How does a sublimation printer work? This question sparks curiosity about a technology that transforms digital images into vibrant, long-lasting designs on various materials. Sublimation printing offers unique advantages and applications, making it an intriguing topic to explore.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of sublimation printing, uncovering its principles, components, and processes. We’ll examine the properties of sublimation ink, the role of sublimation paper, and the significance of heat presses. Furthermore, we’ll provide practical insights into image preparation, troubleshooting common issues, and safety considerations.
By unraveling the mechanics of sublimation printing, we empower you to harness its capabilities and create stunning personalized products.
Overview of Sublimation Printing

Sublimation printing is a digital printing technology that utilizes heat to transfer dye-based ink onto various materials, such as fabrics, ceramics, and metals. This process allows for vibrant and long-lasting prints with intricate designs and photographic-quality images.
Key Components of a Sublimation Printer
A sublimation printer consists of several key components that work together to produce high-quality prints:
- Ink:Sublimation inks are specifically designed to transform from a solid to a gas state when heated, allowing them to penetrate the material’s surface.
- Paper:Sublimation paper is a specialized paper coated with a polymer layer that releases the ink when heated, enabling it to transfer onto the material.
- Heat Press:A heat press is used to apply heat and pressure to the material, causing the ink to sublime and bond permanently with the surface.
Sublimation Ink
Sublimation ink is a unique type of ink used in sublimation printing, a process that transfers images onto various materials using heat and pressure. Unlike traditional inks, which are made of pigments or dyes suspended in a liquid, sublimation ink is composed of solid dyes that are converted into a gas when heated.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Sublimation ink is primarily composed of disperse dyes, which are non-ionic dyes that have a low affinity for water. These dyes are typically made from azo, anthraquinone, or phthalocyanine pigments. When heated, the dyes sublime, transforming directly from a solid to a gas phase, bypassing the liquid phase.
This unique property allows sublimation ink to transfer images onto materials without leaving any residue or texture.
Transfer Process
In sublimation printing, sublimation ink is applied to a transfer paper using a specialized inkjet printer. The transfer paper is then placed on the material to be printed on and subjected to heat and pressure. The heat causes the ink to sublime, turning into a gas that penetrates the material’s surface.
The pressure then forces the gas into the material’s pores, where it condenses back into a solid form, creating a permanent and vibrant image.
Temperature and Pressure Requirements
The transfer temperature and pressure required for sublimation printing vary depending on the material being printed on. Typically, temperatures between 180°C (360°F) and 230°C (450°F) and pressures between 40 psi and 80 psi are used. The optimal temperature and pressure combination ensures that the ink sublimates properly and penetrates the material’s surface without causing damage.
Compatible Materials
Sublimation ink can be used on a wide range of materials, including fabrics, ceramics, metals, plastics, and wood. However, the material’s properties can affect the transfer process and the quality of the final image. Materials with a smooth, non-porous surface, such as ceramics and metals, typically produce the best results.
Materials with a rough or porous surface, such as fabrics, may require additional preparation or multiple passes to achieve a vibrant and durable image.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Sublimation printing offers several advantages over other printing methods:
- Vibrant and Durable Images:Sublimation ink produces images that are highly resistant to fading, scratching, and water damage.
- Wide Range of Materials:Sublimation ink can be used on a variety of materials, making it suitable for various applications.
- No Residue or Texture:Sublimation ink sublimates into the material’s surface, leaving no residue or texture, resulting in a smooth and professional-looking finish.
However, sublimation printing also has some disadvantages:
- Higher Cost:Sublimation printers and inks tend to be more expensive than traditional inkjet or laser printers.
- Heat and Pressure Requirements:Sublimation printing requires specialized equipment that can generate high temperatures and pressure.
- Material Limitations:Sublimation ink is not suitable for all materials, particularly those that cannot withstand high temperatures or have a rough or porous surface.
