How much is utilities for a 2 bedroom apartment – Determining the cost of utilities for a 2-bedroom apartment requires a comprehensive understanding of various factors that influence energy consumption and utility rates. This analysis delves into the intricacies of utility expenses, providing insights into how location, apartment size, energy efficiency, utility types, rate structures, and other factors impact utility bills.
By examining these elements, renters and homeowners can make informed decisions to reduce their energy usage and manage utility costs effectively. This exploration aims to equip readers with the knowledge and strategies necessary to optimize their energy consumption and minimize their financial burden.
Geographic Location and Regional Factors
The geographic location of a 2-bedroom apartment significantly influences its utility costs. Regions with different climates, energy sources, and population densities experience varying utility rates.
For instance, apartments in colder climates typically have higher heating costs during winter months. In regions with abundant renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, electricity costs may be lower. Additionally, urban areas often have higher utility rates compared to rural areas due to increased demand and infrastructure maintenance.
Climate and Weather Conditions
Climate and weather conditions directly impact utility consumption in a 2-bedroom apartment. Apartments in areas with extreme temperatures, such as hot summers or cold winters, require more energy for heating or cooling. Humid climates can also increase electricity usage for air conditioning.
On average, utilities for a 2 bedroom apartment can range from $150 to $300 per month. This includes electricity, gas, water, and trash removal. However, these costs can vary depending on the location, size of the apartment, and usage. It is important to factor in utility costs when budgeting for an apartment.
Recently, utility stocks have been experiencing a decline due to concerns about rising interest rates and the potential impact on earnings. Why are utility stocks down ? Utility companies are often seen as safe investments, but the recent market volatility has caused investors to reconsider.
Despite the recent decline, utility stocks may still be a good investment for those looking for long-term growth.
For example, a study by the U.S. Department of Energy found that apartments in the southern United States consume significantly more energy for cooling than those in the northern United States. Similarly, apartments in coastal areas with high humidity levels tend to have higher electricity bills for air conditioning.
Apartment Size and Energy Efficiency

The size of an apartment is a significant factor in determining its utility costs. Larger apartments typically have more rooms, higher ceilings, and larger windows, all of which contribute to increased energy consumption. This is because heating and cooling a larger space requires more energy, and more windows allow for heat loss during the winter and heat gain during the summer.
Energy-efficient appliances and lighting can significantly reduce utility consumption in apartments. Energy-efficient appliances use less energy to perform the same tasks as their traditional counterparts, while energy-efficient lighting produces the same amount of light while using less energy. These measures can help reduce electricity consumption and lower utility bills.
Insulation and Building Materials
Insulation and building materials play a crucial role in reducing energy usage in apartments. Insulation helps to keep the apartment warm in the winter and cool in the summer by preventing heat transfer. Building materials with high thermal resistance, such as brick and concrete, can also help to reduce energy consumption.
Quantifying Savings
The potential savings associated with energy-efficient upgrades can be substantial. For example, replacing traditional light bulbs with LED bulbs can reduce lighting energy consumption by up to 80%. Upgrading to energy-efficient appliances can also lead to significant savings, with some appliances consuming up to 50% less energy than their traditional counterparts.
The average cost of utilities for a 2-bedroom apartment can vary depending on factors such as location, usage, and the efficiency of the appliances. However, according to the US Energy Information Administration , the average monthly utility bill for a 2-bedroom apartment in the United States is around $150-$250.
This includes expenses for electricity, gas, water, and trash removal. The cost of utilities can also fluctuate based on seasonal changes, with higher bills during summer and winter months due to increased usage of heating and cooling systems.
