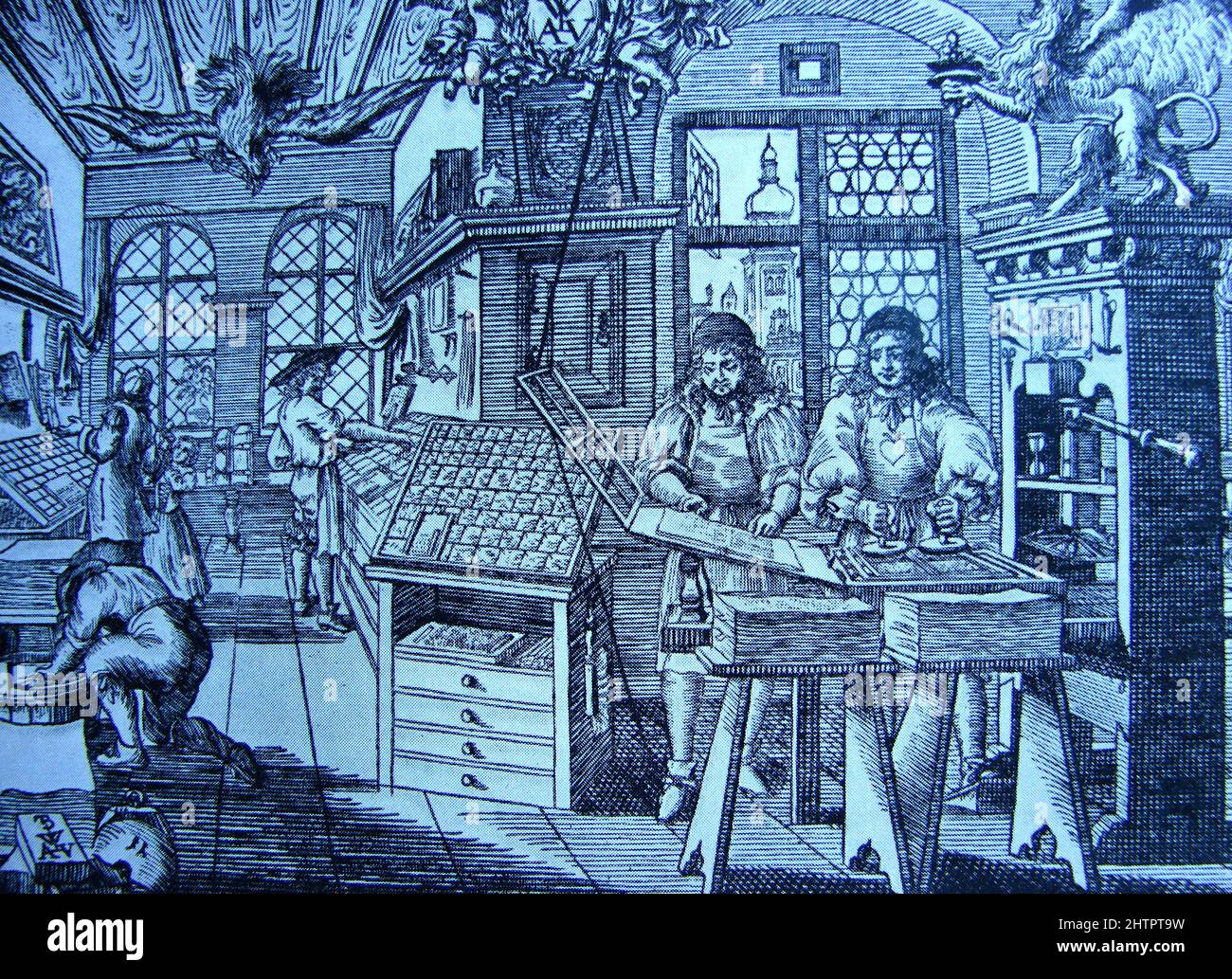
Designing a woodblock print involves creating an image that will be carved into the woodblock and then printed onto paper or fabric. The design process typically begins with a sketch or drawing, which is then transferred to the woodblock. The artist then uses a variety of carving tools to create the image in the wood, removing areas that will not print and leaving raised areas that will.