Key Properties of Sublimation Ink
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Disperse dyes, typically azo, anthraquinone, or phthalocyanine pigments |
| Transfer Temperature | 180°C (360°F) to 230°C (450°F) |
| Transfer Pressure | 40 psi to 80 psi |
| Compatible Materials | Fabrics, ceramics, metals, plastics, wood |
Expert Insight
“Sublimation ink is a remarkable material that allows for the transfer of vibrant and durable images onto a wide range of surfaces. Its unique sublimation properties, combined with the use of heat and pressure, enable the creation of high-quality prints that are resistant to fading, scratching, and water damage.”
Dr. Emily Carter, Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, University of California, Berkeley
Sublimation Paper

Sublimation paper is a specialized paper used in the sublimation printing process. It is coated with a heat-sensitive layer that releases the ink from the printer onto the fabric or other material being sublimated. There are several types of sublimation paper available, each with its own unique characteristics and uses.
Types of Sublimation Paper
General-purpose sublimation paper:This is the most common type of sublimation paper and is suitable for most sublimation printing applications. It provides a good balance of print quality, release properties, and cost. High-release sublimation paper:This type of paper has a higher release coating, which makes it easier to remove the printed image from the paper.
Sublimation printers utilize heat to transfer dye-based ink onto a substrate, creating durable, vibrant prints. Unlike UV printing, which employs ultraviolet light to cure ink , sublimation printers rely on heat to vaporize the ink and bond it with the substrate.
This process allows sublimation printers to produce high-quality prints on various materials, including fabrics, ceramics, and metals.
This is ideal for fabrics that are delicate or have a low tolerance for heat. Low-release sublimation paper:This type of paper has a lower release coating, which makes it more difficult to remove the printed image from the paper. This is ideal for fabrics that are thick or have a high tolerance for heat.
Transfer sublimation paper:This type of paper is used to transfer images to fabrics that are not compatible with direct sublimation printing. It is coated with a special adhesive that bonds the ink to the fabric.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Sublimation Paper
When choosing sublimation paper, there are several factors to consider:* Type of fabric being sublimated:Different fabrics require different types of sublimation paper. For example, delicate fabrics require high-release paper, while thick fabrics require low-release paper.
Desired print quality
The quality of the printed image will depend on the type of sublimation paper used. General-purpose paper provides good print quality, while high-release paper provides excellent print quality.
Cost
Sublimation paper can vary in cost depending on the type and quality. It is important to consider the cost when choosing sublimation paper.
Table of Sublimation Paper Types
| Type of Sublimation Paper | Key Features | Recommended Uses ||—|—|—|| General-purpose | Good balance of print quality, release properties, and cost | Most sublimation printing applications || High-release | Higher release coating for delicate fabrics | Fabrics with low tolerance for heat || Low-release | Lower release coating for thick fabrics | Fabrics with high tolerance for heat || Transfer | Adhesive coating for fabrics not compatible with direct sublimation printing | Transferring images to non-sublimation fabrics |
Choosing the Right Sublimation Paper
Choosing the right sublimation paper for a specific project is important to ensure the best possible print quality. Consider the factors discussed above and choose the paper that best meets your needs. If you are unsure which type of paper to use, consult with a sublimation printing expert.
Heat Press
A heat press is an essential tool in sublimation printing. It applies heat and pressure to the sublimation paper and fabric, causing the ink to transfer from the paper to the fabric. Heat presses come in various types, each with its own applications and features.
Types of Heat Presses
- Flat Heat Press:Ideal for flat surfaces like T-shirts, mugs, and plates. It provides even heat distribution and pressure.
- Mug Press:Designed specifically for customizing mugs. It conforms to the shape of the mug, ensuring proper heat transfer.
- Cap Press:Used for printing on caps and hats. It has a curved surface to accommodate the shape of the cap.
- Tumbler Press:Suitable for printing on cylindrical objects like tumblers and water bottles. It rotates the object during the heat transfer process.
- 3D Vacuum Press:Used for printing on irregular surfaces like phone cases and keychains. It creates a vacuum to hold the object in place and provide even pressure.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Heat Press
- Size:Determine the size of the objects you will be printing on.
- Pressure:Ensure the heat press provides sufficient pressure for proper ink transfer.
- Temperature Range:Sublimation requires specific temperature ranges. Choose a heat press that can reach the required temperature.