Energy-Saving Measures
Several energy-saving measures can be implemented in apartments to reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills. These measures include:
- Installing energy-efficient appliances and lighting
- Improving insulation
- Using weatherstripping and caulking to seal air leaks
- Unplugging electronics when not in use
- Turning off lights when leaving a room
Key Factors Influencing Energy Consumption
The following table summarizes the key factors that influence energy consumption in apartments:
| Factor | Impact on Energy Consumption |
|---|---|
| Apartment size | Larger apartments typically have higher energy consumption |
| Energy-efficient appliances and lighting | Energy-efficient appliances and lighting can reduce energy consumption |
| Insulation and building materials | Insulation and building materials with high thermal resistance can reduce energy consumption |
| Occupancy | The number of occupants in an apartment can affect energy consumption |
| Climate | The climate in which an apartment is located can affect energy consumption |
Tips for Reducing Energy Usage
In addition to the energy-saving measures discussed above, the following tips can help reduce energy usage in apartments:
- Keep the thermostat set at a moderate temperature
- Close curtains and blinds during the summer to keep the apartment cool
- Open windows and doors during the winter to let in fresh air
- Take shorter showers
- Wash clothes in cold water
- Dry clothes on a clothesline instead of in a dryer
Utility Types and Consumption Patterns
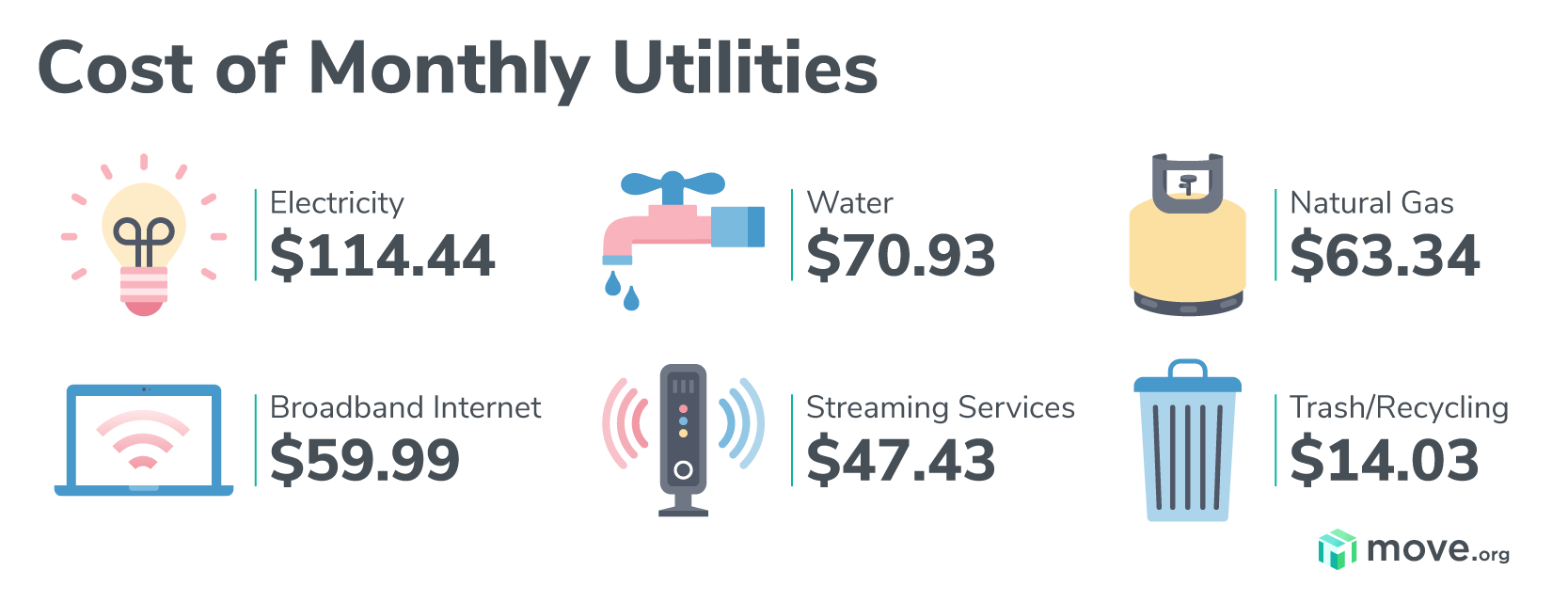
Apartment rentals typically include three main utility types: electricity, gas, and water. Consumption patterns for these utilities can vary depending on several factors, including the number of occupants, lifestyle, and apartment size.
Electricity consumption is primarily driven by lighting, appliances, and heating/cooling systems. On average, a two-bedroom apartment may consume around 500-750 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per month. However, this can vary depending on the efficiency of appliances, the number of occupants, and the climate.
Gas Consumption
Gas consumption is typically associated with heating, cooking, and water heating. The average gas consumption for a two-bedroom apartment can range from 50 to 150 therms per month. Factors influencing gas consumption include the efficiency of heating systems, cooking habits, and the number of occupants.
Water Consumption
Water consumption in a two-bedroom apartment typically ranges from 3,000 to 5,000 gallons per month. This can be influenced by factors such as the number of occupants, water-saving fixtures, and outdoor water usage.