There are a number of factors to consider when designing a woodblock print, including the size and shape of the block, the type of wood used, and the desired effect. The artist must also take into account the limitations of the woodblock printing process, such as the fact that it is a relief printing process, meaning that only the raised areas of the block will print.
There are a variety of different woodblock design styles, each with its own unique characteristics. Some of the most common styles include:
Ukiyo-e
Ukiyo-e is a style of Japanese woodblock printing that flourished during the Edo period (1603-1868). Ukiyo-e prints typically depict scenes from everyday life, such as landscapes, portraits, and kabuki theater scenes. Ukiyo-e prints are often characterized by their bold colors and simple, elegant lines.
Moku hanga
Moku hanga is a style of Japanese woodblock printing that developed in the early 20th century. Moku hanga prints are typically characterized by their use of water-based inks and their focus on natural subjects, such as landscapes and plants. Moku hanga prints are often printed on handmade paper, which gives them a unique, textured look.
Sosaku hanga
Sosaku hanga is a style of Japanese woodblock printing that developed in the early 20th century. Sosaku hanga prints are typically characterized by their use of experimental techniques and their focus on personal expression. Sosaku hanga prints are often printed on a variety of materials, including paper, fabric, and metal.
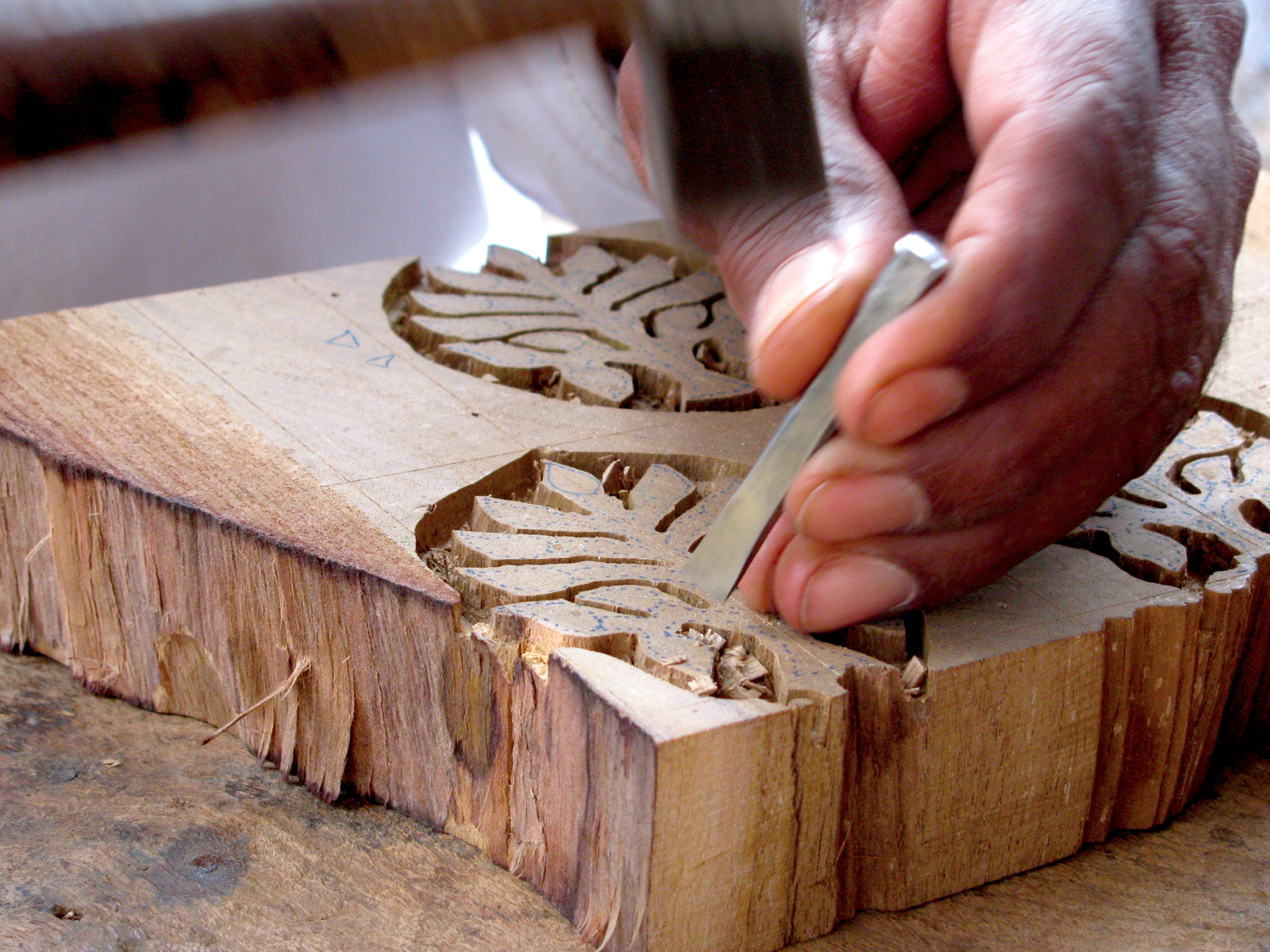
Carving Techniques

Carving techniques in woodblock printing involve using specialized tools to remove specific areas of the woodblock, creating a raised design that will transfer ink onto paper. The choice of carving tools and techniques depends on the desired level of detail, the hardness of the wood, and the artist’s personal style.