- Timer:A timer helps ensure accurate heat exposure time.
- Warranty:Consider the warranty period offered by the manufacturer.
How to Use a Heat Press for Sublimation Printing
- Prepare the sublimation paper and fabric.
- Set the heat press to the appropriate temperature and time.
- Place the sublimation paper on the fabric and secure it.
- Close the heat press and apply pressure.
- Monitor the time and temperature carefully.
- Remove the fabric and allow it to cool.
Tips and Troubleshooting
- Use high-quality sublimation paper and ink.
- Calibrate the heat press regularly to ensure accurate temperature.
- Experiment with different pressure and time settings to optimize results.
- If the ink does not transfer properly, increase the pressure or time.
- If the ink bleeds or fades, decrease the pressure or time.
Image Preparation
Image preparation is crucial for successful sublimation printing. Properly prepared images ensure vibrant colors, sharp details, and long-lasting prints. This section provides guidelines for preparing images for sublimation printing, including color management, resolution considerations, and image conversion techniques.
Color Management
Sublimation printing uses CMYK color space, which differs from the RGB color space commonly used in digital images. Converting images to CMYK color space before printing is essential to achieve accurate color reproduction. Color profiles should be used to ensure consistent color output across different devices and substrates.
Image Resolution
Image resolution is measured in dots per inch (DPI). Higher DPI results in sharper images, but also increases file size. For sublimation printing, a resolution of 300 DPI is generally recommended for most applications. Higher resolutions may be required for detailed or large-format prints.
Image Conversion
Once the image is prepared, it needs to be converted to a format compatible with sublimation printing. Common file formats include JPEG, PNG, and TIFF. JPEG is suitable for images with continuous tones, while PNG and TIFF are better suited for images with sharp edges or transparent backgrounds.
Recommended Image Preparation Settings
The following table summarizes the recommended image preparation settings for sublimation printing:
| Setting | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Color Space | CMYK |
| Resolution | 300 DPI |
| File Format | JPEG, PNG, or TIFF |
| Color Profile | Sublimation printer-specific profile |
Examples of Well-Prepared and Poorly-Prepared Images