Utility Rate Structures
Utility rate structures determine how much customers are charged for the utilities they consume. Different rate structures can have a significant impact on utility bills, so it’s important to understand the different types and how they work.
Flat Rate
With a flat rate structure, customers are charged a fixed amount per unit of utility consumed, regardless of when or how much they use. This type of structure is simple and easy to understand, but it can be unfair to customers who use more utilities than others.
Tiered Pricing
With tiered pricing, customers are charged different rates for different levels of usage. For example, a customer might be charged a lower rate for the first 100 kilowatt-hours of electricity they use, and a higher rate for any usage above that amount.
This type of structure can encourage customers to conserve energy, but it can also be more complex and difficult to understand than a flat rate structure.
Time-of-Use
With time-of-use pricing, customers are charged different rates for using utilities during different times of day. For example, electricity rates might be higher during peak hours (when demand is highest) and lower during off-peak hours (when demand is lowest). This type of structure can encourage customers to shift their usage to off-peak hours, which can help to reduce overall demand and costs.
Peak Demand Charges
Some utilities also impose peak demand charges on customers who use a large amount of energy during peak hours. These charges can be significant, so it’s important to be aware of them if you’re a heavy energy user.
Utility Providers and Competition

The provision of utilities is typically handled by various types of entities, including public utilities, private companies, and cooperatives. Each type of provider operates under different ownership structures and regulatory frameworks, which can impact the cost and availability of utility services.
Public Utilities
- Owned and operated by local or state governments.
- May operate on a non-profit basis, with the primary goal of providing essential services to the community.
- Often have lower rates than private companies due to their non-profit status and access to government funding.
Private Utilities
- Owned and operated by for-profit companies.
- Driven by the goal of maximizing profits for shareholders.
- May have higher rates than public utilities, as they need to cover operating costs and generate a return for investors.
Cooperatives
- Owned and operated by their members, who are typically the customers receiving the utility services.
- Non-profit organizations that aim to provide affordable and reliable services to their members.
- May offer lower rates than private companies due to their non-profit status and the absence of profit margins.
Role of Competition
The presence of competition among utility providers can drive down rates and improve service quality. In areas with multiple providers, customers have the option to choose the company that offers the most competitive rates and services.
Comparing Providers
To compare different utility providers and choose the most cost-effective option, consumers should consider the following factors:
- Rates: Compare the rates for the same type of service from different providers.
- Fees: Check for any additional fees, such as connection fees or monthly service charges.
- Customer service: Read reviews and check online forums to assess the reputation and responsiveness of different providers.
- Reliability: Consider the frequency and duration of power outages or other service disruptions experienced by each provider.
Government Programs and Incentives
Government programs offer financial assistance to low-income households and individuals struggling to pay their utility bills. These programs aim to alleviate the financial burden of utility costs and promote energy efficiency.
Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP)
LIHEAP is a federally funded program that provides financial assistance to low-income households with their heating and cooling costs. The program offers a one-time payment each year, which can be used to pay for heating fuel, electricity, or natural gas.
Eligibility:To be eligible for LIHEAP, households must meet income guidelines set by the federal government. Income limits vary by state and household size.
Application Process:Applications for LIHEAP can be obtained from local community action agencies or online through the LIHEAP website.
Weatherization Assistance Program (WAP)
WAP is a federally funded program that provides free home energy efficiency upgrades to low-income households. These upgrades can include insulation, weatherstripping, and energy-efficient appliances.
Eligibility:To be eligible for WAP, households must meet income guidelines set by the federal government. Income limits vary by state and household size.
Application Process:Applications for WAP can be obtained from local community action agencies or online through the WAP website.
State Energy Assistance Program (SEAP)
SEAPs are state-funded programs that provide financial assistance to low-income households with their utility bills. The programs vary by state, but they typically offer a one-time payment each year, which can be used to pay for heating fuel, electricity, or natural gas.
Eligibility:Eligibility requirements for SEAPs vary by state. Households must typically meet income guidelines and other criteria set by the state.
Application Process:Applications for SEAPs can be obtained from local community action agencies or online through the state’s website.
Incentives for Energy-Efficient Upgrades
In addition to government programs, many states and utilities offer incentives for energy-efficient upgrades. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, and low-interest loans.
Tax credits are a direct reduction in the amount of taxes owed. Rebates are a refund of a portion of the cost of an energy-efficient upgrade. Low-interest loans can help households finance the cost of energy-efficient upgrades.
Incentives for energy-efficient upgrades can significantly reduce the cost of these upgrades, making them more affordable for low-income households.