Gouges
Gouges are curved carving tools that come in various shapes and sizes. They are used to create smooth, rounded contours and remove large areas of wood. Gouges are held at an angle to the woodblock and pushed or pulled to create the desired shape.
Chisels
Chisels are straight, flat-edged tools used for creating sharp lines and precise details. They are held perpendicular to the woodblock and tapped with a mallet or hammer to remove small amounts of wood.
Knives
Knives are versatile tools that can be used for both carving and cutting. They are held at a low angle to the woodblock and used to create fine lines, textures, and details.
Safety Precautions
When carving woodblocks, it is important to take safety precautions to prevent injuries:
- Always wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves, safety glasses, and a dust mask.
- Use sharp tools and keep them in good condition.
- Carve in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling wood dust.
- Never carve towards yourself or others.
- Be aware of the direction of the grain in the wood and carve accordingly.
Ink and Paper Selection

The selection of ink and paper is crucial in woodblock printing, as they significantly influence the final appearance and quality of the print. Understanding the characteristics and compatibility of different types of ink and paper is essential for achieving desired results.
Ink
These prints were mass produced using a woodblock printing process, which involved carving an image into a block of wood and then applying ink to the block. The inked block was then pressed onto paper, transferring the image. Similar to modern printers, the ink used in woodblock printing could also dry out over time.
To prevent this, printers would often store their ink in sealed containers or use techniques to slow down the drying process. Just like modern printers, which can experience issues such as does printer ink dry out , woodblock printers had to be mindful of ink maintenance to ensure the longevity of their prints.
- Oil-based inks:Traditional inks used in woodblock printing, known for their rich colors and durability. They require longer drying times and are less suitable for fine details.
- Water-based inks:Modern inks that are easier to clean up and offer more vibrant colors. They dry quickly, allowing for faster printing.
- Pigment inks:Inks made with finely ground pigments, resulting in opaque and matte prints. They are often used for creating bold and striking images.
Paper
- Japanese paper:Traditional paper used in woodblock printing, known for its strength, durability, and ability to absorb ink evenly. It is available in various textures and thicknesses.
- Western paper:Paper made from wood pulp, offering a smoother surface and brighter white color. It is less absorbent than Japanese paper, but can be used for fine details.
- Handmade paper:Paper made by hand using traditional techniques. It offers unique textures and variations in thickness, adding character to prints.
Factors to Consider
- Compatibility:Ensure that the ink and paper are compatible to avoid smudging, bleeding, or other issues.
- Drying time:Consider the drying time of the ink when selecting paper. Faster-drying inks require less absorbent paper.
- Texture and finish:The texture and finish of the paper can affect the appearance of the print. Rougher papers create a more rustic look, while smoother papers provide finer details.
Recommendations
- For traditional woodblock prints, oil-based inks on Japanese paper are a classic combination.
- For vibrant colors and faster printing, water-based inks on Western paper are a good choice.
- For bold and striking images, pigment inks on handmade paper can create unique and expressive prints.