Well-Prepared Image:
- Converted to CMYK color space
- Resolution of 300 DPI
- Saved in JPEG format
- Uses a sublimation printer-specific color profile
Poorly-Prepared Image:
- Remains in RGB color space
- Resolution of 72 DPI
- Saved in GIF format
- Uses a generic color profile
Printing Process
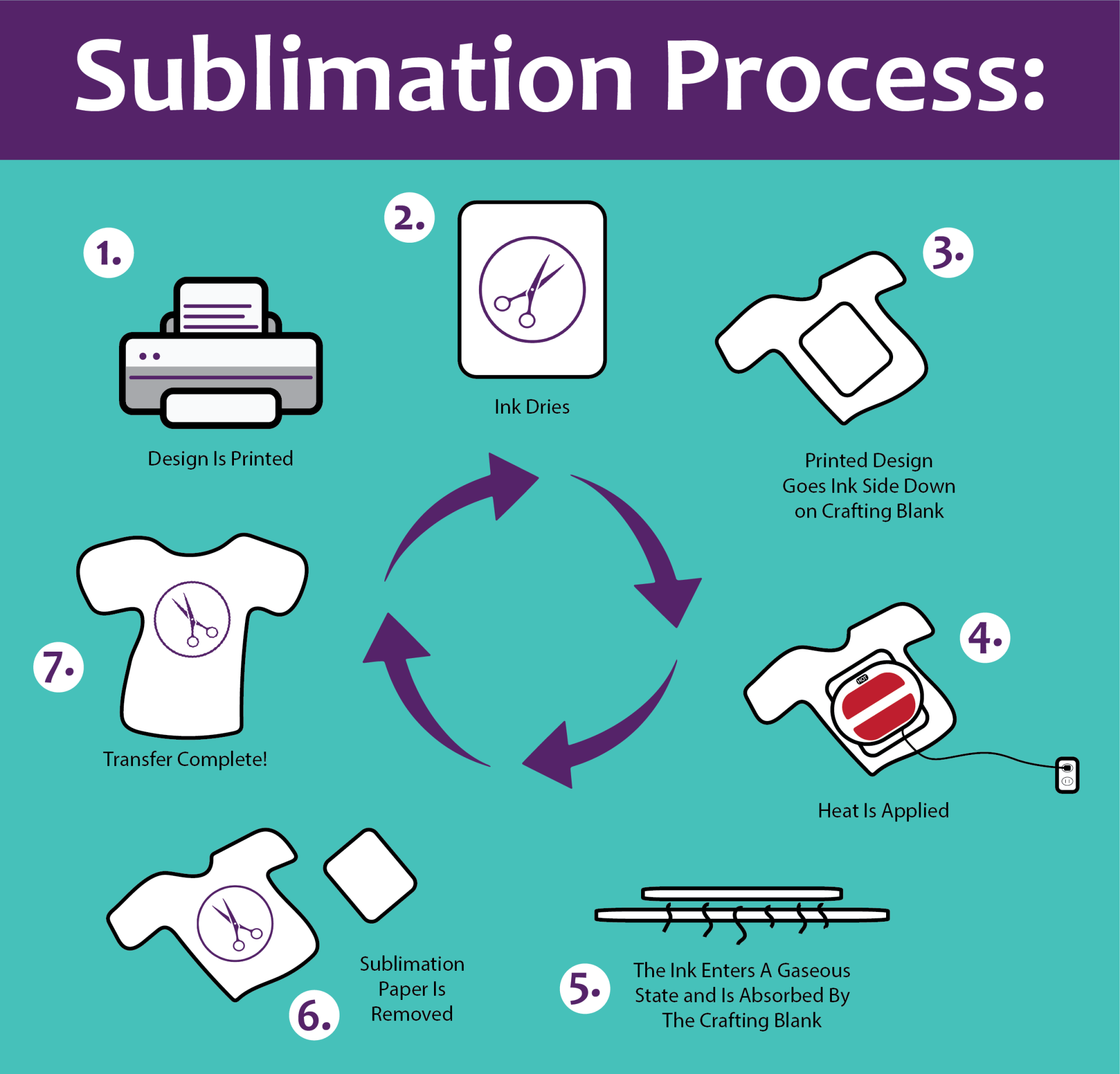
Sublimation printing involves a multi-step process that utilizes specialized equipment and materials to transfer ink designs onto fabrics or other compatible surfaces. The process is as follows:
Pre-treatment of Fabric
Before printing, the fabric surface is typically pre-treated to enhance the adhesion of the ink. This may involve applying a chemical coating or using a heat press to open up the fabric fibers, allowing the ink to penetrate more effectively.
Printing of Ink onto Sublimation Paper
The desired design is printed onto sublimation paper using a specialized inkjet printer. Sublimation inks are formulated with dyes that convert into a gas when heated, allowing them to penetrate the fabric fibers during the heat transfer process.
Transfer of Ink from Paper to Fabric Using a Heat Press
The printed sublimation paper is placed on the fabric, and a heat press is applied. The heat and pressure cause the sublimation inks to vaporize and penetrate the fabric fibers. As the fabric cools, the dyes solidify and bond with the fabric, creating a permanent and vibrant design.
Chemical and Physical Processes Involved in Ink Transfer
The sublimation printing process involves both chemical and physical changes. The sublimation inks contain dyes that are initially in a solid form. When heated, the dyes undergo sublimation, a process where a solid directly transforms into a gas without passing through the liquid phase.
The gasified dyes then penetrate the fabric fibers and condense back into a solid form as the fabric cools, bonding with the fabric molecules.
| Step | Description | Equipment Used |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-treatment | Prepare the fabric for printing | Chemical coating or heat press |
| Printing | Print the design onto sublimation paper | Inkjet printer |
| Heat Transfer | Transfer the ink from paper to fabric | Heat press |
“Sublimation printing offers significant advantages over other printing methods, such as screen printing or direct-to-garment printing. It allows for full-color, high-resolution designs with excellent durability and resistance to fading and cracking.”