Tips for Applying for Government Assistance Programs
- Gather all necessary documentation, such as proof of income, household size, and utility bills.
- Apply early, as funds are limited and may run out.
- Be patient, as the application process can take time.
- Contact a local community action agency for assistance with the application process.
Sample Letter to a Government Agency Requesting Assistance with Utility Costs, How much is utilities for a 2 bedroom apartment
[Your Name][Your Address][City, State, Zip Code][Date][Government Agency Name][Government Agency Address][City, State, Zip Code]Dear Sir or Madam,I am writing to request assistance with my utility costs. I am a low-income household with [number] members. My household income is [amount].I am currently struggling to pay my utility bills.
My monthly utility costs are [amount]. I have been late on my utility bills several times in the past year.I have applied for LIHEAP and WAP, but I have not yet received any assistance. I am also looking into other government programs and incentives that may be available to me.I am committed to reducing my energy consumption and making my home more energy-efficient.
I have already made some changes, such as turning off lights when I leave a room and unplugging appliances when I am not using them.I would be grateful for any assistance that you can provide me with. I am available to meet with you at your convenience to discuss my situation further.Thank you for your time and consideration.Sincerely,[Your Name]
Energy Conservation Tips

Reducing energy consumption in a 2-bedroom apartment can significantly lower utility costs and contribute to environmental sustainability. By implementing simple energy-saving measures, tenants can enjoy a more comfortable living environment while minimizing their energy footprint.
Here are practical tips for reducing energy consumption in a 2-bedroom apartment, organized into categories for easy implementation:
Lighting
- Switch to LED bulbs:Replace incandescent or fluorescent bulbs with energy-efficient LED bulbs, which consume up to 85% less energy and last longer.
- Utilize natural light:Open curtains and blinds during the day to take advantage of natural sunlight, reducing the need for artificial lighting.
- Install dimmer switches:Adjust the brightness of lights to suit different activities, reducing energy consumption when full illumination is not required.
Appliances
- Choose energy-efficient appliances:Look for appliances with the Energy Star label, indicating they meet strict energy efficiency standards.
- Unplug unused appliances:Devices like phone chargers and toasters continue to draw power even when not in use. Unplug them to eliminate standby power consumption.
- Use cold water for laundry:Most of the energy used by washing machines goes towards heating water. Opting for cold water washes can save significant energy.
Heating/Cooling Systems
- Insulate your apartment:Proper insulation prevents heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems.
- Use ceiling fans:Ceiling fans circulate air, creating a wind chill effect that can make a room feel cooler without increasing energy consumption.
- Programmable thermostats:Install programmable thermostats to automatically adjust the temperature based on your schedule, saving energy when you’re away or asleep.
Implementing these energy conservation tips can lead to substantial cost savings. For example, switching to LED bulbs can reduce lighting costs by up to 80%, while unplugging unused appliances can save up to $100 per year.
By adopting these simple measures, tenants can reduce their energy consumption, lower their utility bills, and contribute to a more sustainable living environment. Remember, every kilowatt-hour saved not only reduces your energy expenses but also helps preserve our planet’s resources.
Budget Planning and Forecasting
Planning and forecasting utility costs are essential for effective financial management in a 2-bedroom apartment. By understanding the factors that influence utility consumption and implementing proactive strategies, tenants can minimize unexpected expenses and ensure a comfortable living environment while staying within their budget.
Estimating Utility Expenses
Estimating utility expenses involves considering factors such as location, consumption patterns, and historical data. Historical utility bills can provide valuable insights into past consumption and serve as a basis for projections. Additionally, online tools and resources can provide estimates based on regional averages and specific appliance usage.
Managing Utility Costs
Managing utility costs effectively requires a combination of energy-efficient practices, usage monitoring, and negotiating with providers. Energy-efficient appliances, lighting, and insulation can significantly reduce consumption. Monitoring usage through smart meters or online dashboards helps identify areas for improvement. Negotiating with utility providers for lower rates or payment plans can also help reduce expenses.
| Location | Consumption Level | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|
| New York City | Average | $150-$250 per month |
| Los Angeles | High | $200-$350 per month |
| Dallas | Low | $100-$175 per month |
Creating a Utility Budget
Creating a utility budget involves the following steps:
- Estimate utility expenses based on historical data and projections.
- Set realistic monthly or annual budget limits.
- Track actual expenses regularly.
- Identify areas for savings and implement cost-effective measures.