Registration and Printing
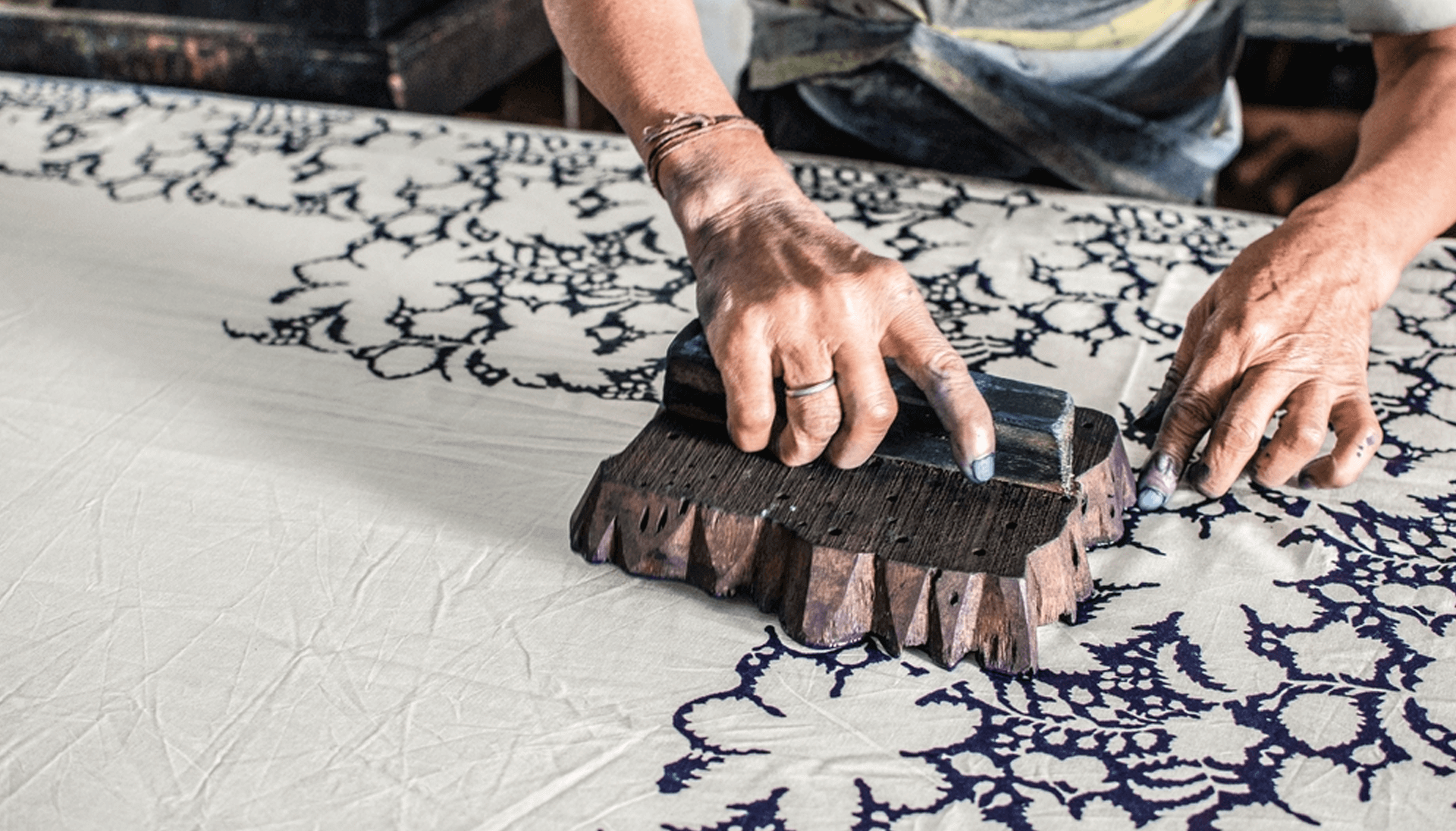

Registering and printing woodblocks involves aligning multiple blocks to create a cohesive image. Accurate registration is crucial to ensure precise placement of colors and details.
To register woodblocks, align them using registration marks or pins. Registration marks are small crosses or lines carved into the edges of the blocks. Pins are inserted into holes drilled into the blocks. Once aligned, the blocks are secured with tape or clamps.
Challenges and Troubleshooting
- Misalignment:Blocks can shift during printing, causing misalignment. Ensure blocks are securely fastened and use registration marks or pins for precise alignment.