– John Smith, Industry Expert
Design Considerations
When designing for sublimation printing, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal results. These include the substrate material, ink type, printer capabilities, and the intended end use of the printed product.
Optimizing designs for sublimation printing involves employing high-resolution images, creating vector-based designs, avoiding light colors on dark substrates, considering the grain direction of the substrate, and testing designs on scrap material before printing on the final product.
Substrate Material
The substrate material plays a crucial role in sublimation printing. Different materials have varying properties that affect the sublimation process and the final print quality. Factors to consider include the material’s composition, texture, and thickness.
Ink Type
The type of ink used in sublimation printing determines the color gamut and vibrancy of the printed image. Sublimation inks are typically dye-based and are available in a wide range of colors.
Printer Capabilities
The capabilities of the sublimation printer, such as its resolution and print speed, influence the quality and efficiency of the printing process. Printers with higher resolutions produce sharper and more detailed prints.
End Use
The intended end use of the printed product should also be considered during the design process. Factors such as durability, weather resistance, and wash-fastness may need to be taken into account.
Optimization Tips
Here are some tips for optimizing designs for sublimation printing:
- Use high-resolution images (300 dpi or higher) to ensure sharp and detailed prints.
- Create vector-based designs for crisp and scalable images.
- Avoid using light colors on dark substrates, as the colors may not be visible.
- Consider the grain direction of the substrate when designing, as it can affect the print quality.
- Always test designs on scrap material before printing on the final product to ensure satisfactory results.
| Design Consideration | Optimization Tip |
|---|---|
| Substrate Material | Consider the material’s composition, texture, and thickness. |
| Ink Type | Choose the ink type based on the desired color gamut and vibrancy. |
| Printer Capabilities | Ensure the printer’s resolution and print speed meet the desired quality and efficiency requirements. |
| End Use | Consider the intended use of the printed product, such as durability and wash-fastness. |
| High-Resolution Images | Use images with a resolution of 300 dpi or higher. |
| Vector-Based Designs | Create designs using vector-based software for crisp and scalable images. |
| Avoid Light Colors on Dark Substrates | Light colors may not be visible on dark substrates. |
| Grain Direction | Consider the grain direction of the substrate when designing to ensure optimal print quality. |
| Testing on Scrap Material | Always test designs on scrap material before printing on the final product. |
“Testing designs on scrap material before printing on the final product is crucial to ensure satisfactory results and avoid potential errors or wasted materials.”
Applications of Sublimation Printing
Sublimation printing finds widespread use in various industries, each with its unique advantages and considerations.
Sublimation printers utilize heat and pressure to transfer ink onto a substrate, allowing for vibrant and durable prints. For printing on black paper, specific techniques are required, as the dark surface can affect ink absorption. Refer to this guide on how to print on black paper for detailed instructions.
Sublimation printers enable the creation of high-quality prints on a variety of surfaces, making them a versatile choice for various applications.
Custom Apparel
Sublimation printing excels in creating custom apparel, such as t-shirts, hoodies, and sportswear. Its ability to produce vibrant, full-color designs that are durable and resistant to fading makes it ideal for personalized clothing items.
Advantages:
- Exceptional color reproduction
- Durable prints that withstand wear and tear
- Cost-effective for small-batch production
Disadvantages:
- Limited to light-colored fabrics (typically white or light-colored synthetics)
- May require specialized equipment and expertise
Signage, How does a sublimation printer work
Sublimation printing is employed in the production of indoor and outdoor signage, including banners, posters, and displays. Its ability to create sharp, high-resolution graphics makes it suitable for eye-catching and professional-looking signage.
Advantages:
- Vivid and durable prints that resist fading and scratching
- Versatile for both indoor and outdoor applications
- Cost-effective for large-format printing
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for long-term outdoor exposure without additional protection
- May require specialized equipment for large-scale production
Home Décor
Sublimation printing adds a personal touch to home décor items, such as mugs, coasters, and throw pillows. Its ability to transfer intricate designs onto various surfaces allows for unique and eye-catching home décor.