- Adjust the budget as needed based on changes in consumption or rates.
Budgeting Tools and Software
Budgeting tools and software can simplify the process of tracking utility expenses and identifying areas for savings. These tools offer features such as automatic expense tracking, expense categorization, and budget alerts. They can help tenants stay organized, identify trends, and make informed decisions about their utility consumption.
Case Study
A tenant in a 2-bedroom apartment in Chicago implemented the following strategies:
- Installed energy-efficient appliances and lighting.
- Monitored usage through a smart meter and identified areas for improvement.
- Negotiated a lower rate with their utility provider.
As a result, the tenant reduced their monthly utility costs by 20%, saving over $200 per year.
Key Points
- Budgeting for utility costs is essential for financial management in a 2-bedroom apartment.
- Estimating utility expenses involves considering location, consumption patterns, and historical data.
- Managing utility costs effectively requires a combination of energy-efficient practices, usage monitoring, and negotiating with providers.
- Creating a utility budget involves setting realistic limits, tracking expenses, and identifying areas for savings.
- Budgeting tools and software can simplify the process of tracking utility expenses and identifying areas for savings.
Recommendations
- Create a comprehensive utility budget and stick to it.
- Implement energy-efficient measures to reduce consumption.
- Monitor usage regularly and identify areas for improvement.
- Negotiate with utility providers for lower rates or payment plans.
- Use budgeting tools and software to simplify expense tracking and identify savings opportunities.
Smart Home Technologies for Utility Cost Reduction in 2-Bedroom Apartments
Smart home technologies offer significant potential for reducing utility costs in 2-bedroom apartments. By automating energy-intensive tasks, optimizing device usage, and providing real-time insights into energy consumption, smart devices can help tenants and homeowners save money on their utility bills.
Smart Thermostats
Smart thermostats are a key component of any smart home energy management system. They learn user preferences and adjust the temperature accordingly, ensuring that the apartment is comfortable while minimizing energy waste. Additionally, smart thermostats can be programmed to automatically switch to energy-saving modes when the apartment is unoccupied or during off-peak hours.
Smart Lighting
Smart lighting systems allow users to control the brightness and color of their lights remotely. This enables them to turn off lights that are not in use, dim them when natural light is available, and create customized lighting schedules to reduce energy consumption.
Smart lighting can also be integrated with motion sensors to automatically turn on lights when someone enters a room and turn them off when the room is empty.
Smart Plugs
Smart plugs are another effective way to reduce utility costs. They allow users to remotely control the power supply to any plugged-in device. This makes it easy to turn off devices that are not in use, such as chargers, appliances, and entertainment systems.
Smart plugs can also be used to monitor energy consumption and create schedules for device usage.
Utility Bill Analysis
Analyzing utility bills is crucial for understanding energy consumption, identifying potential savings, and detecting errors. Here’s a step-by-step guide to analyzing a utility bill for a 2-bedroom apartment:
Identifying Usage Patterns
- Review the billing period and compare it to previous bills to track usage over time.
- Check for any unusual spikes or drops in consumption that may indicate changes in lifestyle or equipment efficiency.
- Monitor usage patterns by hour, day, or week to identify peak and off-peak periods.
Calculating Costs
- Multiply the energy usage (kWh, therms, gallons) by the unit cost provided on the bill.
- Add up all the charges for different utilities (electricity, gas, water, etc.) to determine the total utility cost.
- Compare the current bill with previous bills to track changes in costs and identify areas for potential savings.
Detecting Errors or Inefficiencies
- Check the meter readings and compare them to your own readings to identify any discrepancies.
- Review the charges for fixed fees, taxes, and other surcharges to ensure they are accurate.
- If you suspect an error, contact the utility provider immediately to investigate and resolve the issue.
Landlord-Tenant Responsibilities

In a 2-bedroom apartment, landlords and tenants have specific responsibilities regarding utility costs. Understanding these responsibilities helps avoid disputes and ensures fair billing practices.
Typically, landlords are responsible for:
- Maintaining the property’s utility infrastructure (e.g., electrical wiring, plumbing)
- Paying for utilities if included in the rent
- Providing access for utility inspections and repairs
Tenants are typically responsible for:
- Paying for utilities if not included in the rent
- Using utilities responsibly to avoid excessive consumption
- Reporting any utility issues or leaks promptly
Lease Agreements
Lease agreements should clearly Artikel utility responsibilities. For example:
“The landlord shall pay for water and sewage utilities. The tenant shall pay for electricity and gas utilities.”