- Ink bleeding:Excess ink can spread beyond the intended areas, creating unwanted bleeding. Use appropriate ink viscosity and apply thin, even layers.
- Smudging:Wet ink can smudge if the paper is not handled carefully. Allow ample drying time between printing layers and use a light touch when handling.
- Ghosting:Faint images can appear in unwanted areas due to ink residue. Clean blocks thoroughly after each use and ensure the paper is dry before printing.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Carve registration marks or drill holes for pins into each block.
- Align the blocks using registration marks or pins.
- Secure the blocks with tape or clamps.
- Apply ink to the first block and print onto the paper.
- Repeat steps 4-5 for each subsequent block.
- Allow the print to dry completely.
Challenges and Troubleshooting Techniques Table
| Challenge | Troubleshooting Technique |
|---|---|
| Misalignment | Use registration marks or pins, secure blocks securely |
| Ink bleeding | Use appropriate ink viscosity, apply thin, even layers |
| Smudging | Allow ample drying time, handle paper carefully |
| Ghosting | Clean blocks thoroughly, ensure paper is dry before printing |
Color Printing
Color printing in woodblock printing involves creating prints using multiple woodblocks, each carved with a different color. Techniques for color printing include keyblock printing, reduction printing, and multiple-block printing.
Keyblock Printing
Keyblock printing uses a single woodblock carved with the Artikels of the design. This block is printed in a neutral color, usually black or brown, to create the key image. Additional woodblocks are then carved for each color, and these are registered and printed over the keyblock to create the final image.
Reduction Printing
Reduction printing is a technique where a single woodblock is used to create multiple colors. The block is progressively carved away, and different colors are applied to the remaining surface. This technique allows for a wide range of color combinations and effects.
Multiple-Block Printing
Multiple-block printing uses separate woodblocks for each color in the design. Each block is carved with the portion of the design that corresponds to its color, and the blocks are registered and printed in succession to create the final image.
Registration and Printing
Registering and printing multiple woodblocks requires careful alignment to ensure that the colors align correctly. Registration marks are often used to guide the placement of the blocks, and the blocks are typically printed using a press to ensure even pressure and alignment.
Challenges and Opportunities
Color printing in woodblock printing offers both challenges and opportunities. The limitations of the medium, such as the number of colors that can be used and the difficulty of aligning multiple blocks, can be seen as creative constraints that inspire innovative solutions.
While woodblock printing was a groundbreaking technique that allowed for mass production of images, its modern counterpart, the inkjet printer, faces a different challenge. Printer ink cartridges, the lifeblood of these devices, are prone to drying out over time. This phenomenon, explored in detail at do printer ink cartridges dry out , can significantly impact print quality and even damage the printer itself.
Despite these advancements, the art of woodblock printing remains a testament to the enduring power of human ingenuity and the transformative impact of printing technology.
The technique also offers the opportunity to create unique and expressive prints with a rich and vibrant color palette.
Summary of Color Printing Techniques
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages | Examples ||—|—|—|—|| Keyblock Printing | Simple and efficient | Limited color range | Utamaro Kitagawa, Katsushika Hokusai || Reduction Printing | Wide range of colors and effects | Complex and time-consuming | Albrecht Dürer, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner || Multiple-Block Printing | Precise color control | Requires multiple blocks and careful registration | Ando Hiroshige, Toyohara Kunichika |
“Color printing in woodblock printing is a challenging but rewarding technique that allows artists to create vibrant and expressive prints. The limitations of the medium force artists to be creative and resourceful, and the results can be truly stunning.”