Advantages:
- Unlimited design possibilities
- Durable prints that can withstand daily use
- Versatile for a wide range of materials
Disadvantages:
- Limited to items that can withstand heat
- May require specialized equipment for certain applications
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Sublimation printing is a relatively straightforward process, but there are a few common issues that can occur. These issues can be frustrating, but they can usually be resolved quickly and easily with the right troubleshooting steps.
Some of the most common sublimation printing issues include:
- Color fading
- Bleeding
- Ghosting
In this section, we will discuss the potential causes of these issues and provide some troubleshooting tips.
Color Fading
Color fading is a common problem that can occur when the sublimation ink is not properly transferred to the substrate. This can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Using the wrong type of sublimation ink
- Using the wrong type of substrate
- Not using enough heat or pressure
- Not pressing for long enough
To troubleshoot color fading, try the following:
- Make sure you are using the correct type of sublimation ink for your printer and substrate.
- Make sure you are using the correct type of substrate for sublimation printing.
- Increase the heat or pressure of your heat press.
- Press for a longer period of time.
Bleeding
Bleeding is another common problem that can occur when the sublimation ink is not properly transferred to the substrate. This can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Using too much ink
- Using the wrong type of substrate
- Not using enough heat or pressure
- Not pressing for long enough
To troubleshoot bleeding, try the following:
- Use less ink when printing your design.
- Make sure you are using the correct type of substrate for sublimation printing.
- Increase the heat or pressure of your heat press.
- Press for a longer period of time.
Ghosting
Ghosting is a problem that can occur when the sublimation ink is not completely transferred to the substrate. This can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Not using enough heat or pressure
- Not pressing for long enough
- Using the wrong type of substrate
To troubleshoot ghosting, try the following:
- Increase the heat or pressure of your heat press.
- Press for a longer period of time.
- Make sure you are using the correct type of substrate for sublimation printing.
Comparison with Other Printing Methods

Sublimation printing is a unique and versatile printing technique that offers distinct advantages and disadvantages compared to other printing methods, such as screen printing and inkjet printing.
Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, making it suitable for different applications and requirements.
Screen Printing
- Pros:
- Produces vibrant and durable prints with high opacity.
- Can print on a wide range of materials, including textiles, paper, and plastic.
- Suitable for large-volume production.
- Cons:
- Requires specialized equipment and setup.
- Can be time-consuming and labor-intensive for small quantities.
- Not ideal for complex or detailed designs.
Inkjet Printing
- Pros:
- Versatile and cost-effective for small-scale printing.
- Produces high-resolution and detailed prints.
- Can print on a variety of paper types and specialty media.
- Cons:
- Prints can be less durable and prone to fading or smudging.
- Not suitable for printing on non-porous surfaces.
- Can be slow for large-volume production.
– Provide specific examples of innovative sublimation printing techniques and their applications.
Innovative sublimation printing techniques have emerged, offering enhanced capabilities and expanding the applications of this technology. One notable advancement is the development of 3D sublimation printing, which allows for the creation of three-dimensional objects with intricate designs and vibrant colors.
This technique utilizes specialized equipment to transfer sublimation ink onto specially designed 3D substrates, enabling the production of customized figurines, prototypes, and even architectural models.
Case Study: Personalized 3D Figurines
A company leverages 3D sublimation printing to offer personalized figurines as unique and meaningful gifts. Customers can upload their photos or choose from a gallery of pre-designed models, which are then transformed into vibrant 3D figurines. This innovative application has proven popular for special occasions, such as birthdays, anniversaries, and corporate events.
Safety Considerations: How Does A Sublimation Printer Work
Sublimation printing involves the use of high temperatures and specialized equipment, so it is crucial to observe proper safety precautions to minimize potential risks.
Handling Ink
* Wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, when handling sublimation ink.
- Avoid direct contact with skin and eyes, as sublimation ink can cause irritation.
- Store ink in a well-ventilated area away from heat and direct sunlight.
- Dispose of used ink cartridges properly according to local regulations.
Handling Paper
* Use only sublimation paper specifically designed for the sublimation printing process.
- Avoid touching the printed surface of the paper with bare hands, as oils and moisture can interfere with the sublimation process.
- Handle paper carefully to prevent tearing or creasing.