Potential Disputes
Disputes may arise due to:
- Unclear lease agreements
- Excessive utility consumption by one party
- Misunderstanding of billing statements
To prevent disputes, open communication, accurate record-keeping, and clear lease agreements are essential.
Utility Cost Comparison: How Much Is Utilities For A 2 Bedroom Apartment
Understanding utility costs is essential for budgeting and making informed decisions about housing choices. This section provides a comprehensive comparison of utility costs for 2-bedroom apartments in different cities or regions, considering factors such as average monthly usage, rate structures, and total estimated costs.
Data Table
The following table presents a comparison of utility costs for 2-bedroom apartments in different cities or regions. The data includes average monthly usage, rate structures, and total estimated costs for both electric and gas utilities. The average cost per square foot is also calculated for each city or region.
| City/Region | Electric Usage (kWh/month) | Electric Rate (¢/kWh) | Electric Cost (USD/month) | Gas Usage (therms/month) | Gas Rate (¢/therm) | Gas Cost (USD/month) | Total Utility Cost (USD/month) | Average Cost per Sq. Ft. (USD/sq. ft.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City A | 750 | 12 | 90 | 50 | 80 | 40 | 130 | 0.10 |
| City B | 800 | 15 | 120 | 60 | 90 | 54 | 174 | 0.12 |
| City C | 650 | 10 | 65 | 40 | 70 | 28 | 93 | 0.08 |
| City D | 700 | 13 | 91 | 55 | 85 | 46 | 137 | 0.11 |
| City E | 850 | 14 | 119 | 65 | 95 | 61 | 180 | 0.13 |
Advantages and Limitations
Comparing utility costs can provide valuable insights for decision-making. However, it is important to consider the advantages and limitations of such comparisons.
- Advantages:
- Helps identify cities or regions with lower utility costs.
- Provides a basis for budgeting and forecasting utility expenses.
- Facilitates comparisons between different housing options.
- Limitations:
- Data may not be readily available or accurate for all cities or regions.
- Utility rates can fluctuate over time, affecting the accuracy of comparisons.
- Comparisons may not account for individual usage patterns or energy efficiency measures.
Summary
The table presented provides a snapshot of utility costs for 2-bedroom apartments in different cities or regions. The average cost per square foot ranges from 0.08 USD to 0.13 USD. City C has the lowest overall utility cost, while City E has the highest.
It is important to note the advantages and limitations of such comparisons and consider individual usage patterns and energy efficiency measures when making decisions based on utility costs.
Energy Audits and Home Assessments

Conducting an energy audit or home assessment for a 2-bedroom apartment offers valuable benefits. These assessments identify areas where energy efficiency can be improved, leading to potential cost savings and environmental benefits.
Energy audits typically cover a comprehensive checklist of items, including:
Assessment Checklist
- Appliance and lighting energy consumption
- Insulation levels in walls, ceilings, and floors
- Air sealing and weatherstripping
- Heating and cooling system efficiency
- Water heater efficiency
Implementing recommendations from an energy audit can result in significant cost savings. By reducing energy consumption, you can lower your utility bills. Additionally, energy-efficient upgrades can enhance the comfort and livability of your apartment.
Energy audits also contribute to environmental benefits. Reducing energy consumption helps minimize greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner and healthier planet.
– Include a table comparing the costs and benefits of different renewable energy options.

The table below compares the costs and benefits of different renewable energy options for 2-bedroom apartments.
Note:The costs and benefits of renewable energy systems can vary depending on a number of factors, including the size of the system, the location of the apartment, and the availability of government incentives.
| Renewable Energy Option | Cost | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Solar panels | $15,000-$25,000 | – Can reduce utility costs by up to 50%
|
| Wind turbines | $5,000-$15,000 | – Can reduce utility costs by up to 30%
|
| Geothermal heat pumps | $10,000-$20,000 | – Can reduce utility costs by up to 40%
|
Answers to Common Questions
What are the typical utility types included in apartment rentals?
The most common utility types included in apartment rentals are electricity, gas, and water.
How can I reduce my energy consumption in a 2-bedroom apartment?
There are several ways to reduce energy consumption in a 2-bedroom apartment, including using energy-efficient appliances and lighting, improving insulation, and implementing smart home technologies.
What are some government programs that offer financial assistance for utility costs?
Government programs that offer financial assistance for utility costs include the Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP), the Weatherization Assistance Program (WAP), and the State Energy Assistance Program (SEAP).