Utamaro Kitagawa, Japanese woodblock print artist
Woodblock Printing in Different Cultures
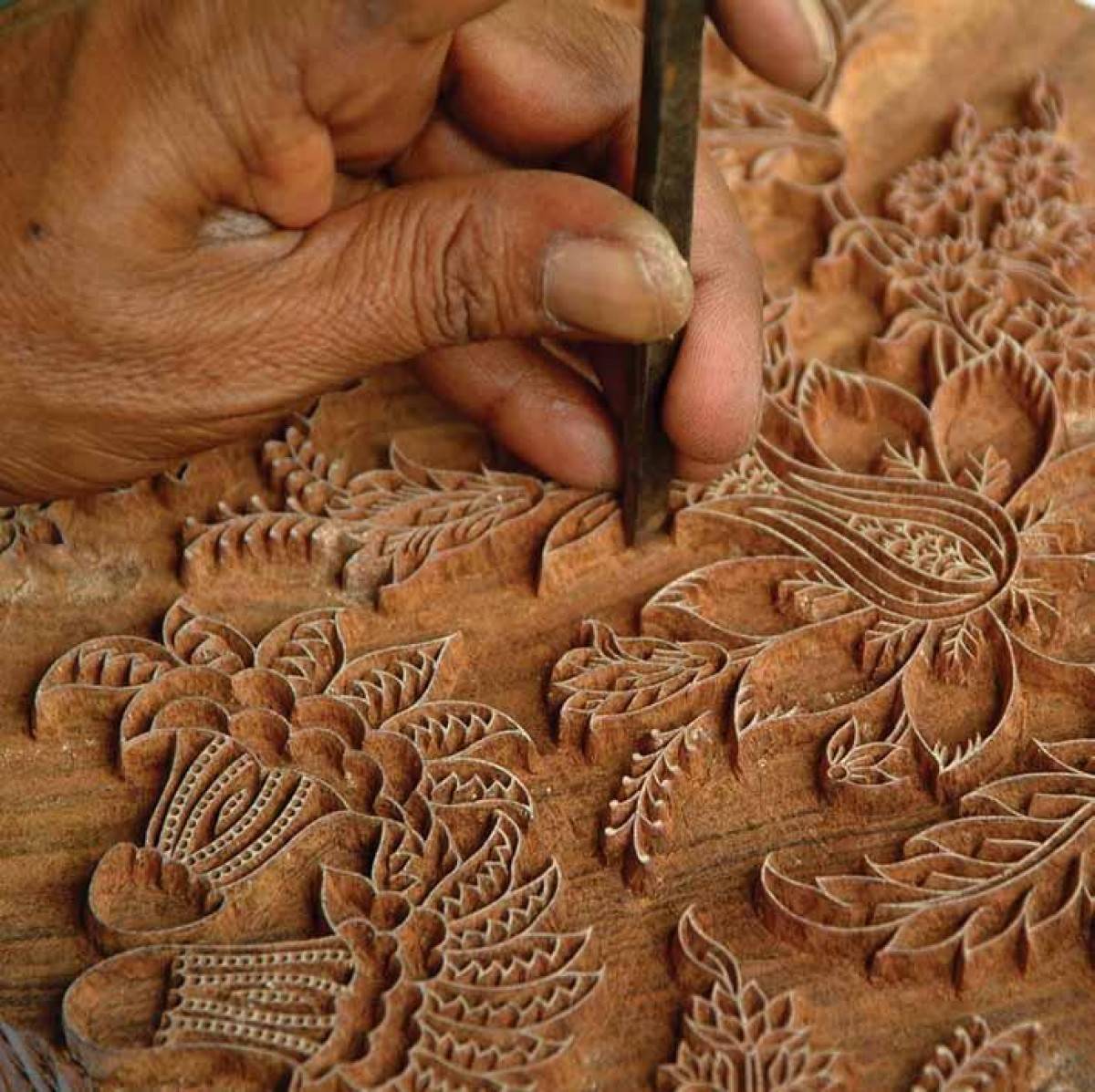

Woodblock printing is an ancient art form with a rich history in many cultures around the world. Each culture has developed its own unique styles and techniques, resulting in a diverse range of woodblock prints.
China
China is considered the birthplace of woodblock printing, with the earliest known prints dating back to the 7th century. Chinese woodblock prints are characterized by their intricate designs, often featuring landscapes, flowers, and birds. The technique of color printing was also developed in China, allowing for the creation of vibrant and colorful prints.
Japan
Japanese woodblock printing, known as ukiyo-e, flourished during the Edo period (1603-1868). Ukiyo-e prints depicted scenes from everyday life, including landscapes, portraits, and kabuki theater. Japanese woodblock prints are known for their bold colors and dynamic compositions.
Korea
Korean woodblock printing, known as jangseungdo, has a long history dating back to the Goryeo period (918-1392). Jangseungdo prints often feature guardian deities and other folk motifs. Korean woodblock prints are characterized by their use of strong lines and vibrant colors.