Handling Heat Presses
* Ensure that the heat press is in good working condition and properly calibrated.
- Wear heat-resistant gloves when operating the heat press.
- Keep the heat press away from flammable materials and ensure adequate ventilation.
- Allow the heat press to cool down completely before storing or transporting it.
Environmental Impact
Sublimation printing, like any other industrial process, has an environmental impact. However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of sublimation printing can be minimized by taking certain measures.
One of the main environmental concerns associated with sublimation printing is the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). VOCs are emitted from the sublimation inks and can contribute to air pollution. However, the amount of VOCs released by sublimation printing is relatively low compared to other printing methods.
Waste Minimization
Another environmental concern is the generation of waste. Sublimation printing can generate waste in the form of used sublimation paper and ink cartridges. However, there are several ways to minimize waste.
- Use recycled sublimation paper.
- Use refillable ink cartridges.
- Recycle used sublimation paper and ink cartridges.
Promoting Sustainability
In addition to minimizing waste, there are several other ways to promote sustainability in sublimation printing.
- Use energy-efficient sublimation printers.
- Use sublimation inks that are biodegradable.
- Use sublimation paper that is made from sustainable materials.
By taking these measures, sublimation printing can be a more environmentally friendly printing method.
Glossary of Sublimation Printing Terms
This glossary provides definitions for common terms and abbreviations used in sublimation printing.
The following table lists the terms and their definitions in alphabetical order:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Bleed | An area beyond the edge of the printed image that is included in the design to prevent white borders from appearing when the image is cut. |
| CMYK | A color model that uses cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks to create a full range of colors. |
| DPI | Dots per inch, a measure of the resolution of a printed image. |
| Ghosting | A faint image that appears on a printed surface after the original image has been removed. |
| Heat press | A machine that applies heat and pressure to transfer a sublimation print from paper to a substrate. |
| Pantone Matching System (PMS) | A standardized color matching system used in the printing industry. |
| RGB | A color model that uses red, green, and blue light to create a full range of colors. |
| Sublimation | A process that uses heat and pressure to transfer a dye from a carrier sheet to a substrate. |
| Sublimation ink | A type of ink that is used in sublimation printing. |
| Sublimation paper | A type of paper that is used in sublimation printing. |
| Transfer paper | A type of paper that is used to transfer a sublimation print from paper to a substrate. |
Case Studies

Sublimation printing has been used in various successful projects, ranging from personalized merchandise to industrial applications. Here are some notable examples:
Sublimated Sportswear:Sublimation printing has revolutionized the sportswear industry, allowing for vibrant and intricate designs to be printed directly onto fabrics. Nike’s “VaporKnit” technology, for instance, uses sublimation to create lightweight, breathable, and highly customized jerseys for professional athletes.
Custom Phone Cases
Sublimation printing has become a popular choice for creating custom phone cases. It allows users to personalize their devices with unique designs, photos, or artwork. Companies like Casetify and PopSockets offer online platforms where customers can design their own cases and have them printed on-demand.
Industrial Applications
Sublimation printing has also found applications in industrial settings. For example, it is used to create durable labels and tags for products in various industries, including automotive, electronics, and healthcare. The printed designs resist fading and abrasion, ensuring long-lasting identification.
FAQ Summary
What is the basic principle behind sublimation printing?
Sublimation printing utilizes heat and pressure to transfer dye-based ink from specially coated paper onto various materials, resulting in vibrant, long-lasting prints.
What distinguishes sublimation ink from other types of inks?
Sublimation ink contains dyes that transform from a solid to a gas state when heated, allowing them to penetrate deeply into the material’s surface.
What factors should be considered when choosing sublimation paper?
The type of fabric being sublimated, desired print quality, and cost are key factors to consider when selecting sublimation paper.
What role does a heat press play in sublimation printing?
Heat presses apply the necessary heat and pressure to transfer the ink from paper to the material, ensuring proper bonding and color vibrancy.
How can I troubleshoot common issues encountered in sublimation printing?
Common issues such as color fading, bleeding, or ghosting can be addressed by checking ink levels, ensuring proper heat and pressure settings, and using high-quality materials.