Europe
Woodblock printing was introduced to Europe in the 14th century. European woodblock prints were initially used for religious purposes, but later became popular for secular subjects such as maps, playing cards, and broadsides. European woodblock prints are often characterized by their detailed and realistic depictions.
Woodblock Printing as a Fine Art

Woodblock printing has emerged as a significant medium in the realm of fine art, captivating collectors and enthusiasts alike. Its unique blend of artistic expression and technical proficiency has propelled it to the forefront of contemporary art.
Techniques and Styles
Contemporary woodblock printmakers employ diverse techniques and styles, showcasing their mastery of the medium. Some artists adhere to traditional Japanese methods, utilizing water-based inks and meticulous carving techniques to create intricate designs. Others experiment with innovative approaches, incorporating Western influences, mixed media, and unconventional materials.
Market and Value
The market for woodblock prints as fine art has witnessed a steady rise in recent years. Prestigious galleries and art fairs showcase the works of established and emerging printmakers, attracting collectors and investors alike. The value of woodblock prints varies significantly depending on factors such as the artist’s reputation, the edition size, and the quality of the craftsmanship.
Woodblock Printing in Education
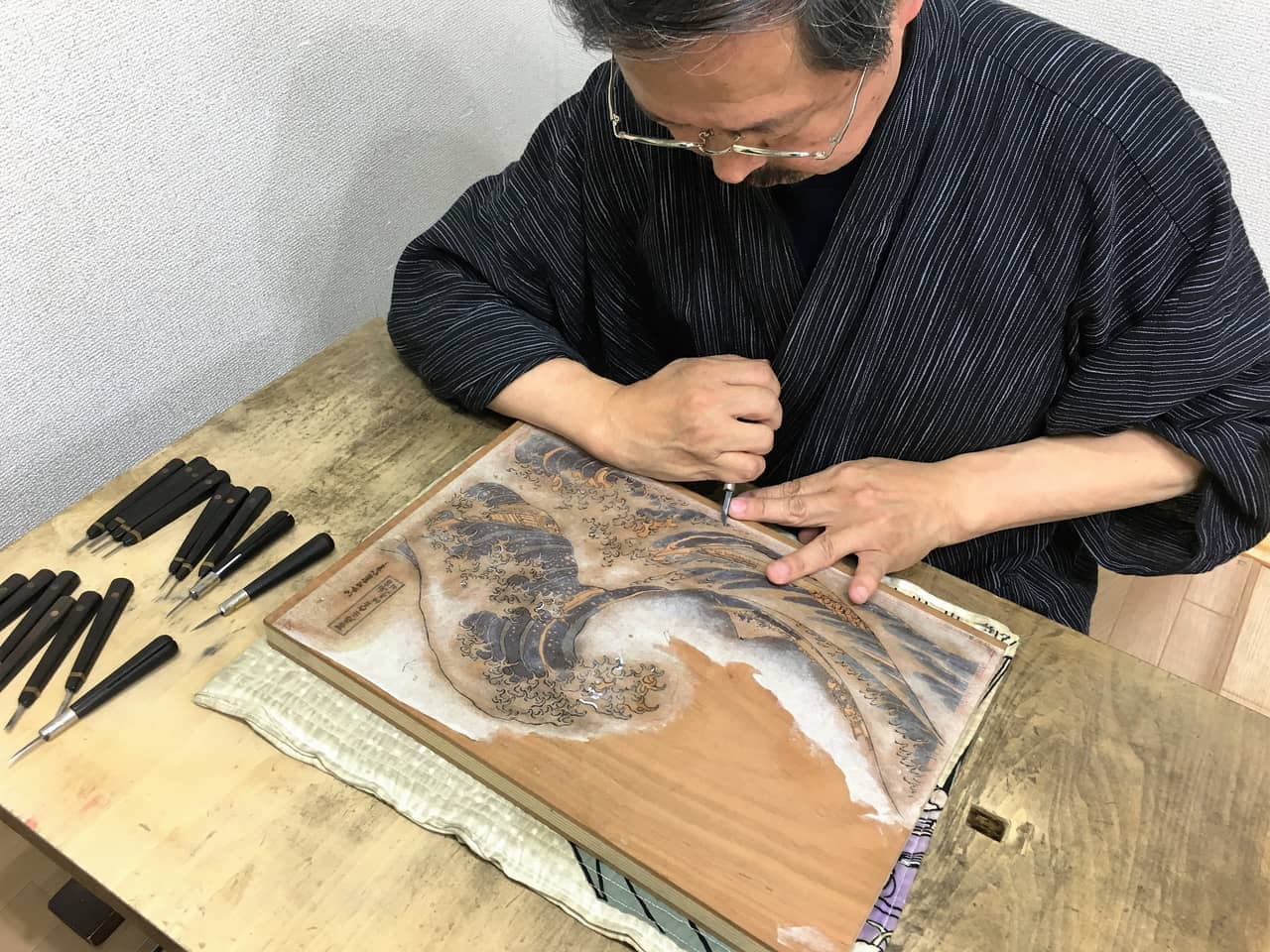

Woodblock printing offers a rich and engaging educational experience that can foster creativity, critical thinking, and an appreciation for art and history. This ancient art form has been used for centuries to teach a variety of subjects, from art and design to history, literature, and science.
Educational Value of Woodblock Printing, Were mass produced using a woodblock printing process
- Develops Fine Motor Skills:Carving and printing require precise hand movements, enhancing dexterity and coordination.
- Encourages Creativity and Expression:Students can design and create their own unique prints, fostering imagination and self-expression.
- Teaches Art and Design Principles:Woodblock printing introduces concepts such as composition, color theory, and printing techniques.
- Connects to History and Culture:Woodblock printing has a long and rich history, allowing students to explore different cultures and time periods.
- Promotes Collaboration and Teamwork:Students can work together to create larger prints or collaborate on designs.
Using Woodblock Printing in Education
Woodblock printing can be incorporated into various educational settings, including art classes, history lessons, and interdisciplinary projects. Here are some examples:
- Art Education:Students can learn about different printing techniques, experiment with colors and textures, and create original artwork.
- History Education:Woodblock printing can be used to illustrate historical events, explore different cultures, and create timelines or maps.
- Science Education:Students can use woodblock printing to create scientific illustrations, demonstrate scientific concepts, or design experiments.
- Language Arts Education:Woodblock printing can be combined with writing assignments, allowing students to illustrate their stories or poems.
Benefits of Using Woodblock Printing in Education
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Fosters Creativity | Encourages students to think outside the box and develop their artistic skills. |
| Develops Fine Motor Skills | Improves hand-eye coordination and dexterity through carving and printing. |
| Enhances Historical Understanding | Provides a tangible connection to past cultures and events. |
| Promotes Interdisciplinary Learning | Can be integrated into various subjects, such as art, history, science, and language arts. |
| Supports Collaboration | Encourages students to work together on projects. |
Resources for Using Woodblock Printing in Education
- Websites:
- Organizations:
Lesson Plan: Woodblock Printing for Historical Exploration
Subject:History
Grade Level:4-8
Objectives:
- Students will learn about the history of woodblock printing.
- Students will create their own woodblock prints to illustrate a historical event.
Materials:
- Woodblocks
- Carving tools
- Ink
- Paper
- Historical images or texts
Procedure:
- Introduce students to the history of woodblock printing.
- Have students select a historical event to illustrate.
- Guide students in sketching their designs onto the woodblocks.
- Supervise students as they carve their designs into the woodblocks.
- Instruct students on how to apply ink and print their woodblocks.
- Discuss the finished prints and their historical significance.
Assessment:
- Design:Evaluate the originality and historical accuracy of the student’s design.
- Carving:Assess the precision and detail of the student’s carving.
- Printing:Grade the student’s ability to apply ink and print their woodblock effectively.
- Presentation:Evaluate the student’s presentation of their finished print and its historical context.
Questions Often Asked
What is the significance of woodblock printing in mass production?
Woodblock printing enabled the mass production of printed materials, such as books, newspapers, and religious texts, making knowledge and information more accessible to a wider audience.
How did woodblock printing impact the spread of literacy?
The affordability and widespread availability of printed materials through woodblock printing contributed to increased literacy rates, particularly in East Asia.
What are some notable examples of woodblock prints used for religious purposes?
The Diamond Sutra (868 CE) and the Lotus Sutra (1057) are renowned examples of woodblock prints used to disseminate religious teachings and promote spiritual practices.


